Max Sobol Mark
BPP: Long-Context Robot Imitation Learning by Focusing on Key History Frames
Feb 16, 2026Abstract:Many robot tasks require attending to the history of past observations. For example, finding an item in a room requires remembering which places have already been searched. However, the best-performing robot policies typically condition only on the current observation, limiting their applicability to such tasks. Naively conditioning on past observations often fails due to spurious correlations: policies latch onto incidental features of training histories that do not generalize to out-of-distribution trajectories upon deployment. We analyze why policies latch onto these spurious correlations and find that this problem stems from limited coverage over the space of possible histories during training, which grows exponentially with horizon. Existing regularization techniques provide inconsistent benefits across tasks, as they do not fundamentally address this coverage problem. Motivated by these findings, we propose Big Picture Policies (BPP), an approach that conditions on a minimal set of meaningful keyframes detected by a vision-language model. By projecting diverse rollouts onto a compact set of task-relevant events, BPP substantially reduces distribution shift between training and deployment, without sacrificing expressivity. We evaluate BPP on four challenging real-world manipulation tasks and three simulation tasks, all requiring history conditioning. BPP achieves 70% higher success rates than the best comparison on real-world evaluations.
Policy Agnostic RL: Offline RL and Online RL Fine-Tuning of Any Class and Backbone
Dec 09, 2024Abstract:Recent advances in learning decision-making policies can largely be attributed to training expressive policy models, largely via imitation learning. While imitation learning discards non-expert data, reinforcement learning (RL) can still learn from suboptimal data. However, instantiating RL training of a new policy class often presents a different challenge: most deep RL machinery is co-developed with assumptions on the policy class and backbone, resulting in poor performance when the policy class changes. For instance, SAC utilizes a low-variance reparameterization policy gradient for Gaussian policies, but this is unstable for diffusion policies and intractable for autoregressive categorical policies. To address this issue, we develop an offline RL and online fine-tuning approach called policy-agnostic RL (PA-RL) that can effectively train multiple policy classes, with varying architectures and sizes. We build off the basic idea that a universal supervised learning loss can replace the policy improvement step in RL, as long as it is applied on "optimized" actions. To obtain these optimized actions, we first sample multiple actions from a base policy, and run global optimization (i.e., re-ranking multiple action samples using the Q-function) and local optimization (i.e., running gradient steps on an action sample) to maximize the critic on these candidates. PA-RL enables fine-tuning diffusion and transformer policies with either autoregressive tokens or continuous action outputs, at different sizes, entirely via actor-critic RL. Moreover, PA-RL improves the performance and sample-efficiency by up to 2 times compared to existing offline RL and online fine-tuning methods. We show the first result that successfully fine-tunes OpenVLA, a 7B generalist robot policy, autonomously with Cal-QL, an online RL fine-tuning algorithm, improving from 40% to 70% in the real world in 40 minutes.
Robot Fine-Tuning Made Easy: Pre-Training Rewards and Policies for Autonomous Real-World Reinforcement Learning
Oct 23, 2023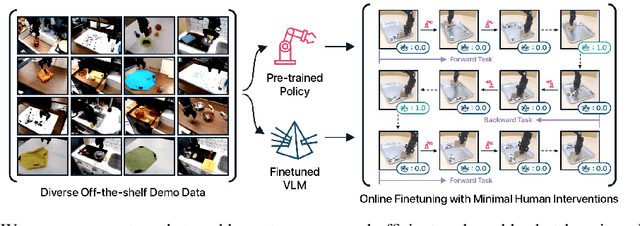
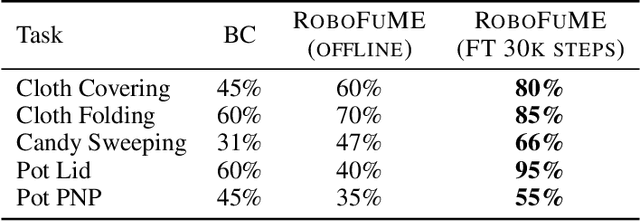
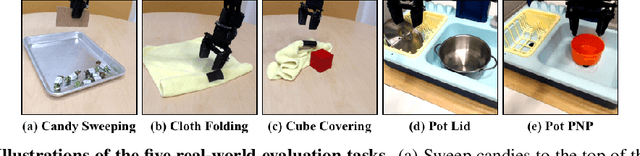
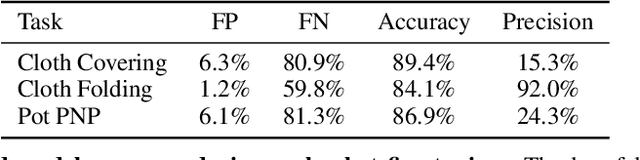
Abstract:The pre-train and fine-tune paradigm in machine learning has had dramatic success in a wide range of domains because the use of existing data or pre-trained models on the internet enables quick and easy learning of new tasks. We aim to enable this paradigm in robotic reinforcement learning, allowing a robot to learn a new task with little human effort by leveraging data and models from the Internet. However, reinforcement learning often requires significant human effort in the form of manual reward specification or environment resets, even if the policy is pre-trained. We introduce RoboFuME, a reset-free fine-tuning system that pre-trains a multi-task manipulation policy from diverse datasets of prior experiences and self-improves online to learn a target task with minimal human intervention. Our insights are to utilize calibrated offline reinforcement learning techniques to ensure efficient online fine-tuning of a pre-trained policy in the presence of distribution shifts and leverage pre-trained vision language models (VLMs) to build a robust reward classifier for autonomously providing reward signals during the online fine-tuning process. In a diverse set of five real robot manipulation tasks, we show that our method can incorporate data from an existing robot dataset collected at a different institution and improve on a target task within as little as 3 hours of autonomous real-world experience. We also demonstrate in simulation experiments that our method outperforms prior works that use different RL algorithms or different approaches for predicting rewards. Project website: https://robofume.github.io
Offline Retraining for Online RL: Decoupled Policy Learning to Mitigate Exploration Bias
Oct 12, 2023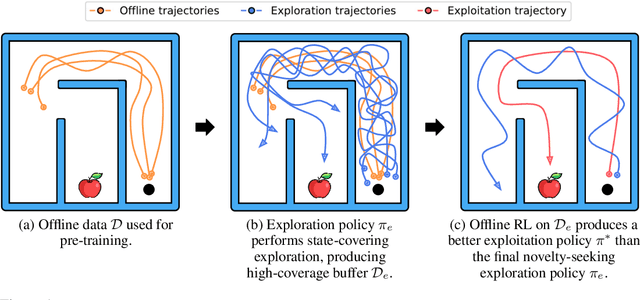
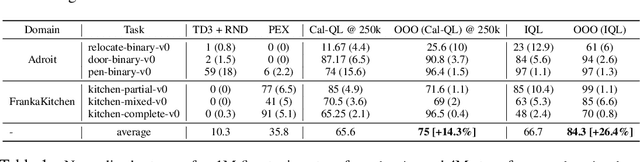
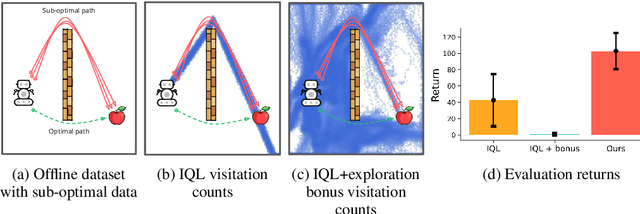
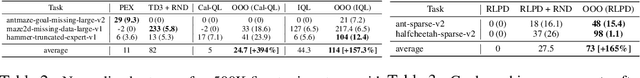
Abstract:It is desirable for policies to optimistically explore new states and behaviors during online reinforcement learning (RL) or fine-tuning, especially when prior offline data does not provide enough state coverage. However, exploration bonuses can bias the learned policy, and our experiments find that naive, yet standard use of such bonuses can fail to recover a performant policy. Concurrently, pessimistic training in offline RL has enabled recovery of performant policies from static datasets. Can we leverage offline RL to recover better policies from online interaction? We make a simple observation that a policy can be trained from scratch on all interaction data with pessimistic objectives, thereby decoupling the policies used for data collection and for evaluation. Specifically, we propose offline retraining, a policy extraction step at the end of online fine-tuning in our Offline-to-Online-to-Offline (OOO) framework for reinforcement learning (RL). An optimistic (exploration) policy is used to interact with the environment, and a separate pessimistic (exploitation) policy is trained on all the observed data for evaluation. Such decoupling can reduce any bias from online interaction (intrinsic rewards, primacy bias) in the evaluation policy, and can allow more exploratory behaviors during online interaction which in turn can generate better data for exploitation. OOO is complementary to several offline-to-online RL and online RL methods, and improves their average performance by 14% to 26% in our fine-tuning experiments, achieves state-of-the-art performance on several environments in the D4RL benchmarks, and improves online RL performance by 165% on two OpenAI gym environments. Further, OOO can enable fine-tuning from incomplete offline datasets where prior methods can fail to recover a performant policy. Implementation: https://github.com/MaxSobolMark/OOO
Cal-QL: Calibrated Offline RL Pre-Training for Efficient Online Fine-Tuning
Mar 09, 2023Abstract:A compelling use case of offline reinforcement learning (RL) is to obtain a policy initialization from existing datasets, which allows efficient fine-tuning with limited amounts of active online interaction. However, several existing offline RL methods tend to exhibit poor online fine-tuning performance. On the other hand, online RL methods can learn effectively through online interaction, but struggle to incorporate offline data, which can make them very slow in settings where exploration is challenging or pre-training is necessary. In this paper, we devise an approach for learning an effective initialization from offline data that also enables fast online fine-tuning capabilities. Our approach, calibrated Q-learning (Cal-QL) accomplishes this by learning a conservative value function initialization that underestimates the value of the learned policy from offline data, while also being calibrated, in the sense that the learned Q-values are at a reasonable scale. We refer to this property as calibration, and define it formally as providing a lower bound on the true value function of the learned policy and an upper bound on the value of some other (suboptimal) reference policy, which may simply be the behavior policy. We show that offline RL algorithms that learn such calibrated value functions lead to effective online fine-tuning, enabling us to take the benefits of offline initializations in online fine-tuning. In practice, Cal-QL can be implemented on top of existing conservative methods for offline RL within a one-line code change. Empirically, Cal-QL outperforms state-of-the-art methods on 10/11 fine-tuning benchmark tasks that we study in this paper.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge