Kyusu Ahn
Integrating Spatial and Frequency Information for Under-Display Camera Image Restoration
Jan 30, 2025
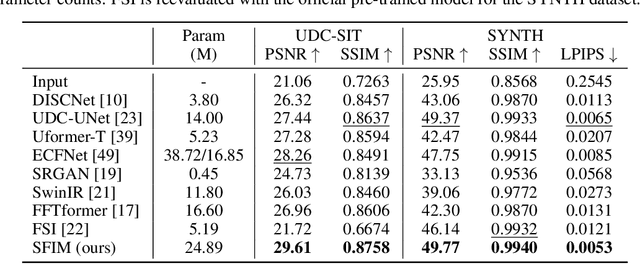
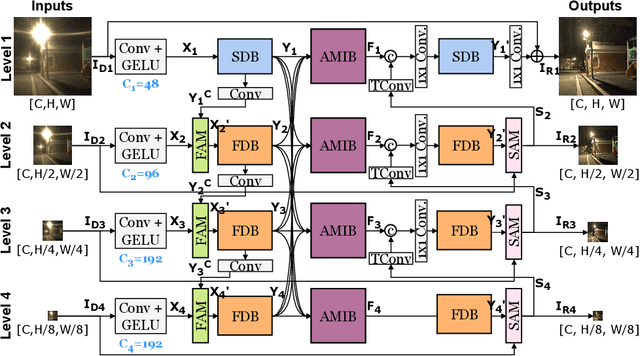
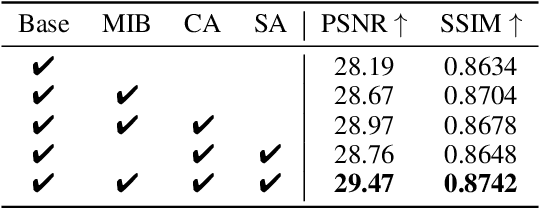
Abstract:Under-Display Camera (UDC) houses a digital camera lens under a display panel. However, UDC introduces complex degradations such as noise, blur, decrease in transmittance, and flare. Despite the remarkable progress, previous research on UDC mainly focuses on eliminating diffraction in the spatial domain and rarely explores its potential in the frequency domain. It is essential to consider both the spatial and frequency domains effectively. For example, degradations, such as noise and blur, can be addressed by local information (e.g., CNN kernels in the spatial domain). At the same time, tackling flares may require leveraging global information (e.g., the frequency domain). In this paper, we revisit the UDC degradations in the Fourier space and figure out intrinsic frequency priors that imply the presence of the flares. Based on this observation, we propose a novel multi-level DNN architecture called SFIM. It efficiently restores UDC-distorted images by integrating local and global (the collective contribution of all points in the image) information. The architecture exploits CNNs to capture local information and FFT-based models to capture global information. SFIM comprises a spatial domain block (SDB), a Frequency Domain Block (FDB), and an Attention-based Multi-level Integration Block (AMIB). Specifically, SDB focuses more on detailed textures such as noise and blur, FDB emphasizes irregular texture loss in extensive areas such as flare, and AMIB enables effective cross-domain interaction. SFIM's superior performance over state-of-the-art approaches is demonstrated through rigorous quantitative and qualitative assessments across three UDC benchmarks.
UDC-VIT: A Real-World Video Dataset for Under-Display Cameras
Jan 30, 2025



Abstract:Under Display Camera (UDC) is an advanced imaging system that places a digital camera lens underneath a display panel, effectively concealing the camera. However, the display panel significantly degrades captured images or videos, introducing low transmittance, blur, noise, and flare issues. Tackling such issues is challenging because of the complex degradation of UDCs, including diverse flare patterns. Despite extensive research on UDC images and their restoration models, studies on videos have yet to be significantly explored. While two UDC video datasets exist, they primarily focus on unrealistic or synthetic UDC degradation rather than real-world UDC degradation. In this paper, we propose a real-world UDC video dataset called UDC-VIT. Unlike existing datasets, only UDC-VIT exclusively includes human motions that target facial recognition. We propose a video-capturing system to simultaneously acquire non-degraded and UDC-degraded videos of the same scene. Then, we align a pair of captured videos frame by frame, using discrete Fourier transform (DFT). We compare UDC-VIT with six representative UDC still image datasets and two existing UDC video datasets. Using six deep-learning models, we compare UDC-VIT and an existing synthetic UDC video dataset. The results indicate the ineffectiveness of models trained on earlier synthetic UDC video datasets, as they do not reflect the actual characteristics of UDC-degraded videos. We also demonstrate the importance of effective UDC restoration by evaluating face recognition accuracy concerning PSNR, SSIM, and LPIPS scores. UDC-VIT enables further exploration in the UDC video restoration and offers better insights into the challenge. UDC-VIT is available at our project site.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge