Shutong Niu
Exploring Speaker Diarization with Mixture of Experts
Jun 17, 2025Abstract:In this paper, we propose a novel neural speaker diarization system using memory-aware multi-speaker embedding with sequence-to-sequence architecture (NSD-MS2S), which integrates a memory-aware multi-speaker embedding module with a sequence-to-sequence architecture. The system leverages a memory module to enhance speaker embeddings and employs a Seq2Seq framework to efficiently map acoustic features to speaker labels. Additionally, we explore the application of mixture of experts in speaker diarization, and introduce a Shared and Soft Mixture of Experts (SS-MoE) module to further mitigate model bias and enhance performance. Incorporating SS-MoE leads to the extended model NSD-MS2S-SSMoE. Experiments on multiple complex acoustic datasets, including CHiME-6, DiPCo, Mixer 6 and DIHARD-III evaluation sets, demonstrate meaningful improvements in robustness and generalization. The proposed methods achieve state-of-the-art results, showcasing their effectiveness in challenging real-world scenarios.
EmotiveTalk: Expressive Talking Head Generation through Audio Information Decoupling and Emotional Video Diffusion
Nov 23, 2024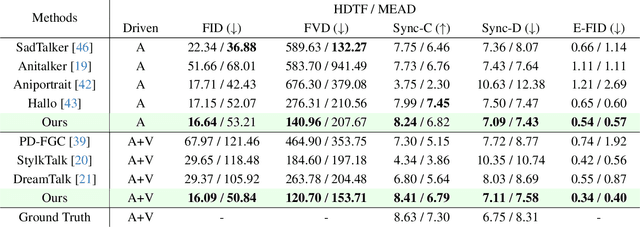
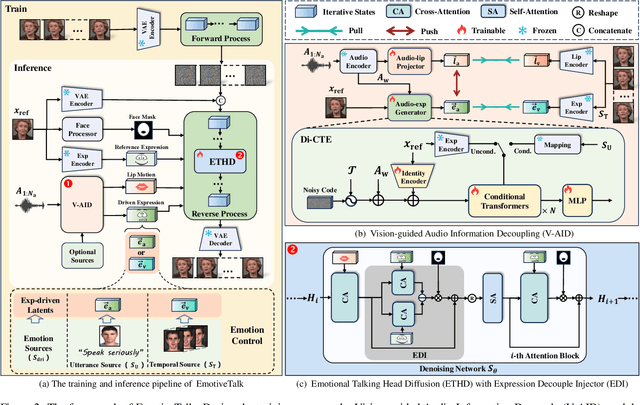
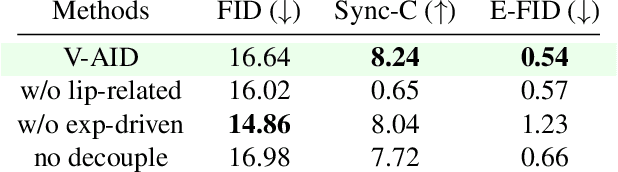
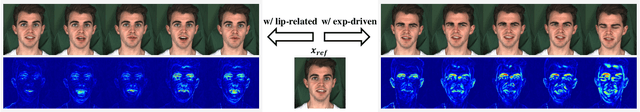
Abstract:Diffusion models have revolutionized the field of talking head generation, yet still face challenges in expressiveness, controllability, and stability in long-time generation. In this research, we propose an EmotiveTalk framework to address these issues. Firstly, to realize better control over the generation of lip movement and facial expression, a Vision-guided Audio Information Decoupling (V-AID) approach is designed to generate audio-based decoupled representations aligned with lip movements and expression. Specifically, to achieve alignment between audio and facial expression representation spaces, we present a Diffusion-based Co-speech Temporal Expansion (Di-CTE) module within V-AID to generate expression-related representations under multi-source emotion condition constraints. Then we propose a well-designed Emotional Talking Head Diffusion (ETHD) backbone to efficiently generate highly expressive talking head videos, which contains an Expression Decoupling Injection (EDI) module to automatically decouple the expressions from reference portraits while integrating the target expression information, achieving more expressive generation performance. Experimental results show that EmotiveTalk can generate expressive talking head videos, ensuring the promised controllability of emotions and stability during long-time generation, yielding state-of-the-art performance compared to existing methods.
Enhancing Multimodal Sentiment Analysis for Missing Modality through Self-Distillation and Unified Modality Cross-Attention
Oct 19, 2024
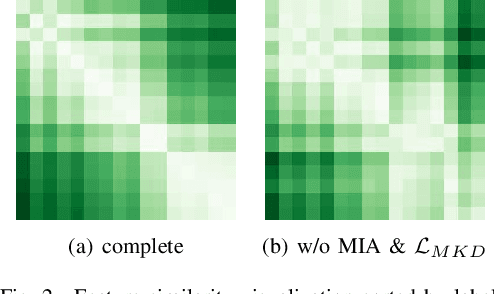


Abstract:In multimodal sentiment analysis, collecting text data is often more challenging than video or audio due to higher annotation costs and inconsistent automatic speech recognition (ASR) quality. To address this challenge, our study has developed a robust model that effectively integrates multimodal sentiment information, even in the absence of text modality. Specifically, we have developed a Double-Flow Self-Distillation Framework, including Unified Modality Cross-Attention (UMCA) and Modality Imagination Autoencoder (MIA), which excels at processing both scenarios with complete modalities and those with missing text modality. In detail, when the text modality is missing, our framework uses the LLM-based model to simulate the text representation from the audio modality, while the MIA module supplements information from the other two modalities to make the simulated text representation similar to the real text representation. To further align the simulated and real representations, and to enable the model to capture the continuous nature of sample orders in sentiment valence regression tasks, we have also introduced the Rank-N Contrast (RNC) loss function. When testing on the CMU-MOSEI, our model achieved outstanding performance on MAE and significantly outperformed other models when text modality is missing. The code is available at: https://github.com/WarmCongee/SDUMC
Incorporating Spatial Cues in Modular Speaker Diarization for Multi-channel Multi-party Meetings
Sep 25, 2024



Abstract:Although fully end-to-end speaker diarization systems have made significant progress in recent years, modular systems often achieve superior results in real-world scenarios due to their greater adaptability and robustness. Historically, modular speaker diarization methods have seldom discussed how to leverage spatial cues from multi-channel speech. This paper proposes a three-stage modular system to enhance single-channel neural speaker diarization systems and recognition performance by utilizing spatial cues from multi-channel speech to provide more accurate initialization for each stage of neural speaker diarization (NSD) decoding: (1) Overlap detection and continuous speech separation (CSS) on multi-channel speech are used to obtain cleaner single speaker speech segments for clustering, followed by the first NSD decoding pass. (2) The results from the first pass initialize a complex Angular Central Gaussian Mixture Model (cACGMM) to estimate speaker-wise masks on multi-channel speech, and through Overlap-add and Mask-to-VAD, achieve initialization with lower speaker error (SpkErr), followed by the second NSD decoding pass. (3) The second decoding results are used for guided source separation (GSS), recognizing and filtering short segments containing less one word to obtain cleaner speech segments, followed by re-clustering and the final NSD decoding pass. We presented the progressively explored evaluation results from the CHiME-8 NOTSOFAR-1 (Natural Office Talkers in Settings Of Far-field Audio Recordings) challenge, demonstrating the effectiveness of our system and its contribution to improving recognition performance. Our final system achieved the first place in the challenge.
The USTC-NERCSLIP Systems for the CHiME-8 NOTSOFAR-1 Challenge
Sep 03, 2024
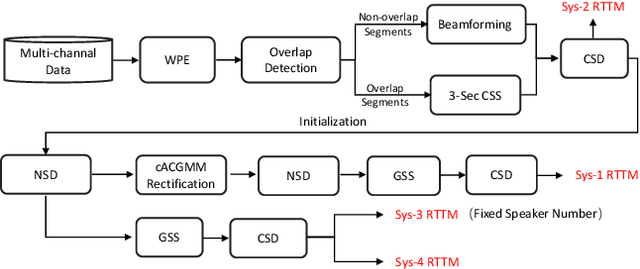
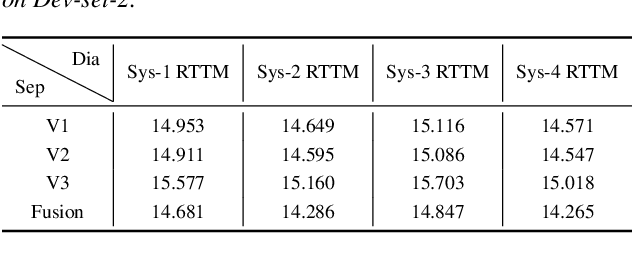
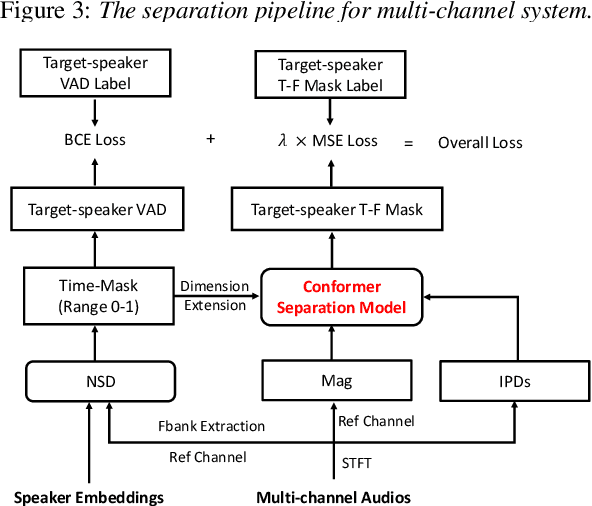
Abstract:This technical report outlines our submission system for the CHiME-8 NOTSOFAR-1 Challenge. The primary difficulty of this challenge is the dataset recorded across various conference rooms, which captures real-world complexities such as high overlap rates, background noises, a variable number of speakers, and natural conversation styles. To address these issues, we optimized the system in several aspects: For front-end speech signal processing, we introduced a data-driven joint training method for diarization and separation (JDS) to enhance audio quality. Additionally, we also integrated traditional guided source separation (GSS) for multi-channel track to provide complementary information for the JDS. For back-end speech recognition, we enhanced Whisper with WavLM, ConvNeXt, and Transformer innovations, applying multi-task training and Noise KLD augmentation, to significantly advance ASR robustness and accuracy. Our system attained a Time-Constrained minimum Permutation Word Error Rate (tcpWER) of 14.265% and 22.989% on the CHiME-8 NOTSOFAR-1 Dev-set-2 multi-channel and single-channel tracks, respectively.
Neural Speaker Diarization Using Memory-Aware Multi-Speaker Embedding with Sequence-to-Sequence Architecture
Sep 17, 2023



Abstract:We propose a novel neural speaker diarization system using memory-aware multi-speaker embedding with sequence-to-sequence architecture (NSD-MS2S), which integrates the strengths of memory-aware multi-speaker embedding (MA-MSE) and sequence-to-sequence (Seq2Seq) architecture, leading to improvement in both efficiency and performance. Next, we further decrease the memory occupation of decoding by incorporating input features fusion and then employ a multi-head attention mechanism to capture features at different levels. NSD-MS2S achieved a macro diarization error rate (DER) of 15.9% on the CHiME-7 EVAL set, which signifies a relative improvement of 49% over the official baseline system, and is the key technique for us to achieve the best performance for the main track of CHiME-7 DASR Challenge. Additionally, we introduce a deep interactive module (DIM) in MA-MSE module to better retrieve a cleaner and more discriminative multi-speaker embedding, enabling the current model to outperform the system we used in the CHiME-7 DASR Challenge. Our code will be available at https://github.com/liyunlongaaa/NSD-MS2S.
The USTC-NERCSLIP Systems for the CHiME-7 DASR Challenge
Aug 28, 2023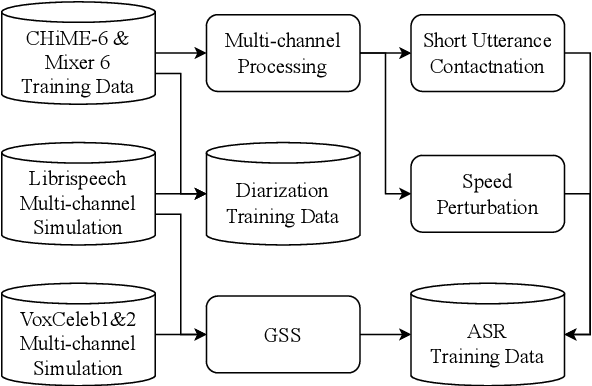
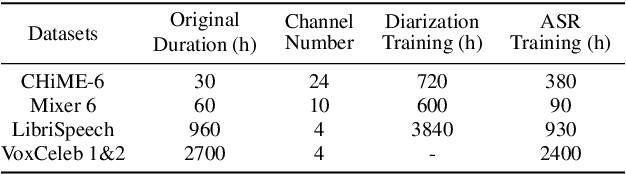
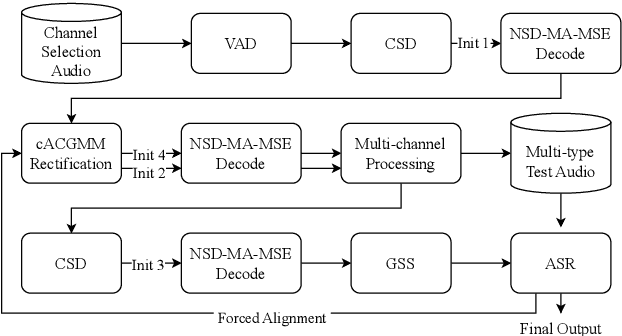
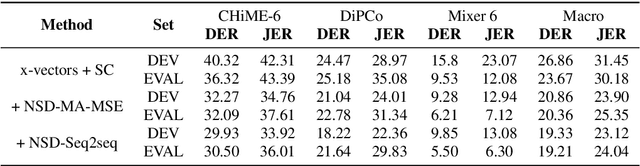
Abstract:This technical report details our submission system to the CHiME-7 DASR Challenge, which focuses on speaker diarization and speech recognition under complex multi-speaker settings. Additionally, it also evaluates the efficiency of systems in handling diverse array devices. To address these issues, we implemented an end-to-end speaker diarization system and introduced a rectification strategy based on multi-channel spatial information. This approach significantly diminished the word error rates (WER). In terms of recognition, we utilized publicly available pre-trained models as the foundational models to train our end-to-end speech recognition models. Our system attained a macro-averaged diarization-attributed WER (DA-WER) of 22.4\% on the CHiME-7 development set, which signifies a relative improvement of 52.5\% over the official baseline system.
Semi-supervised multi-channel speaker diarization with cross-channel attention
Jul 17, 2023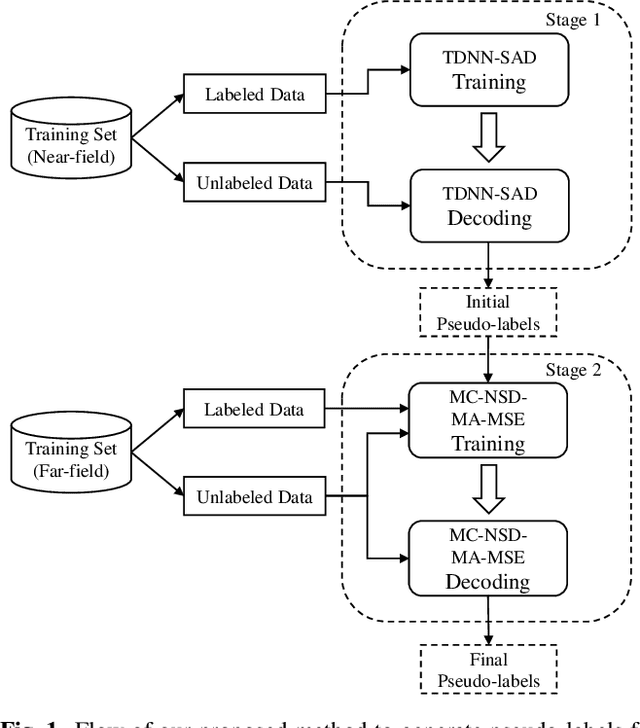
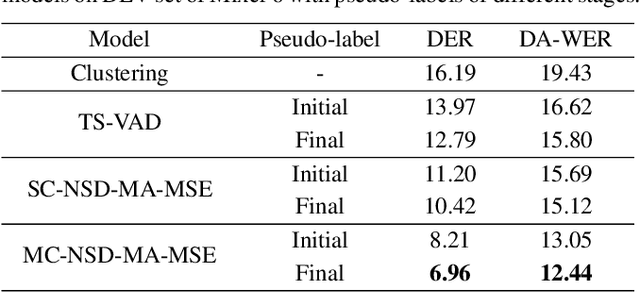
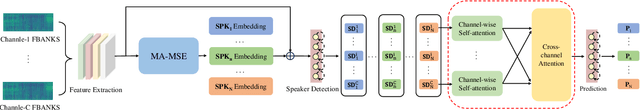
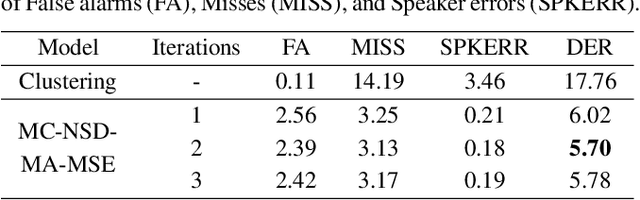
Abstract:Most neural speaker diarization systems rely on sufficient manual training data labels, which are hard to collect under real-world scenarios. This paper proposes a semi-supervised speaker diarization system to utilize large-scale multi-channel training data by generating pseudo-labels for unlabeled data. Furthermore, we introduce cross-channel attention into the Neural Speaker Diarization Using Memory-Aware Multi-Speaker Embedding (NSD-MA-MSE) to learn channel contextual information of speaker embeddings better. Experimental results on the CHiME-7 Mixer6 dataset which only contains partial speakers' labels of the training set, show that our system achieved 57.01% relative DER reduction compared to the clustering-based model on the development set. We further conducted experiments on the CHiME-6 dataset to simulate the scenario of missing partial training set labels. When using 80% and 50% labeled training data, our system performs comparably to the results obtained using 100% labeled data for training.
The USTC-Ximalaya system for the ICASSP 2022 multi-channel multi-party meeting transcription challenge
Feb 10, 2022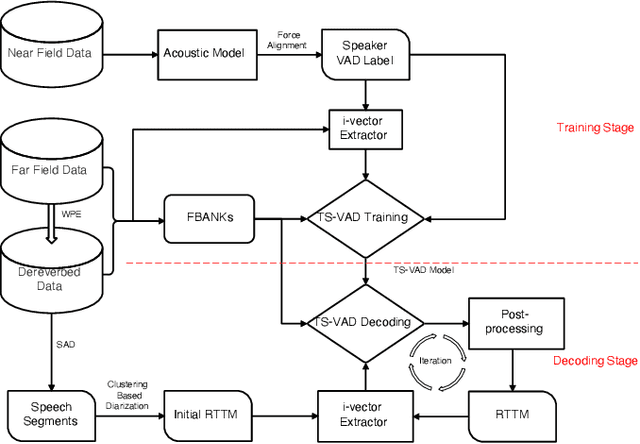
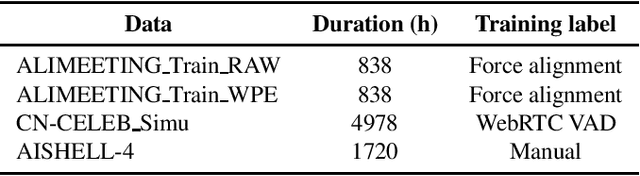
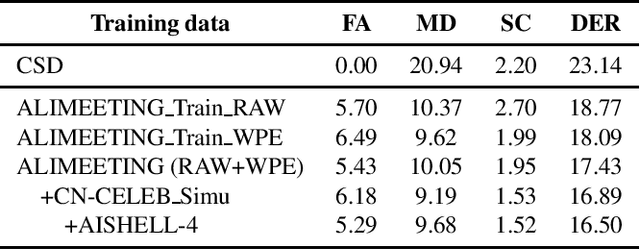
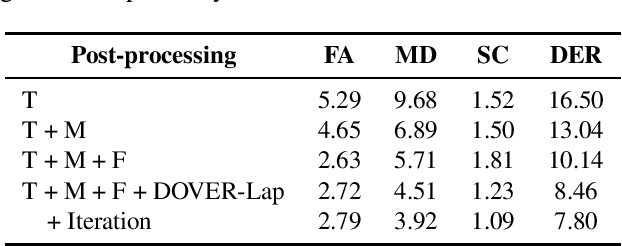
Abstract:We propose two improvements to target-speaker voice activity detection (TS-VAD), the core component in our proposed speaker diarization system that was submitted to the 2022 Multi-Channel Multi-Party Meeting Transcription (M2MeT) challenge. These techniques are designed to handle multi-speaker conversations in real-world meeting scenarios with high speaker-overlap ratios and under heavy reverberant and noisy condition. First, for data preparation and augmentation in training TS-VAD models, speech data containing both real meetings and simulated indoor conversations are used. Second, in refining results obtained after TS-VAD based decoding, we perform a series of post-processing steps to improve the VAD results needed to reduce diarization error rates (DERs). Tested on the ALIMEETING corpus, the newly released Mandarin meeting dataset used in M2MeT, we demonstrate that our proposed system can decrease the DER by up to 66.55/60.59% relatively when compared with classical clustering based diarization on the Eval/Test set.
USTC-NELSLIP System Description for DIHARD-III Challenge
Mar 19, 2021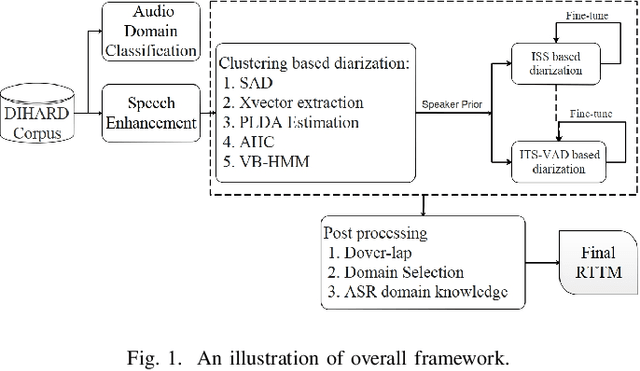
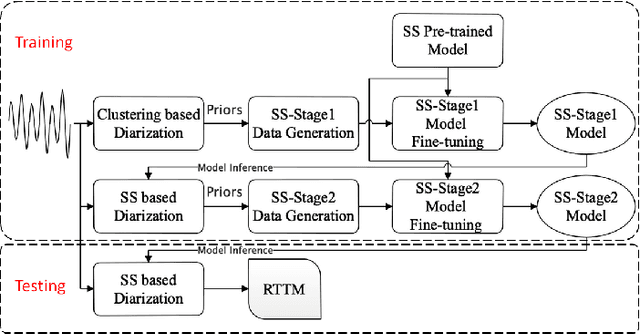
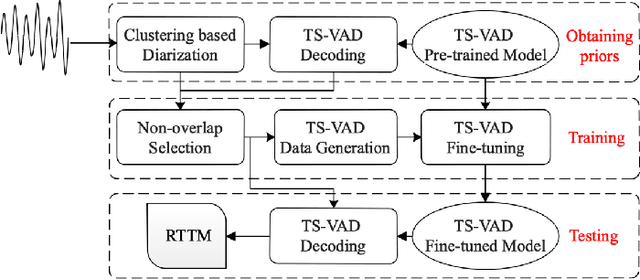
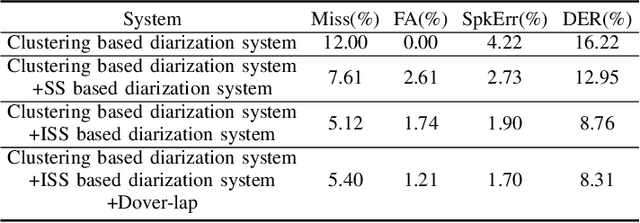
Abstract:This system description describes our submission system to the Third DIHARD Speech Diarization Challenge. Besides the traditional clustering based system, the innovation of our system lies in the combination of various front-end techniques to solve the diarization problem, including speech separation and target-speaker based voice activity detection (TS-VAD), combined with iterative data purification. We also adopted audio domain classification to design domain-dependent processing. Finally, we performed post processing to do system fusion and selection. Our best system achieved DERs of 11.30% in track 1 and 16.78% in track 2 on evaluation set, respectively.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge