Wenli Xiao
VIRAL: Visual Sim-to-Real at Scale for Humanoid Loco-Manipulation
Nov 19, 2025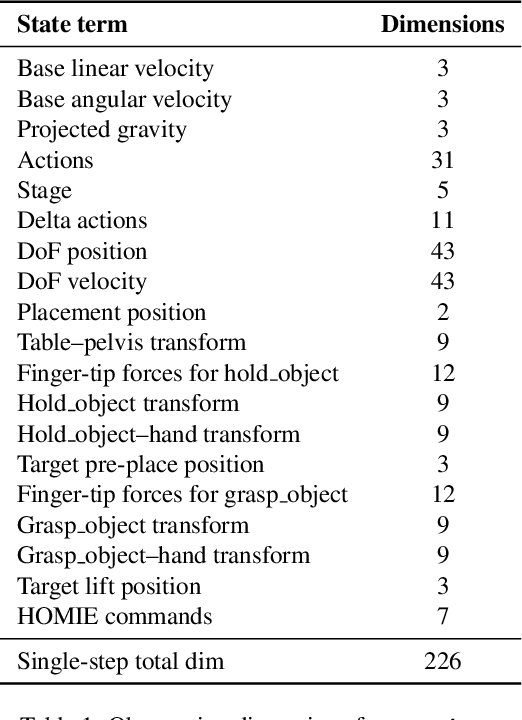
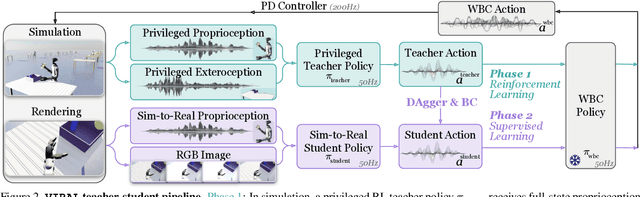
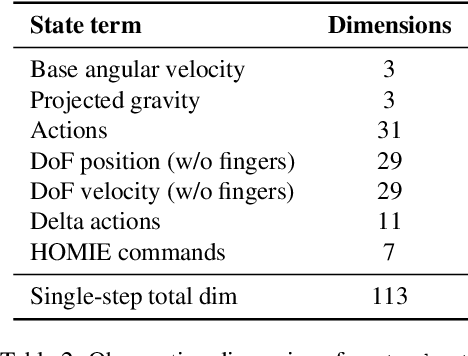
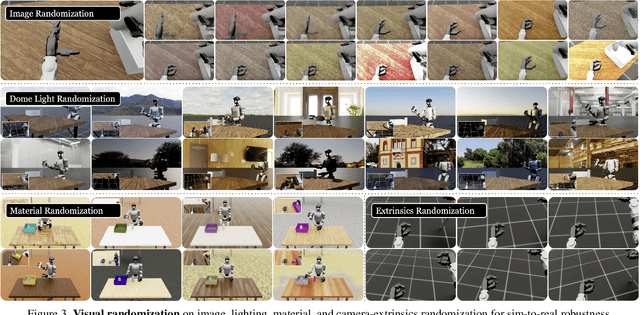
Abstract:A key barrier to the real-world deployment of humanoid robots is the lack of autonomous loco-manipulation skills. We introduce VIRAL, a visual sim-to-real framework that learns humanoid loco-manipulation entirely in simulation and deploys it zero-shot to real hardware. VIRAL follows a teacher-student design: a privileged RL teacher, operating on full state, learns long-horizon loco-manipulation using a delta action space and reference state initialization. A vision-based student policy is then distilled from the teacher via large-scale simulation with tiled rendering, trained with a mixture of online DAgger and behavior cloning. We find that compute scale is critical: scaling simulation to tens of GPUs (up to 64) makes both teacher and student training reliable, while low-compute regimes often fail. To bridge the sim-to-real gap, VIRAL combines large-scale visual domain randomization over lighting, materials, camera parameters, image quality, and sensor delays--with real-to-sim alignment of the dexterous hands and cameras. Deployed on a Unitree G1 humanoid, the resulting RGB-based policy performs continuous loco-manipulation for up to 54 cycles, generalizing to diverse spatial and appearance variations without any real-world fine-tuning, and approaching expert-level teleoperation performance. Extensive ablations dissect the key design choices required to make RGB-based humanoid loco-manipulation work in practice.
SONIC: Supersizing Motion Tracking for Natural Humanoid Whole-Body Control
Nov 11, 2025Abstract:Despite the rise of billion-parameter foundation models trained across thousands of GPUs, similar scaling gains have not been shown for humanoid control. Current neural controllers for humanoids remain modest in size, target a limited behavior set, and are trained on a handful of GPUs over several days. We show that scaling up model capacity, data, and compute yields a generalist humanoid controller capable of creating natural and robust whole-body movements. Specifically, we posit motion tracking as a natural and scalable task for humanoid control, leverageing dense supervision from diverse motion-capture data to acquire human motion priors without manual reward engineering. We build a foundation model for motion tracking by scaling along three axes: network size (from 1.2M to 42M parameters), dataset volume (over 100M frames, 700 hours of high-quality motion data), and compute (9k GPU hours). Beyond demonstrating the benefits of scale, we show the practical utility of our model through two mechanisms: (1) a real-time universal kinematic planner that bridges motion tracking to downstream task execution, enabling natural and interactive control, and (2) a unified token space that supports various motion input interfaces, such as VR teleoperation devices, human videos, and vision-language-action (VLA) models, all using the same policy. Scaling motion tracking exhibits favorable properties: performance improves steadily with increased compute and data diversity, and learned representations generalize to unseen motions, establishing motion tracking at scale as a practical foundation for humanoid control.
Learning Gentle Humanoid Locomotion and End-Effector Stabilization Control
May 30, 2025Abstract:Can your humanoid walk up and hand you a full cup of beer, without spilling a drop? While humanoids are increasingly featured in flashy demos like dancing, delivering packages, traversing rough terrain, fine-grained control during locomotion remains a significant challenge. In particular, stabilizing a filled end-effector (EE) while walking is far from solved, due to a fundamental mismatch in task dynamics: locomotion demands slow-timescale, robust control, whereas EE stabilization requires rapid, high-precision corrections. To address this, we propose SoFTA, a Slow-Fast TwoAgent framework that decouples upper-body and lower-body control into separate agents operating at different frequencies and with distinct rewards. This temporal and objective separation mitigates policy interference and enables coordinated whole-body behavior. SoFTA executes upper-body actions at 100 Hz for precise EE control and lower-body actions at 50 Hz for robust gait. It reduces EE acceleration by 2-5x relative to baselines and performs much closer to human-level stability, enabling delicate tasks such as carrying nearly full cups, capturing steady video during locomotion, and disturbance rejection with EE stability.
Emergent Active Perception and Dexterity of Simulated Humanoids from Visual Reinforcement Learning
May 18, 2025Abstract:Human behavior is fundamentally shaped by visual perception -- our ability to interact with the world depends on actively gathering relevant information and adapting our movements accordingly. Behaviors like searching for objects, reaching, and hand-eye coordination naturally emerge from the structure of our sensory system. Inspired by these principles, we introduce Perceptive Dexterous Control (PDC), a framework for vision-driven dexterous whole-body control with simulated humanoids. PDC operates solely on egocentric vision for task specification, enabling object search, target placement, and skill selection through visual cues, without relying on privileged state information (e.g., 3D object positions and geometries). This perception-as-interface paradigm enables learning a single policy to perform multiple household tasks, including reaching, grasping, placing, and articulated object manipulation. We also show that training from scratch with reinforcement learning can produce emergent behaviors such as active search. These results demonstrate how vision-driven control and complex tasks induce human-like behaviors and can serve as the key ingredients in closing the perception-action loop for animation, robotics, and embodied AI.
ASAP: Aligning Simulation and Real-World Physics for Learning Agile Humanoid Whole-Body Skills
Feb 03, 2025Abstract:Humanoid robots hold the potential for unparalleled versatility in performing human-like, whole-body skills. However, achieving agile and coordinated whole-body motions remains a significant challenge due to the dynamics mismatch between simulation and the real world. Existing approaches, such as system identification (SysID) and domain randomization (DR) methods, often rely on labor-intensive parameter tuning or result in overly conservative policies that sacrifice agility. In this paper, we present ASAP (Aligning Simulation and Real-World Physics), a two-stage framework designed to tackle the dynamics mismatch and enable agile humanoid whole-body skills. In the first stage, we pre-train motion tracking policies in simulation using retargeted human motion data. In the second stage, we deploy the policies in the real world and collect real-world data to train a delta (residual) action model that compensates for the dynamics mismatch. Then, ASAP fine-tunes pre-trained policies with the delta action model integrated into the simulator to align effectively with real-world dynamics. We evaluate ASAP across three transfer scenarios: IsaacGym to IsaacSim, IsaacGym to Genesis, and IsaacGym to the real-world Unitree G1 humanoid robot. Our approach significantly improves agility and whole-body coordination across various dynamic motions, reducing tracking error compared to SysID, DR, and delta dynamics learning baselines. ASAP enables highly agile motions that were previously difficult to achieve, demonstrating the potential of delta action learning in bridging simulation and real-world dynamics. These results suggest a promising sim-to-real direction for developing more expressive and agile humanoids.
HOVER: Versatile Neural Whole-Body Controller for Humanoid Robots
Oct 28, 2024



Abstract:Humanoid whole-body control requires adapting to diverse tasks such as navigation, loco-manipulation, and tabletop manipulation, each demanding a different mode of control. For example, navigation relies on root velocity tracking, while tabletop manipulation prioritizes upper-body joint angle tracking. Existing approaches typically train individual policies tailored to a specific command space, limiting their transferability across modes. We present the key insight that full-body kinematic motion imitation can serve as a common abstraction for all these tasks and provide general-purpose motor skills for learning multiple modes of whole-body control. Building on this, we propose HOVER (Humanoid Versatile Controller), a multi-mode policy distillation framework that consolidates diverse control modes into a unified policy. HOVER enables seamless transitions between control modes while preserving the distinct advantages of each, offering a robust and scalable solution for humanoid control across a wide range of modes. By eliminating the need for policy retraining for each control mode, our approach improves efficiency and flexibility for future humanoid applications.
Agile Mobility with Rapid Online Adaptation via Meta-learning and Uncertainty-aware MPPI
Oct 09, 2024Abstract:Modern non-linear model-based controllers require an accurate physics model and model parameters to be able to control mobile robots at their limits. Also, due to surface slipping at high speeds, the friction parameters may continually change (like tire degradation in autonomous racing), and the controller may need to adapt rapidly. Many works derive a task-specific robot model with a parameter adaptation scheme that works well for the task but requires a lot of effort and tuning for each platform and task. In this work, we design a full model-learning-based controller based on meta pre-training that can very quickly adapt using few-shot dynamics data to any wheel-based robot with any model parameters, while also reasoning about model uncertainty. We demonstrate our results in small-scale numeric simulation, the large-scale Unity simulator, and on a medium-scale hardware platform with a wide range of settings. We show that our results are comparable to domain-specific well-engineered controllers, and have excellent generalization performance across all scenarios.
AnyCar to Anywhere: Learning Universal Dynamics Model for Agile and Adaptive Mobility
Sep 24, 2024Abstract:Recent works in the robot learning community have successfully introduced generalist models capable of controlling various robot embodiments across a wide range of tasks, such as navigation and locomotion. However, achieving agile control, which pushes the limits of robotic performance, still relies on specialist models that require extensive parameter tuning. To leverage generalist-model adaptability and flexibility while achieving specialist-level agility, we propose AnyCar, a transformer-based generalist dynamics model designed for agile control of various wheeled robots. To collect training data, we unify multiple simulators and leverage different physics backends to simulate vehicles with diverse sizes, scales, and physical properties across various terrains. With robust training and real-world fine-tuning, our model enables precise adaptation to different vehicles, even in the wild and under large state estimation errors. In real-world experiments, AnyCar shows both few-shot and zero-shot generalization across a wide range of vehicles and environments, where our model, combined with a sampling-based MPC, outperforms specialist models by up to 54%. These results represent a key step toward building a foundation model for agile wheeled robot control. We will also open-source our framework to support further research.
OmniH2O: Universal and Dexterous Human-to-Humanoid Whole-Body Teleoperation and Learning
Jun 13, 2024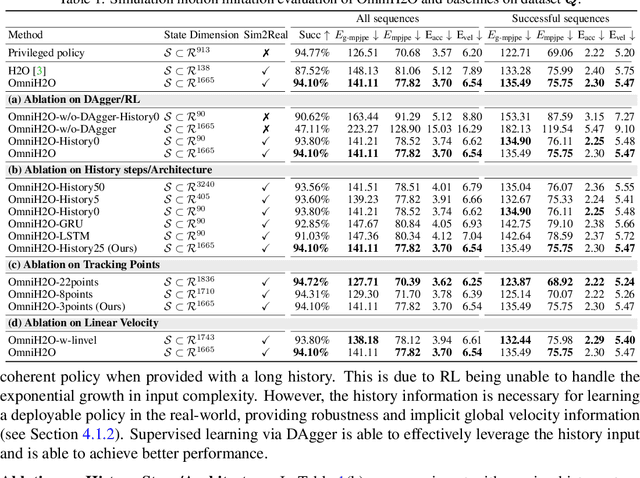
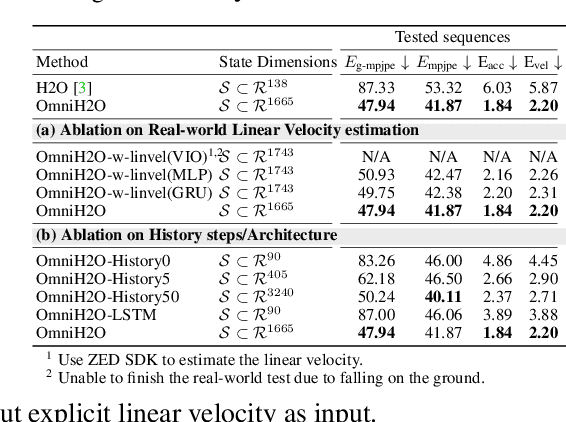
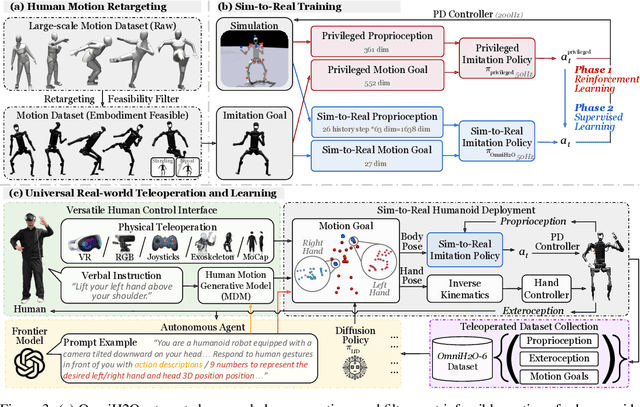
Abstract:We present OmniH2O (Omni Human-to-Humanoid), a learning-based system for whole-body humanoid teleoperation and autonomy. Using kinematic pose as a universal control interface, OmniH2O enables various ways for a human to control a full-sized humanoid with dexterous hands, including using real-time teleoperation through VR headset, verbal instruction, and RGB camera. OmniH2O also enables full autonomy by learning from teleoperated demonstrations or integrating with frontier models such as GPT-4. OmniH2O demonstrates versatility and dexterity in various real-world whole-body tasks through teleoperation or autonomy, such as playing multiple sports, moving and manipulating objects, and interacting with humans. We develop an RL-based sim-to-real pipeline, which involves large-scale retargeting and augmentation of human motion datasets, learning a real-world deployable policy with sparse sensor input by imitating a privileged teacher policy, and reward designs to enhance robustness and stability. We release the first humanoid whole-body control dataset, OmniH2O-6, containing six everyday tasks, and demonstrate humanoid whole-body skill learning from teleoperated datasets.
WoCoCo: Learning Whole-Body Humanoid Control with Sequential Contacts
Jun 10, 2024


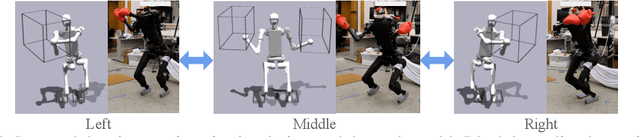
Abstract:Humanoid activities involving sequential contacts are crucial for complex robotic interactions and operations in the real world and are traditionally solved by model-based motion planning, which is time-consuming and often relies on simplified dynamics models. Although model-free reinforcement learning (RL) has become a powerful tool for versatile and robust whole-body humanoid control, it still requires tedious task-specific tuning and state machine design and suffers from long-horizon exploration issues in tasks involving contact sequences. In this work, we propose WoCoCo (Whole-Body Control with Sequential Contacts), a unified framework to learn whole-body humanoid control with sequential contacts by naturally decomposing the tasks into separate contact stages. Such decomposition facilitates simple and general policy learning pipelines through task-agnostic reward and sim-to-real designs, requiring only one or two task-related terms to be specified for each task. We demonstrated that end-to-end RL-based controllers trained with WoCoCo enable four challenging whole-body humanoid tasks involving diverse contact sequences in the real world without any motion priors: 1) versatile parkour jumping, 2) box loco-manipulation, 3) dynamic clap-and-tap dancing, and 4) cliffside climbing. We further show that WoCoCo is a general framework beyond humanoid by applying it in 22-DoF dinosaur robot loco-manipulation tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge