Omid Ghorbanzadeh
Geographical Context Matters: Bridging Fine and Coarse Spatial Information to Enhance Continental Land Cover Mapping
Apr 16, 2025Abstract:Land use and land cover mapping from Earth Observation (EO) data is a critical tool for sustainable land and resource management. While advanced machine learning and deep learning algorithms excel at analyzing EO imagery data, they often overlook crucial geospatial metadata information that could enhance scalability and accuracy across regional, continental, and global scales. To address this limitation, we propose BRIDGE-LC (Bi-level Representation Integration for Disentangled GEospatial Land Cover), a novel deep learning framework that integrates multi-scale geospatial information into the land cover classification process. By simultaneously leveraging fine-grained (latitude/longitude) and coarse-grained (biogeographical region) spatial information, our lightweight multi-layer perceptron architecture learns from both during training but only requires fine-grained information for inference, allowing it to disentangle region-specific from region-agnostic land cover features while maintaining computational efficiency. To assess the quality of our framework, we use an open-access in-situ dataset and adopt several competing classification approaches commonly considered for large-scale land cover mapping. We evaluated all approaches through two scenarios: an extrapolation scenario in which training data encompasses samples from all biogeographical regions, and a leave-one-region-out scenario where one region is excluded from training. We also explore the spatial representation learned by our model, highlighting a connection between its internal manifold and the geographical information used during training. Our results demonstrate that integrating geospatial information improves land cover mapping performance, with the most substantial gains achieved by jointly leveraging both fine- and coarse-grained spatial information.
The Outcome of the 2022 Landslide4Sense Competition: Advanced Landslide Detection from Multi-Source Satellite Imagery
Sep 12, 2022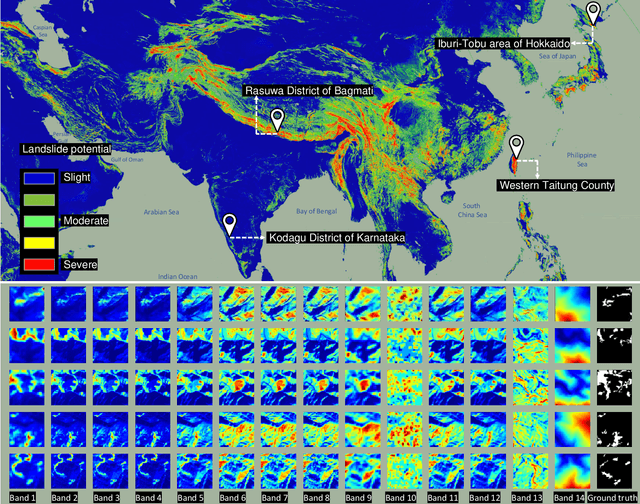
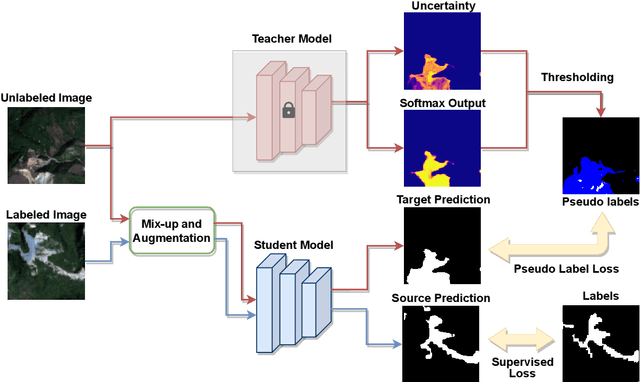
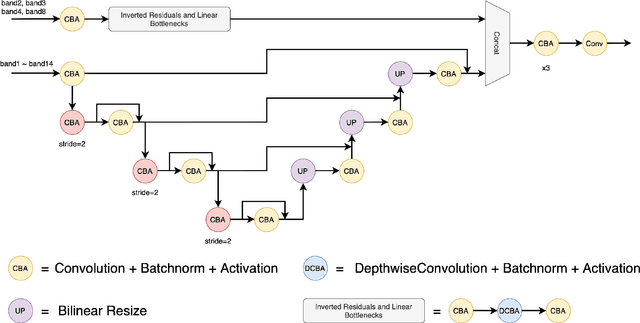
Abstract:The scientific outcomes of the 2022 Landslide4Sense (L4S) competition organized by the Institute of Advanced Research in Artificial Intelligence (IARAI) are presented here. The objective of the competition is to automatically detect landslides based on large-scale multiple sources of satellite imagery collected globally. The 2022 L4S aims to foster interdisciplinary research on recent developments in deep learning (DL) models for the semantic segmentation task using satellite imagery. In the past few years, DL-based models have achieved performance that meets expectations on image interpretation, due to the development of convolutional neural networks (CNNs). The main objective of this article is to present the details and the best-performing algorithms featured in this competition. The winning solutions are elaborated with state-of-the-art models like the Swin Transformer, SegFormer, and U-Net. Advanced machine learning techniques and strategies such as hard example mining, self-training, and mix-up data augmentation are also considered. Moreover, we describe the L4S benchmark data set in order to facilitate further comparisons, and report the results of the accuracy assessment online. The data is accessible on \textit{Future Development Leaderboard} for future evaluation at \url{https://www.iarai.ac.at/landslide4sense/challenge/}, and researchers are invited to submit more prediction results, evaluate the accuracy of their methods, compare them with those of other users, and, ideally, improve the landslide detection results reported in this article.
Landslide4Sense: Reference Benchmark Data and Deep Learning Models for Landslide Detection
Jun 01, 2022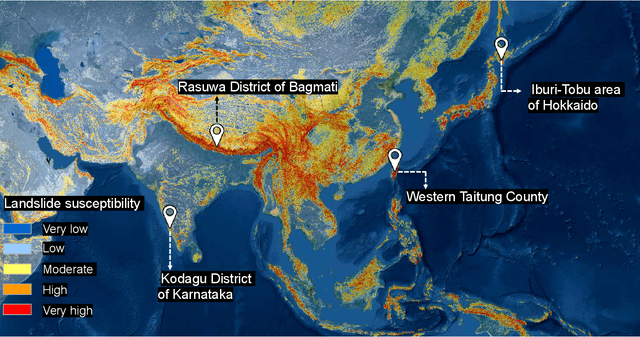
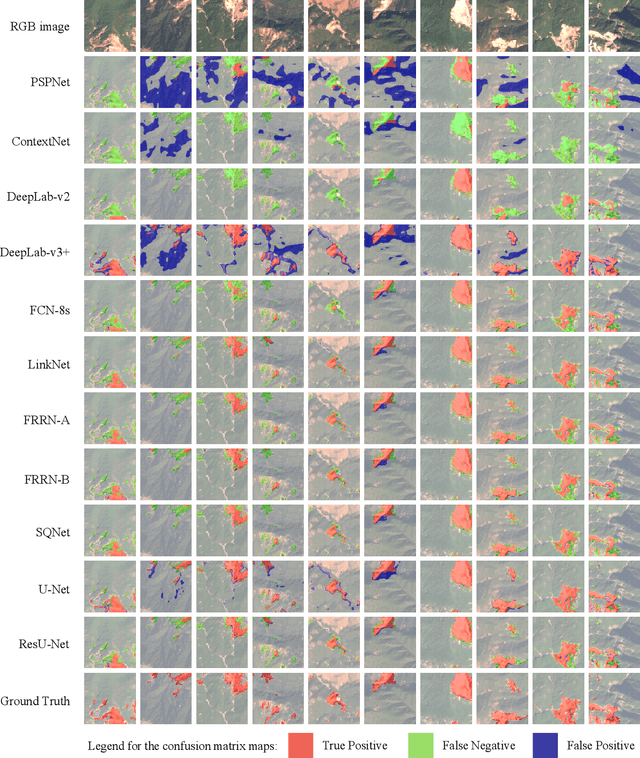
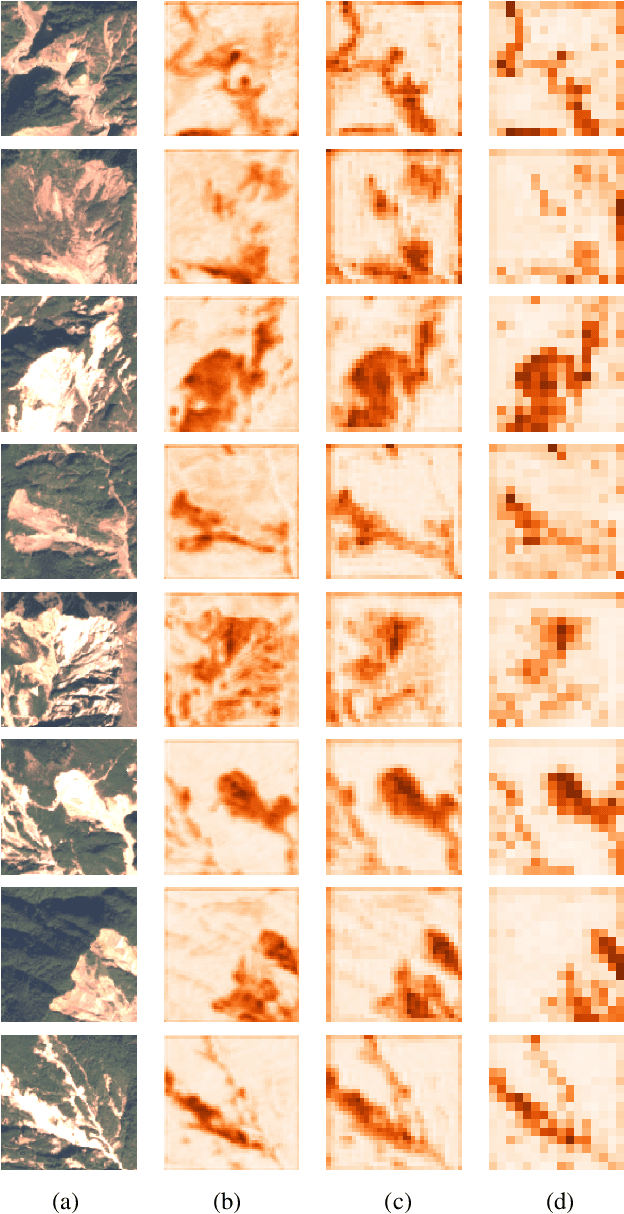
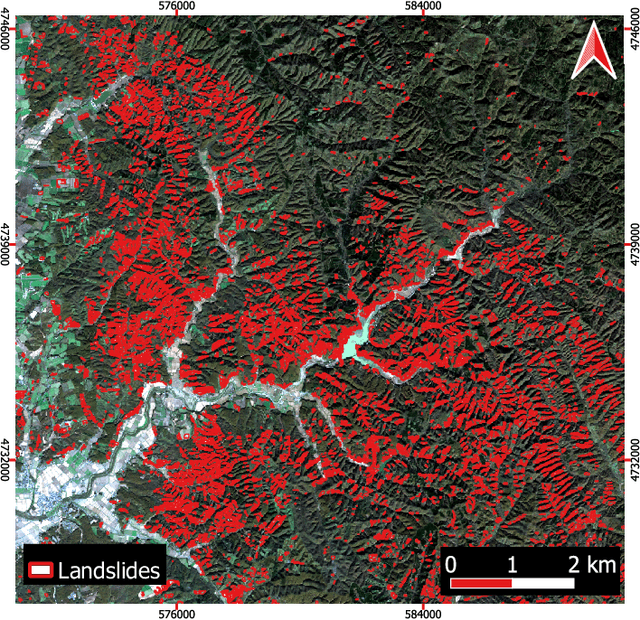
Abstract:This study introduces \textit{Landslide4Sense}, a reference benchmark for landslide detection from remote sensing. The repository features 3,799 image patches fusing optical layers from Sentinel-2 sensors with the digital elevation model and slope layer derived from ALOS PALSAR. The added topographical information facilitates an accurate detection of landslide borders, which recent researches have shown to be challenging using optical data alone. The extensive data set supports deep learning (DL) studies in landslide detection and the development and validation of methods for the systematic update of landslide inventories. The benchmark data set has been collected at four different times and geographical locations: Iburi (September 2018), Kodagu (August 2018), Gorkha (April 2015), and Taiwan (August 2009). Each image pixel is labelled as belonging to a landslide or not, incorporating various sources and thorough manual annotation. We then evaluate the landslide detection performance of 11 state-of-the-art DL segmentation models: U-Net, ResU-Net, PSPNet, ContextNet, DeepLab-v2, DeepLab-v3+, FCN-8s, LinkNet, FRRN-A, FRRN-B, and SQNet. All models were trained from scratch on patches from one quarter of each study area and tested on independent patches from the other three quarters. Our experiments demonstrate that ResU-Net outperformed the other models for the landslide detection task. We make the multi-source landslide benchmark data (Landslide4Sense) and the tested DL models publicly available at \url{www.landslide4sense.org}, establishing an important resource for remote sensing, computer vision, and machine learning communities in studies of image classification in general and applications to landslide detection in particular.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge