Zeji Yi
Whole-Body Model-Predictive Control of Legged Robots with MuJoCo
Mar 06, 2025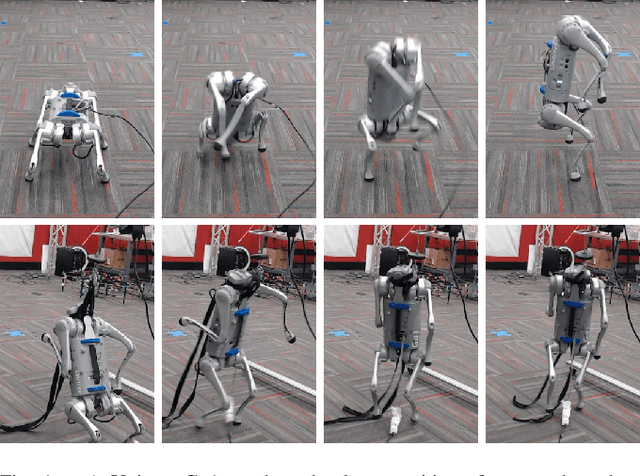
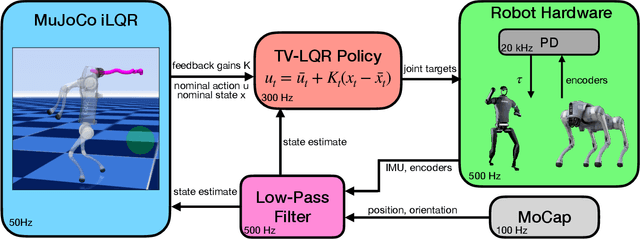
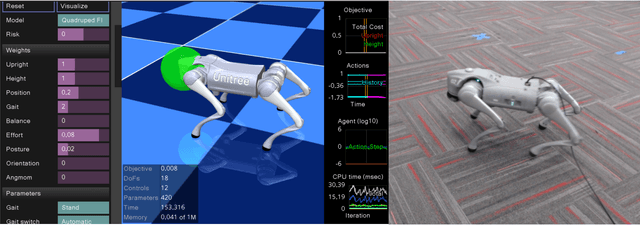
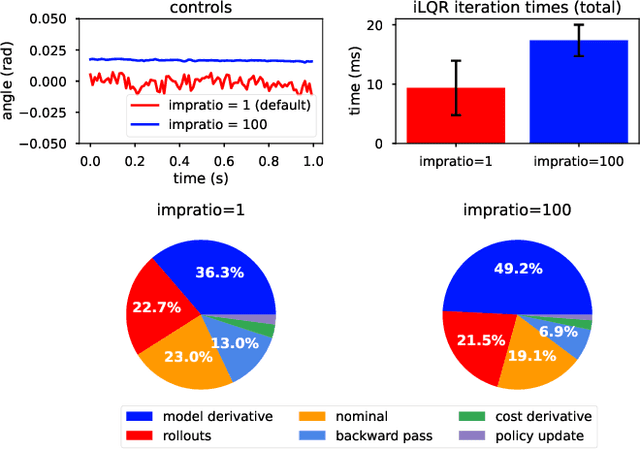
Abstract:We demonstrate the surprising real-world effectiveness of a very simple approach to whole-body model-predictive control (MPC) of quadruped and humanoid robots: the iterative LQR (iLQR) algorithm with MuJoCo dynamics and finite-difference approximated derivatives. Building upon the previous success of model-based behavior synthesis and control of locomotion and manipulation tasks with MuJoCo in simulation, we show that these policies can easily generalize to the real world with few sim-to-real considerations. Our baseline method achieves real-time whole-body MPC on a variety of hardware experiments, including dynamic quadruped locomotion, quadruped walking on two legs, and full-sized humanoid bipedal locomotion. We hope this easy-to-reproduce hardware baseline lowers the barrier to entry for real-world whole-body MPC research and contributes to accelerating research velocity in the community. Our code and experiment videos will be available online at:https://johnzhang3.github.io/mujoco_ilqr
ASAP: Aligning Simulation and Real-World Physics for Learning Agile Humanoid Whole-Body Skills
Feb 03, 2025Abstract:Humanoid robots hold the potential for unparalleled versatility in performing human-like, whole-body skills. However, achieving agile and coordinated whole-body motions remains a significant challenge due to the dynamics mismatch between simulation and the real world. Existing approaches, such as system identification (SysID) and domain randomization (DR) methods, often rely on labor-intensive parameter tuning or result in overly conservative policies that sacrifice agility. In this paper, we present ASAP (Aligning Simulation and Real-World Physics), a two-stage framework designed to tackle the dynamics mismatch and enable agile humanoid whole-body skills. In the first stage, we pre-train motion tracking policies in simulation using retargeted human motion data. In the second stage, we deploy the policies in the real world and collect real-world data to train a delta (residual) action model that compensates for the dynamics mismatch. Then, ASAP fine-tunes pre-trained policies with the delta action model integrated into the simulator to align effectively with real-world dynamics. We evaluate ASAP across three transfer scenarios: IsaacGym to IsaacSim, IsaacGym to Genesis, and IsaacGym to the real-world Unitree G1 humanoid robot. Our approach significantly improves agility and whole-body coordination across various dynamic motions, reducing tracking error compared to SysID, DR, and delta dynamics learning baselines. ASAP enables highly agile motions that were previously difficult to achieve, demonstrating the potential of delta action learning in bridging simulation and real-world dynamics. These results suggest a promising sim-to-real direction for developing more expressive and agile humanoids.
Safe Bayesian Optimization for the Control of High-Dimensional Embodied Systems
Dec 29, 2024



Abstract:Learning to move is a primary goal for animals and robots, where ensuring safety is often important when optimizing control policies on the embodied systems. For complex tasks such as the control of human or humanoid control, the high-dimensional parameter space adds complexity to the safe optimization effort. Current safe exploration algorithms exhibit inefficiency and may even become infeasible with large high-dimensional input spaces. Furthermore, existing high-dimensional constrained optimization methods neglect safety in the search process. In this paper, we propose High-dimensional Safe Bayesian Optimization with local optimistic exploration (HdSafeBO), a novel approach designed to handle high-dimensional sampling problems under probabilistic safety constraints. We introduce a local optimistic strategy to efficiently and safely optimize the objective function, providing a probabilistic safety guarantee and a cumulative safety violation bound. Through the use of isometric embedding, HdSafeBO addresses problems ranging from a few hundred to several thousand dimensions while maintaining safety guarantees. To our knowledge, HdSafeBO is the first algorithm capable of optimizing the control of high-dimensional musculoskeletal systems with high safety probability. We also demonstrate the real-world applicability of HdSafeBO through its use in the safe online optimization of neural stimulation induced human motion control.
CoVO-MPC: Theoretical Analysis of Sampling-based MPC and Optimal Covariance Design
Jan 14, 2024



Abstract:Sampling-based Model Predictive Control (MPC) has been a practical and effective approach in many domains, notably model-based reinforcement learning, thanks to its flexibility and parallelizability. Despite its appealing empirical performance, the theoretical understanding, particularly in terms of convergence analysis and hyperparameter tuning, remains absent. In this paper, we characterize the convergence property of a widely used sampling-based MPC method, Model Predictive Path Integral Control (MPPI). We show that MPPI enjoys at least linear convergence rates when the optimization is quadratic, which covers time-varying LQR systems. We then extend to more general nonlinear systems. Our theoretical analysis directly leads to a novel sampling-based MPC algorithm, CoVariance-Optimal MPC (CoVo-MPC) that optimally schedules the sampling covariance to optimize the convergence rate. Empirically, CoVo-MPC significantly outperforms standard MPPI by 43-54% in both simulations and real-world quadrotor agile control tasks. Videos and Appendices are available at \url{https://lecar-lab.github.io/CoVO-MPC/}.
Improving sample efficiency of high dimensional Bayesian optimization with MCMC
Jan 05, 2024Abstract:Sequential optimization methods are often confronted with the curse of dimensionality in high-dimensional spaces. Current approaches under the Gaussian process framework are still burdened by the computational complexity of tracking Gaussian process posteriors and need to partition the optimization problem into small regions to ensure exploration or assume an underlying low-dimensional structure. With the idea of transiting the candidate points towards more promising positions, we propose a new method based on Markov Chain Monte Carlo to efficiently sample from an approximated posterior. We provide theoretical guarantees of its convergence in the Gaussian process Thompson sampling setting. We also show experimentally that both the Metropolis-Hastings and the Langevin Dynamics version of our algorithm outperform state-of-the-art methods in high-dimensional sequential optimization and reinforcement learning benchmarks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge