Tianyu Zhao
Fast-weight Product Key Memory
Jan 02, 2026Abstract:Sequence modeling layers in modern language models typically face a trade-off between storage capacity and computational efficiency. While Softmax attention offers unbounded storage at prohibitive quadratic costs, linear variants provide efficiency but suffer from limited, fixed-size storage. We propose Fast-weight Product Key Memory (FwPKM), a novel architecture that resolves this tension by transforming the sparse Product Key Memory (PKM) from a static module into a dynamic, "fast-weight" episodic memory. Unlike PKM, FwPKM updates its parameters dynamically at both training and inference time via local chunk-level gradient descent, allowing the model to rapidly memorize and retrieve new key-value pairs from input sequences. Experiments reveal that FwPKM functions as an effective episodic memory that complements the semantic memory of standard modules, yielding significant perplexity reductions on long-context datasets. Notably, in Needle in a Haystack evaluations, FwPKM generalizes to 128K-token contexts despite being trained on only 4K-token sequences.
RePo: Language Models with Context Re-Positioning
Dec 16, 2025



Abstract:In-context learning is fundamental to modern Large Language Models (LLMs); however, prevailing architectures impose a rigid and fixed contextual structure by assigning linear or constant positional indices. Drawing on Cognitive Load Theory (CLT), we argue that this uninformative structure increases extraneous cognitive load, consuming finite working memory capacity that should be allocated to deep reasoning and attention allocation. To address this, we propose RePo, a novel mechanism that reduces extraneous load via context re-positioning. Unlike standard approaches, RePo utilizes a differentiable module, $f_φ$, to assign token positions that capture contextual dependencies, rather than replying on pre-defined integer range. By continually pre-training on the OLMo-2 1B backbone, we demonstrate that RePo significantly enhances performance on tasks involving noisy contexts, structured data, and longer context length, while maintaining competitive performance on general short-context tasks. Detailed analysis reveals that RePo successfully allocate higher attention to distant but relevant information, assign positions in dense and non-linear space, and capture the intrinsic structure of the input context. Our code is available at https://github.com/SakanaAI/repo.
A Systematic Evaluation of Preference Aggregation in Federated RLHF for Pluralistic Alignment of LLMs
Dec 15, 2025Abstract:This paper addresses the challenge of aligning large language models (LLMs) with diverse human preferences within federated learning (FL) environments, where standard methods often fail to adequately represent diverse viewpoints. We introduce a comprehensive evaluation framework that systematically assesses the trade-off between alignment quality and fairness when using different aggregation strategies for human preferences. In our federated setting, each group locally evaluates rollouts and produces reward signals, and the server aggregates these group-level rewards without accessing any raw data. Specifically, we evaluate standard reward aggregation techniques (min, max, and average) and introduce a novel adaptive scheme that dynamically adjusts preference weights based on a group's historical alignment performance. Our experiments on question-answering (Q/A) tasks using a PPO-based RLHF pipeline demonstrate that our adaptive approach consistently achieves superior fairness while maintaining competitive alignment scores. This work offers a robust methodology for evaluating LLM behavior across diverse populations and provides a practical solution for developing truly pluralistic and fairly aligned models.
Task-Specific Sparse Feature Masks for Molecular Toxicity Prediction with Chemical Language Models
Dec 12, 2025Abstract:Reliable in silico molecular toxicity prediction is a cornerstone of modern drug discovery, offering a scalable alternative to experimental screening. However, the black-box nature of state-of-the-art models remains a significant barrier to adoption, as high-stakes safety decisions demand verifiable structural insights alongside predictive performance. To address this, we propose a novel multi-task learning (MTL) framework designed to jointly enhance accuracy and interpretability. Our architecture integrates a shared chemical language model with task-specific attention modules. By imposing an L1 sparsity penalty on these modules, the framework is constrained to focus on a minimal set of salient molecular fragments for each distinct toxicity endpoint. The resulting framework is trained end-to-end and is readily adaptable to various transformer-based backbones. Evaluated on the ClinTox, SIDER, and Tox21 benchmark datasets, our approach consistently outperforms both single-task and standard MTL baselines. Crucially, the sparse attention weights provide chemically intuitive visualizations that reveal the specific fragments influencing predictions, thereby enhancing insight into the model's decision-making process.
OmniDRCA: Parallel Speech-Text Foundation Model via Dual-Resolution Speech Representations and Contrastive Alignment
Jun 11, 2025Abstract:Recent studies on end-to-end speech generation with large language models (LLMs) have attracted significant community attention, with multiple works extending text-based LLMs to generate discrete speech tokens. Existing approaches primarily fall into two categories: (1) Methods that generate discrete speech tokens independently without incorporating them into the LLM's autoregressive process, resulting in text generation being unaware of concurrent speech synthesis. (2) Models that generate interleaved or parallel speech-text tokens through joint autoregressive modeling, enabling mutual modality awareness during generation. This paper presents OmniDRCA, a parallel speech-text foundation model based on joint autoregressive modeling, featuring dual-resolution speech representations and contrastive cross-modal alignment. Our approach processes speech and text representations in parallel while enhancing audio comprehension through contrastive alignment. Experimental results on Spoken Question Answering benchmarks demonstrate that OmniDRCA establishes new state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance among parallel joint speech-text modeling based foundation models, and achieves competitive performance compared to interleaved models. Additionally, we explore the potential of extending the framework to full-duplex conversational scenarios.
Reinforcement Learning Teachers of Test Time Scaling
Jun 10, 2025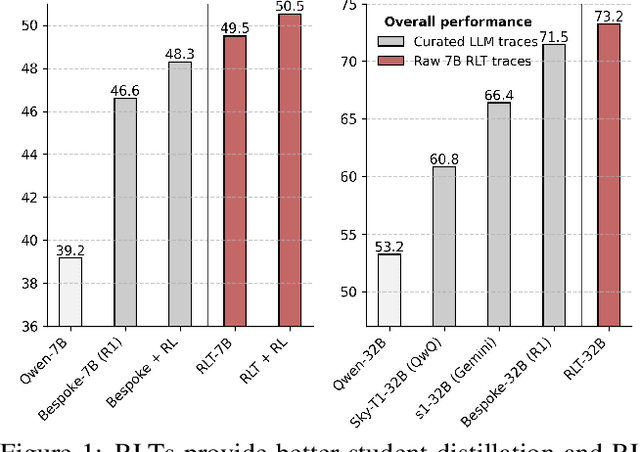
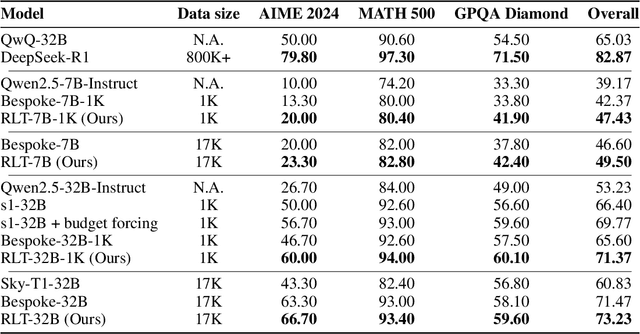
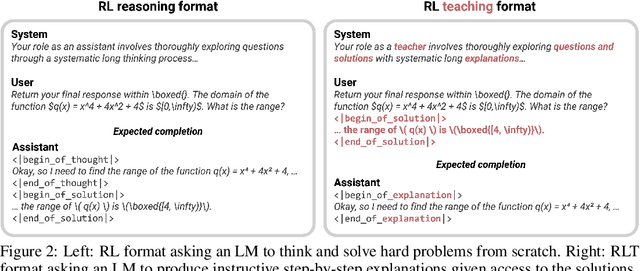
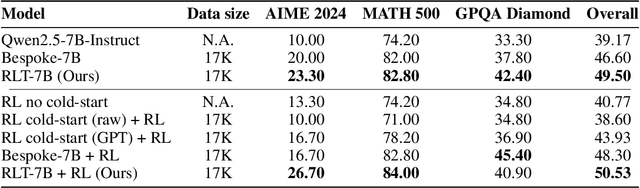
Abstract:Training reasoning language models (LMs) with reinforcement learning (RL) for one-hot correctness inherently relies on the LM being able to explore and solve its task with some chance at initialization. Furthermore, a key use case of reasoning LMs is to act as teachers for distilling new students and cold-starting future RL iterations rather than being deployed themselves. From these considerations, we introduce a new framework that avoids RL's exploration challenge by training a new class of Reinforcement-Learned Teachers (RLTs) focused on yielding the most effective downstream distillation. RLTs are prompted with both the question and solution to each problem, and tasked to simply "connect-the-dots" with detailed explanations tailored for their students. We train RLTs with dense rewards obtained by feeding each explanation to the student and testing its understanding of the problem's solution. In practice, the raw outputs of a 7B RLT provide higher final performance on competition and graduate-level tasks than existing distillation and cold-starting pipelines that collect and postprocess the reasoning traces of orders of magnitude larger LMs. Furthermore, RLTs maintain their effectiveness when training larger students and when applied zero-shot to out-of-distribution tasks, unlocking new levels of efficiency and re-usability for the RL reasoning framework.
CosyVoice 3: Towards In-the-wild Speech Generation via Scaling-up and Post-training
May 23, 2025Abstract:In our prior works, we introduced a scalable streaming speech synthesis model, CosyVoice 2, which integrates a large language model (LLM) and a chunk-aware flow matching (FM) model, and achieves low-latency bi-streaming speech synthesis and human-parity quality. Despite these advancements, CosyVoice 2 exhibits limitations in language coverage, domain diversity, data volume, text formats, and post-training techniques. In this paper, we present CosyVoice 3, an improved model designed for zero-shot multilingual speech synthesis in the wild, surpassing its predecessor in content consistency, speaker similarity, and prosody naturalness. Key features of CosyVoice 3 include: 1) A novel speech tokenizer to improve prosody naturalness, developed via supervised multi-task training, including automatic speech recognition, speech emotion recognition, language identification, audio event detection, and speaker analysis. 2) A new differentiable reward model for post-training applicable not only to CosyVoice 3 but also to other LLM-based speech synthesis models. 3) Dataset Size Scaling: Training data is expanded from ten thousand hours to one million hours, encompassing 9 languages and 18 Chinese dialects across various domains and text formats. 4) Model Size Scaling: Model parameters are increased from 0.5 billion to 1.5 billion, resulting in enhanced performance on our multilingual benchmark due to the larger model capacity. These advancements contribute significantly to the progress of speech synthesis in the wild. We encourage readers to listen to the demo at https://funaudiollm.github.io/cosyvoice3.
Sudoku-Bench: Evaluating creative reasoning with Sudoku variants
May 22, 2025



Abstract:Existing reasoning benchmarks for large language models (LLMs) frequently fail to capture authentic creativity, often rewarding memorization of previously observed patterns. We address this shortcoming with Sudoku-Bench, a curated benchmark of challenging and unconventional Sudoku variants specifically selected to evaluate creative, multi-step logical reasoning. Sudoku variants form an unusually effective domain for reasoning research: each puzzle introduces unique or subtly interacting constraints, making memorization infeasible and requiring solvers to identify novel logical breakthroughs (``break-ins''). Despite their diversity, Sudoku variants maintain a common and compact structure, enabling clear and consistent evaluation. Sudoku-Bench includes a carefully chosen puzzle set, a standardized text-based puzzle representation, and flexible tools compatible with thousands of publicly available puzzles -- making it easy to extend into a general research environment. Baseline experiments show that state-of-the-art LLMs solve fewer than 15\% of puzzles unaided, highlighting significant opportunities to advance long-horizon, strategic reasoning capabilities.
LEMON-Mapping: Loop-Enhanced Large-Scale Multi-Session Point Cloud Merging and Optimization for Globally Consistent Mapping
May 15, 2025Abstract:With the rapid development of robotics, multi-robot collaboration has become critical and challenging. One key problem is integrating data from multiple robots to build a globally consistent and accurate map for robust cooperation and precise localization. While traditional multi-robot pose graph optimization (PGO) maintains basic global consistency, it focuses primarily on pose optimization and ignores the geometric structure of the map. Moreover, PGO only uses loop closure as a constraint between two nodes, failing to fully exploit its capability to maintaining local consistency of multi-robot maps. Therefore, PGO-based multi-robot mapping methods often suffer from serious map divergence and blur, especially in regions with overlapping submaps. To address this issue, we propose Lemon-Mapping, a loop-enhanced framework for large-scale multi-session point cloud map fusion and optimization, which reasonably utilizes loop closure and improves the geometric quality of the map. We re-examine the role of loops for multi-robot mapping and introduce three key innovations. First, we develop a robust loop processing mechanism that effectively rejects outliers and a novel loop recall strategy to recover mistakenly removed loops. Second, we introduce a spatial bundle adjustment method for multi-robot maps that significantly reduces the divergence in overlapping regions and eliminates map blur. Third, we design a PGO strategy that leverages the refined constraints of bundle adjustment to extend the local accuracy to the global map. We validate our framework on several public datasets and a self-collected dataset. Experimental results demonstrate that our method outperforms traditional map merging approaches in terms of mapping accuracy and reduction of map divergence. Scalability experiments also demonstrate the strong capability of our framework to handle scenarios involving numerous robots.
PluralLLM: Pluralistic Alignment in LLMs via Federated Learning
Mar 13, 2025



Abstract:Ensuring Large Language Models (LLMs) align with diverse human preferences while preserving privacy and fairness remains a challenge. Existing methods, such as Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF), rely on centralized data collection, making them computationally expensive and privacy-invasive. We introduce PluralLLM a federated learning-based approach that enables multiple user groups to collaboratively train a transformer-based preference predictor without sharing sensitive data, which can also serve as a reward model for aligning LLMs. Our method leverages Federated Averaging (FedAvg) to aggregate preference updates efficiently, achieving 46% faster convergence, a 4% improvement in alignment scores, and nearly the same group fairness measure as in centralized training. Evaluated on a Q/A preference alignment task, PluralLLM demonstrates that federated preference learning offers a scalable and privacy-preserving alternative for aligning LLMs with diverse human values.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge