Chong Zhang
Tony
TrajAD: Trajectory Anomaly Detection for Trustworthy LLM Agents
Feb 06, 2026Abstract:We address the problem of runtime trajectory anomaly detection, a critical capability for enabling trustworthy LLM agents. Current safety measures predominantly focus on static input/output filtering. However, we argue that ensuring LLM agents reliability requires auditing the intermediate execution process. In this work, we formulate the task of Trajectory Anomaly Detection. The goal is not merely detection, but precise error localization. This capability is essential for enabling efficient rollback-and-retry. To achieve this, we construct TrajBench, a dataset synthesized via a perturb-and-complete strategy to cover diverse procedural anomalies. Using this benchmark, we investigate the capability of models in process supervision. We observe that general-purpose LLMs, even with zero-shot prompting, struggle to identify and localize these anomalies. This reveals that generalized capabilities do not automatically translate to process reliability. To address this, we propose TrajAD, a specialized verifier trained with fine-grained process supervision. Our approach outperforms baselines, demonstrating that specialized supervision is essential for building trustworthy agents.
FGGM: Fisher-Guided Gradient Masking for Continual Learning
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:Catastrophic forgetting impairs the continuous learning of large language models. We propose Fisher-Guided Gradient Masking (FGGM), a framework that mitigates this by strategically selecting parameters for updates using diagonal Fisher Information. FGGM dynamically generates binary masks with adaptive thresholds, preserving critical parameters to balance stability and plasticity without requiring historical data. Unlike magnitude-based methods such as MIGU, our approach offers a mathematically principled parameter importance estimation. On the TRACE benchmark, FGGM shows a 9.6% relative improvement in retaining general capabilities over supervised fine-tuning (SFT) and a 4.4% improvement over MIGU on TRACE tasks. Additional analysis on code generation tasks confirms FGGM's superior performance and reduced forgetting, establishing it as an effective solution.
StealthMark: Harmless and Stealthy Ownership Verification for Medical Segmentation via Uncertainty-Guided Backdoors
Jan 23, 2026Abstract:Annotating medical data for training AI models is often costly and limited due to the shortage of specialists with relevant clinical expertise. This challenge is further compounded by privacy and ethical concerns associated with sensitive patient information. As a result, well-trained medical segmentation models on private datasets constitute valuable intellectual property requiring robust protection mechanisms. Existing model protection techniques primarily focus on classification and generative tasks, while segmentation models-crucial to medical image analysis-remain largely underexplored. In this paper, we propose a novel, stealthy, and harmless method, StealthMark, for verifying the ownership of medical segmentation models under black-box conditions. Our approach subtly modulates model uncertainty without altering the final segmentation outputs, thereby preserving the model's performance. To enable ownership verification, we incorporate model-agnostic explanation methods, e.g. LIME, to extract feature attributions from the model outputs. Under specific triggering conditions, these explanations reveal a distinct and verifiable watermark. We further design the watermark as a QR code to facilitate robust and recognizable ownership claims. We conducted extensive experiments across four medical imaging datasets and five mainstream segmentation models. The results demonstrate the effectiveness, stealthiness, and harmlessness of our method on the original model's segmentation performance. For example, when applied to the SAM model, StealthMark consistently achieved ASR above 95% across various datasets while maintaining less than a 1% drop in Dice and AUC scores, significantly outperforming backdoor-based watermarking methods and highlighting its strong potential for practical deployment. Our implementation code is made available at: https://github.com/Qinkaiyu/StealthMark.
AME-2: Agile and Generalized Legged Locomotion via Attention-Based Neural Map Encoding
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:Achieving agile and generalized legged locomotion across terrains requires tight integration of perception and control, especially under occlusions and sparse footholds. Existing methods have demonstrated agility on parkour courses but often rely on end-to-end sensorimotor models with limited generalization and interpretability. By contrast, methods targeting generalized locomotion typically exhibit limited agility and struggle with visual occlusions. We introduce AME-2, a unified reinforcement learning (RL) framework for agile and generalized locomotion that incorporates a novel attention-based map encoder in the control policy. This encoder extracts local and global mapping features and uses attention mechanisms to focus on salient regions, producing an interpretable and generalized embedding for RL-based control. We further propose a learning-based mapping pipeline that provides fast, uncertainty-aware terrain representations robust to noise and occlusions, serving as policy inputs. It uses neural networks to convert depth observations into local elevations with uncertainties, and fuses them with odometry. The pipeline also integrates with parallel simulation so that we can train controllers with online mapping, aiding sim-to-real transfer. We validate AME-2 with the proposed mapping pipeline on a quadruped and a biped robot, and the resulting controllers demonstrate strong agility and generalization to unseen terrains in simulation and in real-world experiments.
EverMemOS: A Self-Organizing Memory Operating System for Structured Long-Horizon Reasoning
Jan 05, 2026Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) are increasingly deployed as long-term interactive agents, yet their limited context windows make it difficult to sustain coherent behavior over extended interactions. Existing memory systems often store isolated records and retrieve fragments, limiting their ability to consolidate evolving user states and resolve conflicts. We introduce EverMemOS, a self-organizing memory operating system that implements an engram-inspired lifecycle for computational memory. Episodic Trace Formation converts dialogue streams into MemCells that capture episodic traces, atomic facts, and time-bounded Foresight signals. Semantic Consolidation organizes MemCells into thematic MemScenes, distilling stable semantic structures and updating user profiles. Reconstructive Recollection performs MemScene-guided agentic retrieval to compose the necessary and sufficient context for downstream reasoning. Experiments on LoCoMo and LongMemEval show that EverMemOS achieves state-of-the-art performance on memory-augmented reasoning tasks. We further report a profile study on PersonaMem v2 and qualitative case studies illustrating chat-oriented capabilities such as user profiling and Foresight. Code is available at https://github.com/EverMind-AI/EverMemOS.
Improving Pattern Recognition of Scheduling Anomalies through Structure-Aware and Semantically-Enhanced Graphs
Dec 21, 2025Abstract:This paper proposes a structure-aware driven scheduling graph modeling method to improve the accuracy and representation capability of anomaly identification in scheduling behaviors of complex systems. The method first designs a structure-guided scheduling graph construction mechanism that integrates task execution stages, resource node states, and scheduling path information to build dynamically evolving scheduling behavior graphs, enhancing the model's ability to capture global scheduling relationships. On this basis, a multi-scale graph semantic aggregation module is introduced to achieve semantic consistency modeling of scheduling features through local adjacency semantic integration and global topology alignment, thereby strengthening the model's capability to capture abnormal features in complex scenarios such as multi-task concurrency, resource competition, and stage transitions. Experiments are conducted on a real scheduling dataset with multiple scheduling disturbance paths set to simulate different types of anomalies, including structural shifts, resource changes, and task delays. The proposed model demonstrates significant performance advantages across multiple metrics, showing a sensitive response to structural disturbances and semantic shifts. Further visualization analysis reveals that, under the combined effect of structure guidance and semantic aggregation, the scheduling behavior graph exhibits stronger anomaly separability and pattern representation, validating the effectiveness and adaptability of the method in scheduling anomaly detection tasks.
InfoDCL: Informative Noise Enhanced Diffusion Based Contrastive Learning
Dec 18, 2025Abstract:Contrastive learning has demonstrated promising potential in recommender systems. Existing methods typically construct sparser views by randomly perturbing the original interaction graph, as they have no idea about the authentic user preferences. Owing to the sparse nature of recommendation data, this paradigm can only capture insufficient semantic information. To address the issue, we propose InfoDCL, a novel diffusion-based contrastive learning framework for recommendation. Rather than injecting randomly sampled Gaussian noise, we employ a single-step diffusion process that integrates noise with auxiliary semantic information to generate signals and feed them to the standard diffusion process to generate authentic user preferences as contrastive views. Besides, based on a comprehensive analysis of the mutual influence between generation and preference learning in InfoDCL, we build a collaborative training objective strategy to transform the interference between them into mutual collaboration. Additionally, we employ multiple GCN layers only during inference stage to incorporate higher-order co-occurrence information while maintaining training efficiency. Extensive experiments on five real-world datasets demonstrate that InfoDCL significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods. Our InfoDCL offers an effective solution for enhancing recommendation performance and suggests a novel paradigm for applying diffusion method in contrastive learning frameworks.
Uncertainty-Aware Semantic Decoding for LLM-Based Sequential Recommendation
Aug 10, 2025



Abstract:Large language models have been widely applied to sequential recommendation tasks, yet during inference, they continue to rely on decoding strategies developed for natural language processing. This creates a mismatch between text-generation objectives and recommendation next item selection objectives. This paper addresses this limitation by proposing an Uncertainty-aware Semantic Decoding (USD) framework that combines logit-based clustering with adaptive scoring to improve next-item predictions. Our approach clusters items with similar logit vectors into semantic equivalence groups, then redistributes probability mass within these clusters and computes entropy across them to control item scoring and sampling temperature during recommendation inference. Experiments on Amazon Product datasets (six domains) gains of 18.5\% in HR@3, 11.9\% in NDCG@3, and 10.8\% in MRR@3 compared to state-of-the-art baselines. Hyperparameter analysis confirms the optimal parameters among various settings, and experiments on H\&M, and Netflix datasets indicate that the framework can adapt to differing recommendation domains. The experimental results confirm that integrating semantic clustering and uncertainty assessment yields more reliable and accurate recommendations.
Revisiting Adversarial Patch Defenses on Object Detectors: Unified Evaluation, Large-Scale Dataset, and New Insights
Aug 01, 2025

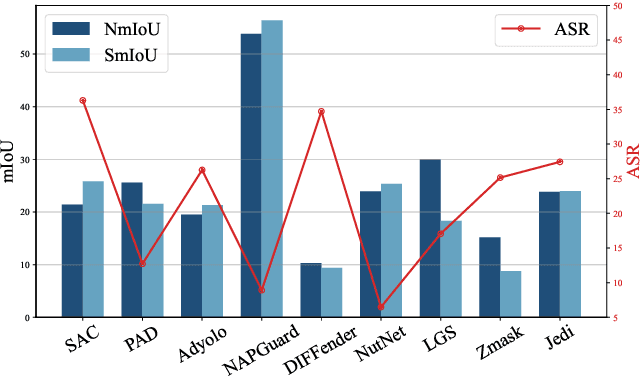
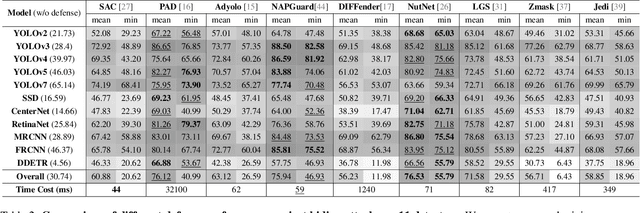
Abstract:Developing reliable defenses against patch attacks on object detectors has attracted increasing interest. However, we identify that existing defense evaluations lack a unified and comprehensive framework, resulting in inconsistent and incomplete assessments of current methods. To address this issue, we revisit 11 representative defenses and present the first patch defense benchmark, involving 2 attack goals, 13 patch attacks, 11 object detectors, and 4 diverse metrics. This leads to the large-scale adversarial patch dataset with 94 types of patches and 94,000 images. Our comprehensive analyses reveal new insights: (1) The difficulty in defending against naturalistic patches lies in the data distribution, rather than the commonly believed high frequencies. Our new dataset with diverse patch distributions can be used to improve existing defenses by 15.09% AP@0.5. (2) The average precision of the attacked object, rather than the commonly pursued patch detection accuracy, shows high consistency with defense performance. (3) Adaptive attacks can substantially bypass existing defenses, and defenses with complex/stochastic models or universal patch properties are relatively robust. We hope that our analyses will serve as guidance on properly evaluating patch attacks/defenses and advancing their design. Code and dataset are available at https://github.com/Gandolfczjh/APDE, where we will keep integrating new attacks/defenses.
Next Tokens Denoising for Speech Synthesis
Jul 30, 2025Abstract:While diffusion and autoregressive (AR) models have significantly advanced generative modeling, they each present distinct limitations. AR models, which rely on causal attention, cannot exploit future context and suffer from slow generation speeds. Conversely, diffusion models struggle with key-value (KV) caching. To overcome these challenges, we introduce Dragon-FM, a novel text-to-speech (TTS) design that unifies AR and flow-matching. This model processes 48 kHz audio codec tokens in chunks at a compact 12.5 tokens per second rate. This design enables AR modeling across chunks, ensuring global coherence, while parallel flow-matching within chunks facilitates fast iterative denoising. Consequently, the proposed model can utilize KV-cache across chunks and incorporate future context within each chunk. Furthermore, it bridges continuous and discrete feature modeling, demonstrating that continuous AR flow-matching can predict discrete tokens with finite scalar quantizers. This efficient codec and fast chunk-autoregressive architecture also makes the proposed model particularly effective for generating extended content. Experiment for demos of our work} on podcast datasets demonstrate its capability to efficiently generate high-quality zero-shot podcasts.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge