Yunyue Wei
Scalable Exploration for High-Dimensional Continuous Control via Value-Guided Flow
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Controlling high-dimensional systems in biological and robotic applications is challenging due to expansive state-action spaces, where effective exploration is critical. Commonly used exploration strategies in reinforcement learning are largely undirected with sharp degradation as action dimensionality grows. Many existing methods resort to dimensionality reduction, which constrains policy expressiveness and forfeits system flexibility. We introduce Q-guided Flow Exploration (Qflex), a scalable reinforcement learning method that conducts exploration directly in the native high-dimensional action space. During training, Qflex traverses actions from a learnable source distribution along a probability flow induced by the learned value function, aligning exploration with task-relevant gradients rather than isotropic noise. Our proposed method substantially outperforms representative online reinforcement learning baselines across diverse high-dimensional continuous-control benchmarks. Qflex also successfully controls a full-body human musculoskeletal model to perform agile, complex movements, demonstrating superior scalability and sample efficiency in very high-dimensional settings. Our results indicate that value-guided flows offer a principled and practical route to exploration at scale.
Embodied Learning of Reward for Musculoskeletal Control with Vision Language Models
Dec 28, 2025Abstract:Discovering effective reward functions remains a fundamental challenge in motor control of high-dimensional musculoskeletal systems. While humans can describe movement goals explicitly such as "walking forward with an upright posture," the underlying control strategies that realize these goals are largely implicit, making it difficult to directly design rewards from high-level goals and natural language descriptions. We introduce Motion from Vision-Language Representation (MoVLR), a framework that leverages vision-language models (VLMs) to bridge the gap between goal specification and movement control. Rather than relying on handcrafted rewards, MoVLR iteratively explores the reward space through iterative interaction between control optimization and VLM feedback, aligning control policies with physically coordinated behaviors. Our approach transforms language and vision-based assessments into structured guidance for embodied learning, enabling the discovery and refinement of reward functions for high-dimensional musculoskeletal locomotion and manipulation. These results suggest that VLMs can effectively ground abstract motion descriptions in the implicit principles governing physiological motor control.
Bipedal Balance Control with Whole-body Musculoskeletal Standing and Falling Simulations
Jun 11, 2025Abstract:Balance control is important for human and bipedal robotic systems. While dynamic balance during locomotion has received considerable attention, quantitative understanding of static balance and falling remains limited. This work presents a hierarchical control pipeline for simulating human balance via a comprehensive whole-body musculoskeletal system. We identified spatiotemporal dynamics of balancing during stable standing, revealed the impact of muscle injury on balancing behavior, and generated fall contact patterns that aligned with clinical data. Furthermore, our simulated hip exoskeleton assistance demonstrated improvement in balance maintenance and reduced muscle effort under perturbation. This work offers unique muscle-level insights into human balance dynamics that are challenging to capture experimentally. It could provide a foundation for developing targeted interventions for individuals with balance impairments and support the advancement of humanoid robotic systems.
Motion Control of High-Dimensional Musculoskeletal Systems with Hierarchical Model-Based Planning
May 13, 2025Abstract:Controlling high-dimensional nonlinear systems, such as those found in biological and robotic applications, is challenging due to large state and action spaces. While deep reinforcement learning has achieved a number of successes in these domains, it is computationally intensive and time consuming, and therefore not suitable for solving large collections of tasks that require significant manual tuning. In this work, we introduce Model Predictive Control with Morphology-aware Proportional Control (MPC^2), a hierarchical model-based learning algorithm for zero-shot and near-real-time control of high-dimensional complex dynamical systems. MPC^2 uses a sampling-based model predictive controller for target posture planning, and enables robust control for high-dimensional tasks by incorporating a morphology-aware proportional controller for actuator coordination. The algorithm enables motion control of a high-dimensional human musculoskeletal model in a variety of motion tasks, such as standing, walking on different terrains, and imitating sports activities. The reward function of MPC^2 can be tuned via black-box optimization, drastically reducing the need for human-intensive reward engineering.
Scalable Bayesian Optimization via Focalized Sparse Gaussian Processes
Dec 29, 2024Abstract:Bayesian optimization is an effective technique for black-box optimization, but its applicability is typically limited to low-dimensional and small-budget problems due to the cubic complexity of computing the Gaussian process (GP) surrogate. While various approximate GP models have been employed to scale Bayesian optimization to larger sample sizes, most suffer from overly-smooth estimation and focus primarily on problems that allow for large online samples. In this work, we argue that Bayesian optimization algorithms with sparse GPs can more efficiently allocate their representational power to relevant regions of the search space. To achieve this, we propose focalized GP, which leverages a novel variational loss function to achieve stronger local prediction, as well as FocalBO, which hierarchically optimizes the focalized GP acquisition function over progressively smaller search spaces. Experimental results demonstrate that FocalBO can efficiently leverage large amounts of offline and online data to achieve state-of-the-art performance on robot morphology design and to control a 585-dimensional musculoskeletal system.
Safe Bayesian Optimization for the Control of High-Dimensional Embodied Systems
Dec 29, 2024



Abstract:Learning to move is a primary goal for animals and robots, where ensuring safety is often important when optimizing control policies on the embodied systems. For complex tasks such as the control of human or humanoid control, the high-dimensional parameter space adds complexity to the safe optimization effort. Current safe exploration algorithms exhibit inefficiency and may even become infeasible with large high-dimensional input spaces. Furthermore, existing high-dimensional constrained optimization methods neglect safety in the search process. In this paper, we propose High-dimensional Safe Bayesian Optimization with local optimistic exploration (HdSafeBO), a novel approach designed to handle high-dimensional sampling problems under probabilistic safety constraints. We introduce a local optimistic strategy to efficiently and safely optimize the objective function, providing a probabilistic safety guarantee and a cumulative safety violation bound. Through the use of isometric embedding, HdSafeBO addresses problems ranging from a few hundred to several thousand dimensions while maintaining safety guarantees. To our knowledge, HdSafeBO is the first algorithm capable of optimizing the control of high-dimensional musculoskeletal systems with high safety probability. We also demonstrate the real-world applicability of HdSafeBO through its use in the safe online optimization of neural stimulation induced human motion control.
Improving sample efficiency of high dimensional Bayesian optimization with MCMC
Jan 05, 2024Abstract:Sequential optimization methods are often confronted with the curse of dimensionality in high-dimensional spaces. Current approaches under the Gaussian process framework are still burdened by the computational complexity of tracking Gaussian process posteriors and need to partition the optimization problem into small regions to ensure exploration or assume an underlying low-dimensional structure. With the idea of transiting the candidate points towards more promising positions, we propose a new method based on Markov Chain Monte Carlo to efficiently sample from an approximated posterior. We provide theoretical guarantees of its convergence in the Gaussian process Thompson sampling setting. We also show experimentally that both the Metropolis-Hastings and the Langevin Dynamics version of our algorithm outperform state-of-the-art methods in high-dimensional sequential optimization and reinforcement learning benchmarks.
An Invariant Information Geometric Method for High-Dimensional Online Optimization
Jan 03, 2024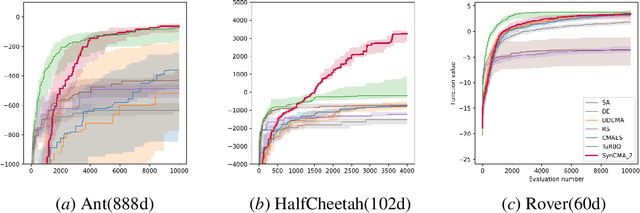
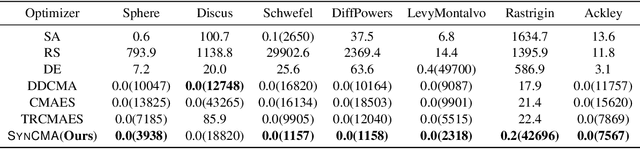
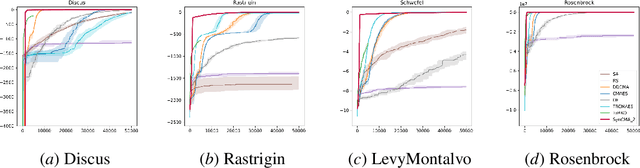
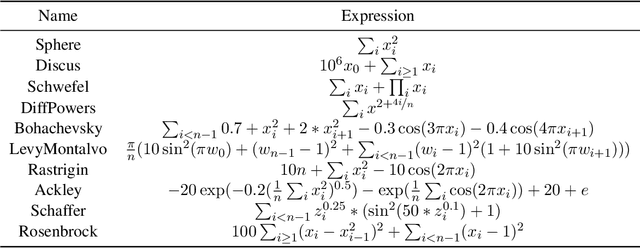
Abstract:Sample efficiency is crucial in optimization, particularly in black-box scenarios characterized by expensive evaluations and zeroth-order feedback. When computing resources are plentiful, Bayesian optimization is often favored over evolution strategies. In this paper, we introduce a full invariance oriented evolution strategies algorithm, derived from its corresponding framework, that effectively rivals the leading Bayesian optimization method in tasks with dimensions at the upper limit of Bayesian capability. Specifically, we first build the framework InvIGO that fully incorporates historical information while retaining the full invariant and computational complexity. We then exemplify InvIGO on multi-dimensional Gaussian, which gives an invariant and scalable optimizer SynCMA . The theoretical behavior and advantages of our algorithm over other Gaussian-based evolution strategies are further analyzed. Finally, We benchmark SynCMA against leading algorithms in Bayesian optimization and evolution strategies on various high dimension tasks, in cluding Mujoco locomotion tasks, rover planning task and synthetic functions. In all scenarios, SynCMA demonstrates great competence, if not dominance, over other algorithms in sample efficiency, showing the underdeveloped potential of property oriented evolution strategies.
Safe Policy Optimization with Local Generalized Linear Function Approximations
Nov 09, 2021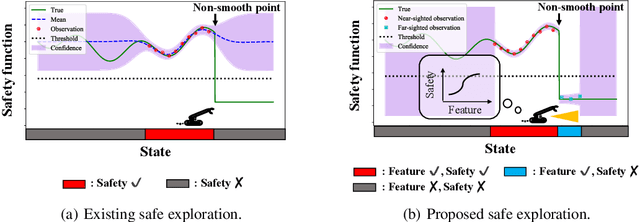

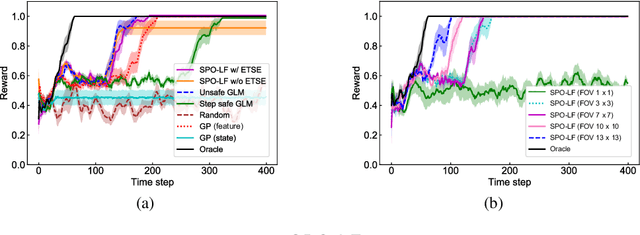
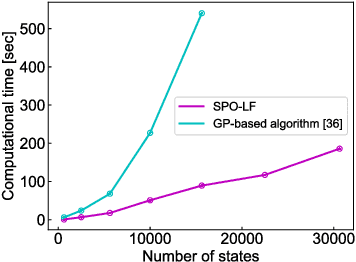
Abstract:Safe exploration is a key to applying reinforcement learning (RL) in safety-critical systems. Existing safe exploration methods guaranteed safety under the assumption of regularity, and it has been difficult to apply them to large-scale real problems. We propose a novel algorithm, SPO-LF, that optimizes an agent's policy while learning the relation between a locally available feature obtained by sensors and environmental reward/safety using generalized linear function approximations. We provide theoretical guarantees on its safety and optimality. We experimentally show that our algorithm is 1) more efficient in terms of sample complexity and computational cost and 2) more applicable to large-scale problems than previous safe RL methods with theoretical guarantees, and 3) comparably sample-efficient and safer compared with existing advanced deep RL methods with safety constraints.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge