Chaoyi Pan
SPIDER: Scalable Physics-Informed Dexterous Retargeting
Nov 12, 2025Abstract:Learning dexterous and agile policy for humanoid and dexterous hand control requires large-scale demonstrations, but collecting robot-specific data is prohibitively expensive. In contrast, abundant human motion data is readily available from motion capture, videos, and virtual reality, which could help address the data scarcity problem. However, due to the embodiment gap and missing dynamic information like force and torque, these demonstrations cannot be directly executed on robots. To bridge this gap, we propose Scalable Physics-Informed DExterous Retargeting (SPIDER), a physics-based retargeting framework to transform and augment kinematic-only human demonstrations to dynamically feasible robot trajectories at scale. Our key insight is that human demonstrations should provide global task structure and objective, while large-scale physics-based sampling with curriculum-style virtual contact guidance should refine trajectories to ensure dynamical feasibility and correct contact sequences. SPIDER scales across diverse 9 humanoid/dexterous hand embodiments and 6 datasets, improving success rates by 18% compared to standard sampling, while being 10X faster than reinforcement learning (RL) baselines, and enabling the generation of a 2.4M frames dynamic-feasible robot dataset for policy learning. As a universal physics-based retargeting method, SPIDER can work with diverse quality data and generate diverse and high-quality data to enable efficient policy learning with methods like RL.
Learning Gentle Humanoid Locomotion and End-Effector Stabilization Control
May 30, 2025Abstract:Can your humanoid walk up and hand you a full cup of beer, without spilling a drop? While humanoids are increasingly featured in flashy demos like dancing, delivering packages, traversing rough terrain, fine-grained control during locomotion remains a significant challenge. In particular, stabilizing a filled end-effector (EE) while walking is far from solved, due to a fundamental mismatch in task dynamics: locomotion demands slow-timescale, robust control, whereas EE stabilization requires rapid, high-precision corrections. To address this, we propose SoFTA, a Slow-Fast TwoAgent framework that decouples upper-body and lower-body control into separate agents operating at different frequencies and with distinct rewards. This temporal and objective separation mitigates policy interference and enables coordinated whole-body behavior. SoFTA executes upper-body actions at 100 Hz for precise EE control and lower-body actions at 50 Hz for robust gait. It reduces EE acceleration by 2-5x relative to baselines and performs much closer to human-level stability, enabling delicate tasks such as carrying nearly full cups, capturing steady video during locomotion, and disturbance rejection with EE stability.
Whole-Body Model-Predictive Control of Legged Robots with MuJoCo
Mar 06, 2025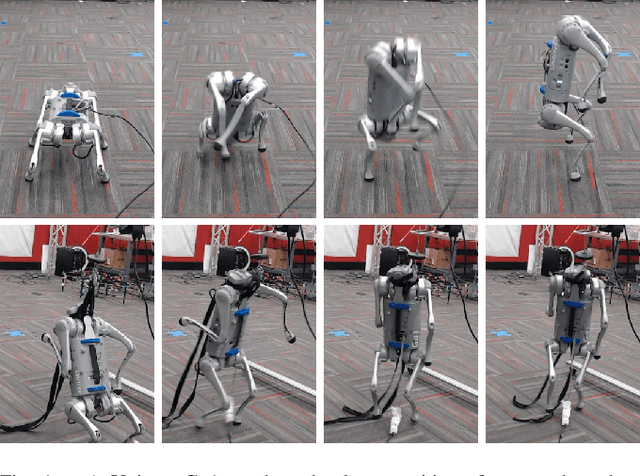
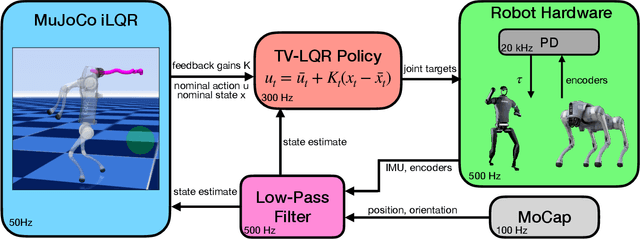
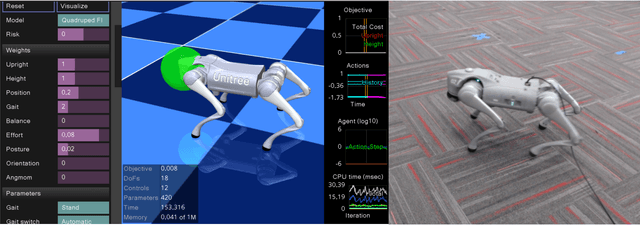
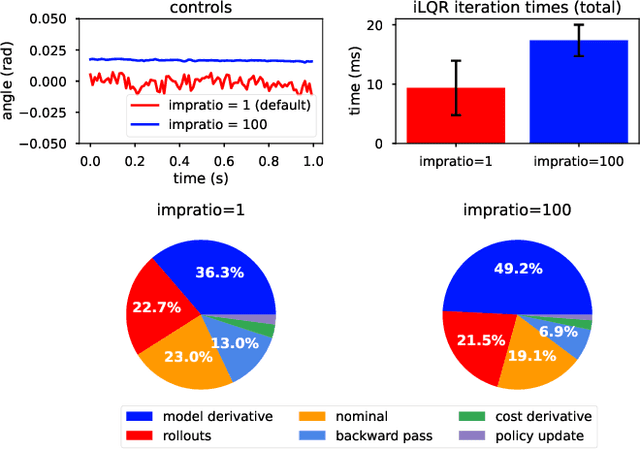
Abstract:We demonstrate the surprising real-world effectiveness of a very simple approach to whole-body model-predictive control (MPC) of quadruped and humanoid robots: the iterative LQR (iLQR) algorithm with MuJoCo dynamics and finite-difference approximated derivatives. Building upon the previous success of model-based behavior synthesis and control of locomotion and manipulation tasks with MuJoCo in simulation, we show that these policies can easily generalize to the real world with few sim-to-real considerations. Our baseline method achieves real-time whole-body MPC on a variety of hardware experiments, including dynamic quadruped locomotion, quadruped walking on two legs, and full-sized humanoid bipedal locomotion. We hope this easy-to-reproduce hardware baseline lowers the barrier to entry for real-world whole-body MPC research and contributes to accelerating research velocity in the community. Our code and experiment videos will be available online at:https://johnzhang3.github.io/mujoco_ilqr
ASAP: Aligning Simulation and Real-World Physics for Learning Agile Humanoid Whole-Body Skills
Feb 03, 2025Abstract:Humanoid robots hold the potential for unparalleled versatility in performing human-like, whole-body skills. However, achieving agile and coordinated whole-body motions remains a significant challenge due to the dynamics mismatch between simulation and the real world. Existing approaches, such as system identification (SysID) and domain randomization (DR) methods, often rely on labor-intensive parameter tuning or result in overly conservative policies that sacrifice agility. In this paper, we present ASAP (Aligning Simulation and Real-World Physics), a two-stage framework designed to tackle the dynamics mismatch and enable agile humanoid whole-body skills. In the first stage, we pre-train motion tracking policies in simulation using retargeted human motion data. In the second stage, we deploy the policies in the real world and collect real-world data to train a delta (residual) action model that compensates for the dynamics mismatch. Then, ASAP fine-tunes pre-trained policies with the delta action model integrated into the simulator to align effectively with real-world dynamics. We evaluate ASAP across three transfer scenarios: IsaacGym to IsaacSim, IsaacGym to Genesis, and IsaacGym to the real-world Unitree G1 humanoid robot. Our approach significantly improves agility and whole-body coordination across various dynamic motions, reducing tracking error compared to SysID, DR, and delta dynamics learning baselines. ASAP enables highly agile motions that were previously difficult to achieve, demonstrating the potential of delta action learning in bridging simulation and real-world dynamics. These results suggest a promising sim-to-real direction for developing more expressive and agile humanoids.
CoVO-MPC: Theoretical Analysis of Sampling-based MPC and Optimal Covariance Design
Jan 14, 2024



Abstract:Sampling-based Model Predictive Control (MPC) has been a practical and effective approach in many domains, notably model-based reinforcement learning, thanks to its flexibility and parallelizability. Despite its appealing empirical performance, the theoretical understanding, particularly in terms of convergence analysis and hyperparameter tuning, remains absent. In this paper, we characterize the convergence property of a widely used sampling-based MPC method, Model Predictive Path Integral Control (MPPI). We show that MPPI enjoys at least linear convergence rates when the optimization is quadratic, which covers time-varying LQR systems. We then extend to more general nonlinear systems. Our theoretical analysis directly leads to a novel sampling-based MPC algorithm, CoVariance-Optimal MPC (CoVo-MPC) that optimally schedules the sampling covariance to optimize the convergence rate. Empirically, CoVo-MPC significantly outperforms standard MPPI by 43-54% in both simulations and real-world quadrotor agile control tasks. Videos and Appendices are available at \url{https://lecar-lab.github.io/CoVO-MPC/}.
Task-Driven In-Hand Manipulation of Unknown Objects with Tactile Sensing
Oct 28, 2022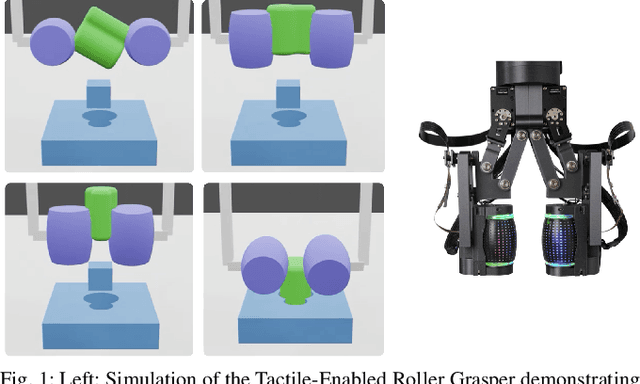
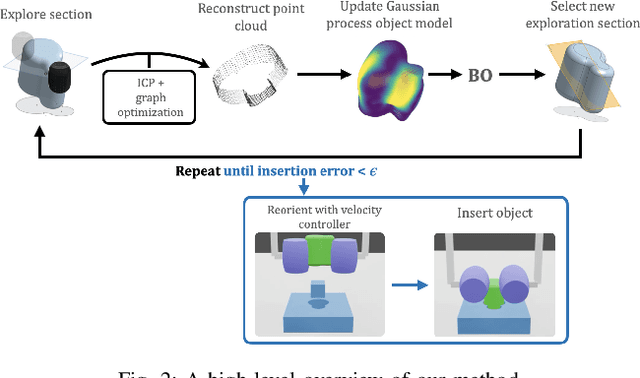
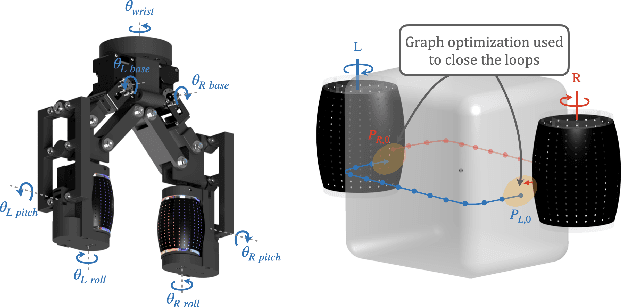
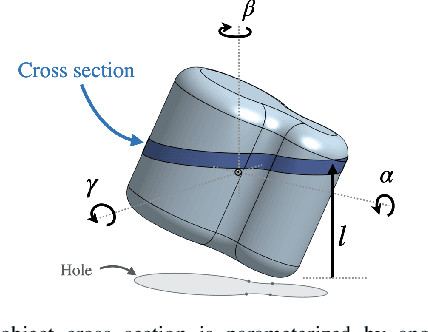
Abstract:Manipulation of objects in-hand without an object model is a foundational skill for many tasks in unstructured environments. In many cases, vision-only approaches may not be feasible; for example, due to occlusion in cluttered spaces. In this paper, we introduce a method to reorient unknown objects by incrementally building a probabilistic estimate of the object shape and pose during task-driven manipulation. Our method leverages Bayesian optimization to strategically trade-off exploration of the global object shape with efficient task completion. We demonstrate our approach on a Tactile-Enabled Roller Grasper, a gripper that rolls objects in hand while continuously collecting tactile data. We evaluate our method in simulation on a set of randomly generated objects and find that our method reliably reorients objects while significantly reducing the exploration time needed to do so. On the Roller Grasper hardware, we show successful qualitative reconstruction of the object model. In summary, this work (1) presents a system capable of simultaneously learning unknown 3D object shape and pose using tactile sensing; and (2) demonstrates that task-driven exploration results in more efficient object manipulation than the common paradigm of complete object exploration before task-completion.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge