Jaejin Lee
Reasoning by Commented Code for Table Question Answering
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:Table Question Answering (TableQA) poses a significant challenge for large language models (LLMs) because conventional linearization of tables often disrupts the two-dimensional relationships intrinsic to structured data. Existing methods, which depend on end-to-end answer generation or single-line program queries, typically exhibit limited numerical accuracy and reduced interpretability. This work introduces a commented, step-by-step code-generation framework that incorporates explicit reasoning into the Python program-generation process. The approach decomposes TableQA reasoning into multi-line executable programs with concise natural language comments, thereby promoting clearer reasoning and increasing the likelihood of generating correct code. On the WikiTableQuestions benchmark, the proposed method achieves 70.9\% accuracy using Qwen2.5-Coder-7B-Instruct, surpassing the Repanda baseline (67.6\%). Integrating the proposed framework with a robust end-to-end TableQA model via a lightweight answer-selection mechanism yields further improvements. This combined approach achieves up to 84.3\% accuracy on the WikiTableQuestions benchmark.
HetCCL: Accelerating LLM Training with Heterogeneous GPUs
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:The rapid growth of large language models is driving organizations to expand their GPU clusters, often with GPUs from multiple vendors. However, current deep learning frameworks lack support for collective communication across heterogeneous GPUs, leading to inefficiency and higher costs. We present HetCCL, a collective communication library that unifies vendor-specific backends and enables RDMA-based communication across GPUs without requiring driver modifications. HetCCL introduces two novel mechanisms that enable cross-vendor communication while leveraging optimized vendor libraries, NVIDIA NCCL and AMD RCCL. Evaluations on a multi-vendor GPU cluster show that HetCCL matches NCCL and RCCL performance in homogeneous setups while uniquely scaling in heterogeneous environments, enabling practical, high-performance training with both NVIDIA and AMD GPUs without changes to existing deep learning applications.
Models Know Models Best: Evaluation via Model-Preferred Formats
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Performance of Large Language Models (LLMs) on multiple-choice tasks differs markedly between symbol-based and cloze-style evaluation formats. The observed discrepancies are systematically attributable to task characteristics: natural language continuation benefits from likelihood scoring, whereas explicit comparison is better suited to symbol-based selection. These trends are consistent across various decoder-based LLMs, indicating model-agnostic effects. To address these inconsistencies, a dynamic format-alignment strategy is introduced that employs a lightweight classifier trained on latent model-preference signals. In contrast to human-designed heuristics, which often degrade performance, this approach uses model-generated signals to determine the optimal format for each problem instance. The proposed method achieves substantial and consistent improvements in zero-shot accuracy across reasoning and knowledge benchmarks, better revealing the models' latent capabilities.
Thunder-KoNUBench: A Corpus-Aligned Benchmark for Korean Negation Understanding
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:Although negation is known to challenge large language models (LLMs), benchmarks for evaluating negation understanding, especially in Korean, are scarce. We conduct a corpus-based analysis of Korean negation and show that LLM performance degrades under negation. We then introduce Thunder-KoNUBench, a sentence-level benchmark that reflects the empirical distribution of Korean negation phenomena. Evaluating 47 LLMs, we analyze the effects of model size and instruction tuning, and show that fine-tuning on Thunder-KoNUBench improves negation understanding and broader contextual comprehension in Korean.
Thunder-Tok: Minimizing Tokens per Word in Tokenizing Korean Texts for Generative Language Models
Jun 18, 2025Abstract:This paper introduces Thunder-Tok, a new Korean tokenizer designed to reduce token fertility without compromising model performance. Our approach uses a rule-based pre-tokenization method that aligns with the linguistic structure of the Korean language. We also create a seed vocabulary containing tokens that resemble linguistic units and employ a branching entropy-based selection algorithm. These techniques increase the average token length, thus lowering fertility while preserving linguistic information. Experimental results indicate that Thunder-Tok reduces fertility by approximately 10% (i.e., reduces the number of tokens by 10%, improving the inference speed by 10%) compared to BPE without compromising performance across various downstream tasks. These findings demonstrate that our linguistically informed approach is effective and practical for designing efficient tokenizers for language models.
Thunder-NUBench: A Benchmark for LLMs' Sentence-Level Negation Understanding
Jun 18, 2025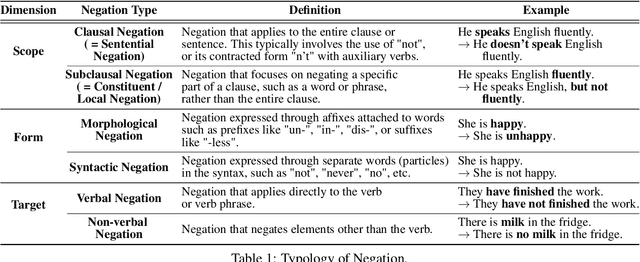
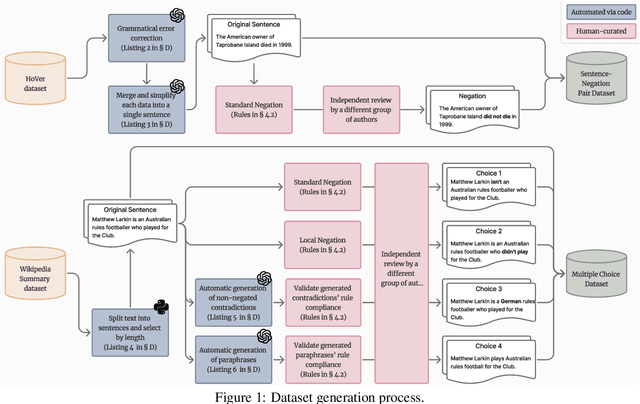
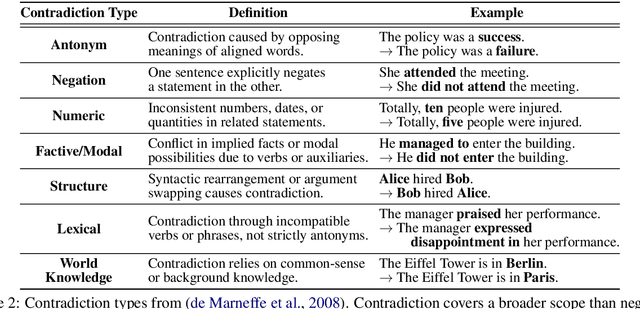
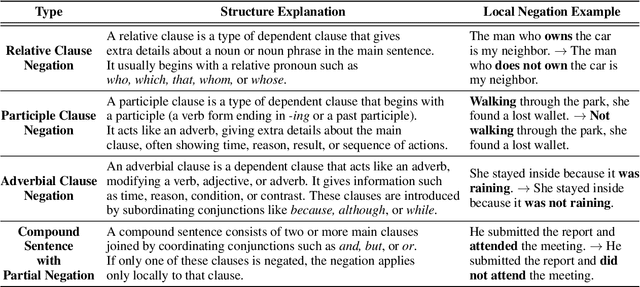
Abstract:Negation is a fundamental linguistic phenomenon that poses persistent challenges for Large Language Models (LLMs), particularly in tasks requiring deep semantic understanding. Existing benchmarks often treat negation as a side case within broader tasks like natural language inference, resulting in a lack of benchmarks that exclusively target negation understanding. In this work, we introduce Thunder-NUBench, a novel benchmark explicitly designed to assess sentence-level negation understanding in LLMs. Thunder-NUBench goes beyond surface-level cue detection by contrasting standard negation with structurally diverse alternatives such as local negation, contradiction, and paraphrase. The benchmark consists of manually curated sentence-negation pairs and a multiple-choice dataset that enables in-depth evaluation of models' negation understanding.
Thunder-DeID: Accurate and Efficient De-identification Framework for Korean Court Judgments
Jun 18, 2025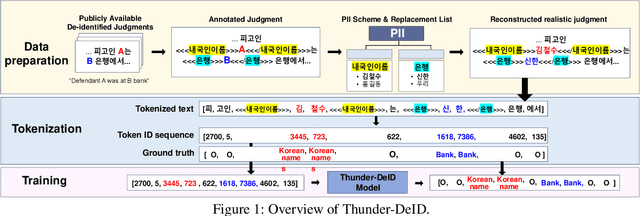
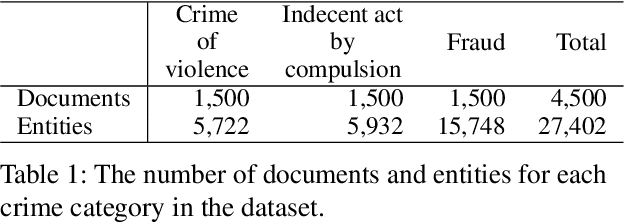
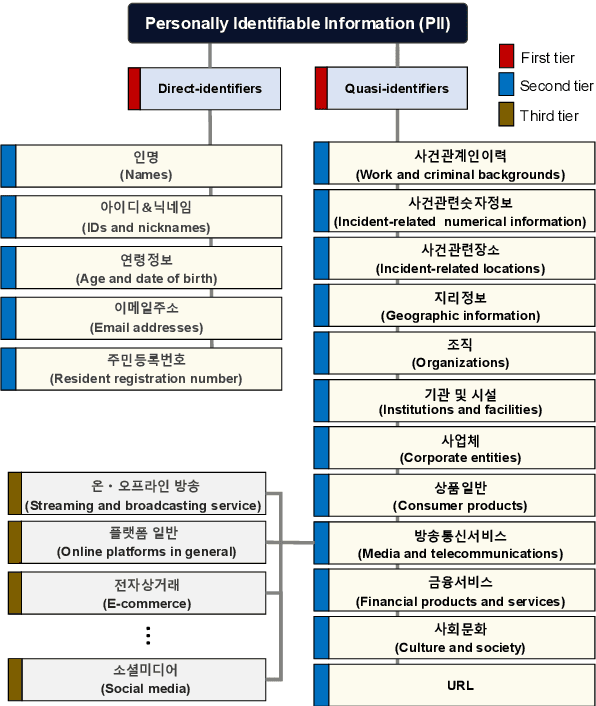
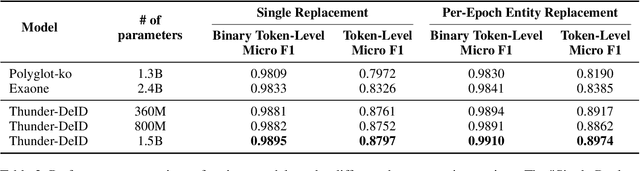
Abstract:To ensure a balance between open access to justice and personal data protection, the South Korean judiciary mandates the de-identification of court judgments before they can be publicly disclosed. However, the current de-identification process is inadequate for handling court judgments at scale while adhering to strict legal requirements. Additionally, the legal definitions and categorizations of personal identifiers are vague and not well-suited for technical solutions. To tackle these challenges, we propose a de-identification framework called Thunder-DeID, which aligns with relevant laws and practices. Specifically, we (i) construct and release the first Korean legal dataset containing annotated judgments along with corresponding lists of entity mentions, (ii) introduce a systematic categorization of Personally Identifiable Information (PII), and (iii) develop an end-to-end deep neural network (DNN)-based de-identification pipeline. Our experimental results demonstrate that our model achieves state-of-the-art performance in the de-identification of court judgments.
ANPMI: Assessing the True Comprehension Capabilities of LLMs for Multiple Choice Questions
Feb 26, 2025Abstract:Multiple-choice benchmarks, consisting of various prompts and choices, are among the most widely used methods to assess a language model's natural language understanding capability. Given a specific prompt, we typically compute $P(Choice|Prompt)$ to evaluate how likely a language model is to generate the correct choice compared to incorrect ones. However, we observe that performance measured using this approach reflects not only the model's comprehension of the prompt but also its inherent biases for certain choices regardless of the prompt. This issue makes it challenging to accurately measure a model's natural language understanding, as models may select the answer without fully understanding the prompt. To address this limitation, we propose a novel metric called ANPMI, which normalizes Pointwise Mutual Information (PMI) by $-\log P(Choice)$. ANPMI provides a more accurate assessment of the model's natural language understanding by ensuring that it is challenging to answer a question without properly understanding the prompt.
Integrating Spatial and Frequency Information for Under-Display Camera Image Restoration
Jan 30, 2025
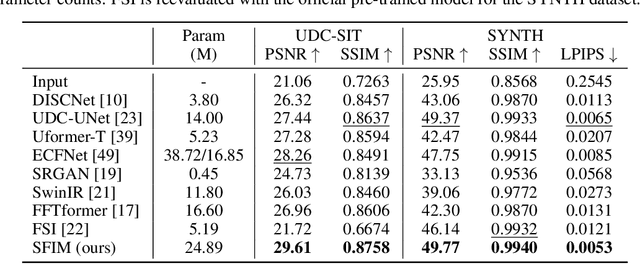
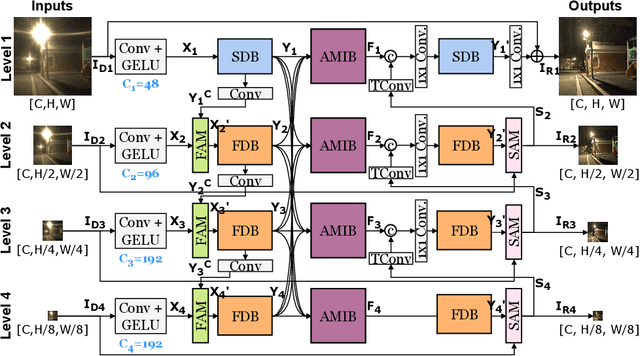
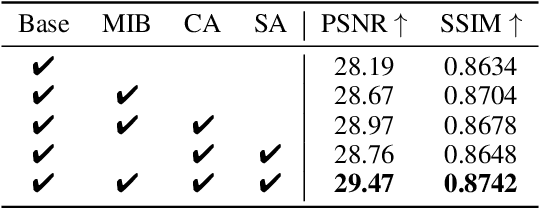
Abstract:Under-Display Camera (UDC) houses a digital camera lens under a display panel. However, UDC introduces complex degradations such as noise, blur, decrease in transmittance, and flare. Despite the remarkable progress, previous research on UDC mainly focuses on eliminating diffraction in the spatial domain and rarely explores its potential in the frequency domain. It is essential to consider both the spatial and frequency domains effectively. For example, degradations, such as noise and blur, can be addressed by local information (e.g., CNN kernels in the spatial domain). At the same time, tackling flares may require leveraging global information (e.g., the frequency domain). In this paper, we revisit the UDC degradations in the Fourier space and figure out intrinsic frequency priors that imply the presence of the flares. Based on this observation, we propose a novel multi-level DNN architecture called SFIM. It efficiently restores UDC-distorted images by integrating local and global (the collective contribution of all points in the image) information. The architecture exploits CNNs to capture local information and FFT-based models to capture global information. SFIM comprises a spatial domain block (SDB), a Frequency Domain Block (FDB), and an Attention-based Multi-level Integration Block (AMIB). Specifically, SDB focuses more on detailed textures such as noise and blur, FDB emphasizes irregular texture loss in extensive areas such as flare, and AMIB enables effective cross-domain interaction. SFIM's superior performance over state-of-the-art approaches is demonstrated through rigorous quantitative and qualitative assessments across three UDC benchmarks.
UDC-VIT: A Real-World Video Dataset for Under-Display Cameras
Jan 30, 2025



Abstract:Under Display Camera (UDC) is an advanced imaging system that places a digital camera lens underneath a display panel, effectively concealing the camera. However, the display panel significantly degrades captured images or videos, introducing low transmittance, blur, noise, and flare issues. Tackling such issues is challenging because of the complex degradation of UDCs, including diverse flare patterns. Despite extensive research on UDC images and their restoration models, studies on videos have yet to be significantly explored. While two UDC video datasets exist, they primarily focus on unrealistic or synthetic UDC degradation rather than real-world UDC degradation. In this paper, we propose a real-world UDC video dataset called UDC-VIT. Unlike existing datasets, only UDC-VIT exclusively includes human motions that target facial recognition. We propose a video-capturing system to simultaneously acquire non-degraded and UDC-degraded videos of the same scene. Then, we align a pair of captured videos frame by frame, using discrete Fourier transform (DFT). We compare UDC-VIT with six representative UDC still image datasets and two existing UDC video datasets. Using six deep-learning models, we compare UDC-VIT and an existing synthetic UDC video dataset. The results indicate the ineffectiveness of models trained on earlier synthetic UDC video datasets, as they do not reflect the actual characteristics of UDC-degraded videos. We also demonstrate the importance of effective UDC restoration by evaluating face recognition accuracy concerning PSNR, SSIM, and LPIPS scores. UDC-VIT enables further exploration in the UDC video restoration and offers better insights into the challenge. UDC-VIT is available at our project site.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge