Brandon Vu
Mobi-$π$: Mobilizing Your Robot Learning Policy
May 29, 2025Abstract:Learned visuomotor policies are capable of performing increasingly complex manipulation tasks. However, most of these policies are trained on data collected from limited robot positions and camera viewpoints. This leads to poor generalization to novel robot positions, which limits the use of these policies on mobile platforms, especially for precise tasks like pressing buttons or turning faucets. In this work, we formulate the policy mobilization problem: find a mobile robot base pose in a novel environment that is in distribution with respect to a manipulation policy trained on a limited set of camera viewpoints. Compared to retraining the policy itself to be more robust to unseen robot base pose initializations, policy mobilization decouples navigation from manipulation and thus does not require additional demonstrations. Crucially, this problem formulation complements existing efforts to improve manipulation policy robustness to novel viewpoints and remains compatible with them. To study policy mobilization, we introduce the Mobi-$\pi$ framework, which includes: (1) metrics that quantify the difficulty of mobilizing a given policy, (2) a suite of simulated mobile manipulation tasks based on RoboCasa to evaluate policy mobilization, (3) visualization tools for analysis, and (4) several baseline methods. We also propose a novel approach that bridges navigation and manipulation by optimizing the robot's base pose to align with an in-distribution base pose for a learned policy. Our approach utilizes 3D Gaussian Splatting for novel view synthesis, a score function to evaluate pose suitability, and sampling-based optimization to identify optimal robot poses. We show that our approach outperforms baselines in both simulation and real-world environments, demonstrating its effectiveness for policy mobilization.
COAST: Constraints and Streams for Task and Motion Planning
May 14, 2024
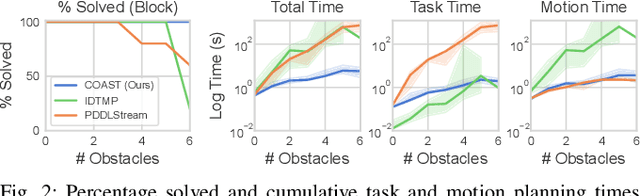
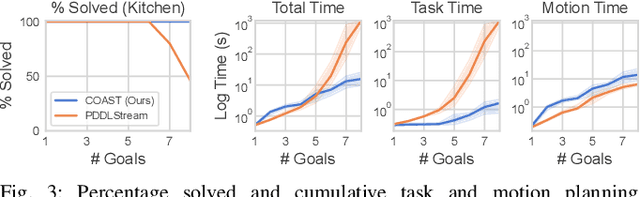
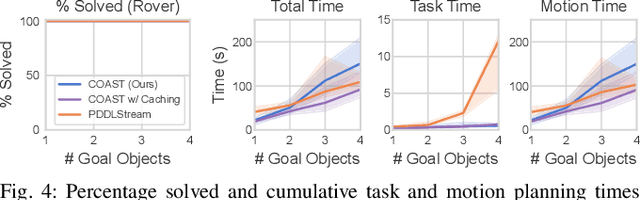
Abstract:Task and Motion Planning (TAMP) algorithms solve long-horizon robotics tasks by integrating task planning with motion planning; the task planner proposes a sequence of actions towards a goal state and the motion planner verifies whether this action sequence is geometrically feasible for the robot. However, state-of-the-art TAMP algorithms do not scale well with the difficulty of the task and require an impractical amount of time to solve relatively small problems. We propose Constraints and Streams for Task and Motion Planning (COAST), a probabilistically-complete, sampling-based TAMP algorithm that combines stream-based motion planning with an efficient, constrained task planning strategy. We validate COAST on three challenging TAMP domains and demonstrate that our method outperforms baselines in terms of cumulative task planning time by an order of magnitude. You can find more supplementary materials on our project \href{https://branvu.github.io/coast.github.io}{website}.
Robot Fine-Tuning Made Easy: Pre-Training Rewards and Policies for Autonomous Real-World Reinforcement Learning
Oct 23, 2023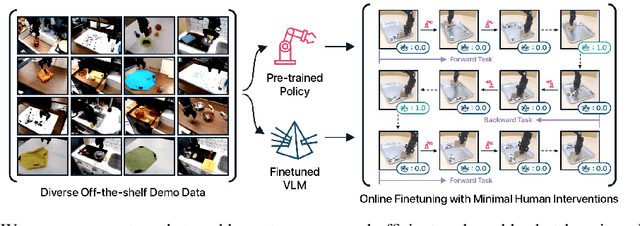
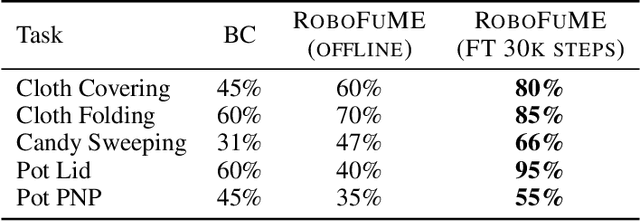
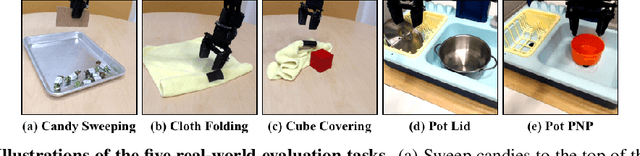
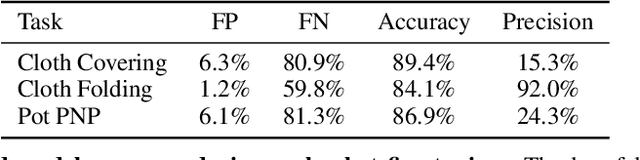
Abstract:The pre-train and fine-tune paradigm in machine learning has had dramatic success in a wide range of domains because the use of existing data or pre-trained models on the internet enables quick and easy learning of new tasks. We aim to enable this paradigm in robotic reinforcement learning, allowing a robot to learn a new task with little human effort by leveraging data and models from the Internet. However, reinforcement learning often requires significant human effort in the form of manual reward specification or environment resets, even if the policy is pre-trained. We introduce RoboFuME, a reset-free fine-tuning system that pre-trains a multi-task manipulation policy from diverse datasets of prior experiences and self-improves online to learn a target task with minimal human intervention. Our insights are to utilize calibrated offline reinforcement learning techniques to ensure efficient online fine-tuning of a pre-trained policy in the presence of distribution shifts and leverage pre-trained vision language models (VLMs) to build a robust reward classifier for autonomously providing reward signals during the online fine-tuning process. In a diverse set of five real robot manipulation tasks, we show that our method can incorporate data from an existing robot dataset collected at a different institution and improve on a target task within as little as 3 hours of autonomous real-world experience. We also demonstrate in simulation experiments that our method outperforms prior works that use different RL algorithms or different approaches for predicting rewards. Project website: https://robofume.github.io
Stabilize to Act: Learning to Coordinate for Bimanual Manipulation
Sep 03, 2023Abstract:Key to rich, dexterous manipulation in the real world is the ability to coordinate control across two hands. However, while the promise afforded by bimanual robotic systems is immense, constructing control policies for dual arm autonomous systems brings inherent difficulties. One such difficulty is the high-dimensionality of the bimanual action space, which adds complexity to both model-based and data-driven methods. We counteract this challenge by drawing inspiration from humans to propose a novel role assignment framework: a stabilizing arm holds an object in place to simplify the environment while an acting arm executes the task. We instantiate this framework with BimanUal Dexterity from Stabilization (BUDS), which uses a learned restabilizing classifier to alternate between updating a learned stabilization position to keep the environment unchanged, and accomplishing the task with an acting policy learned from demonstrations. We evaluate BUDS on four bimanual tasks of varying complexities on real-world robots, such as zipping jackets and cutting vegetables. Given only 20 demonstrations, BUDS achieves 76.9% task success across our task suite, and generalizes to out-of-distribution objects within a class with a 52.7% success rate. BUDS is 56.0% more successful than an unstructured baseline that instead learns a BC stabilizing policy due to the precision required of these complex tasks. Supplementary material and videos can be found at https://sites.google.com/view/stabilizetoact .
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge