Xiangrong Zhang
ACMamba: Fast Unsupervised Anomaly Detection via An Asymmetrical Consensus State Space Model
Apr 16, 2025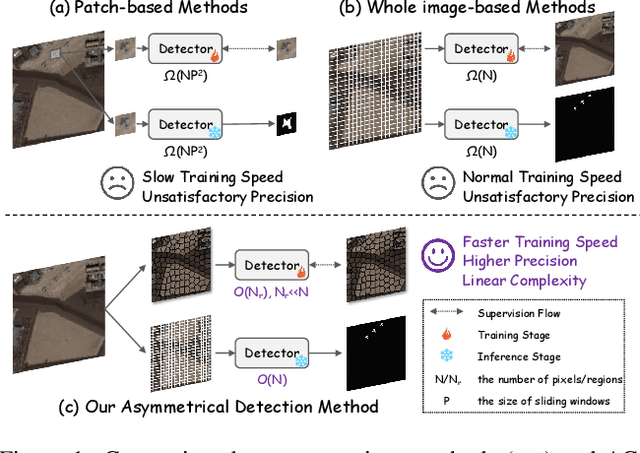
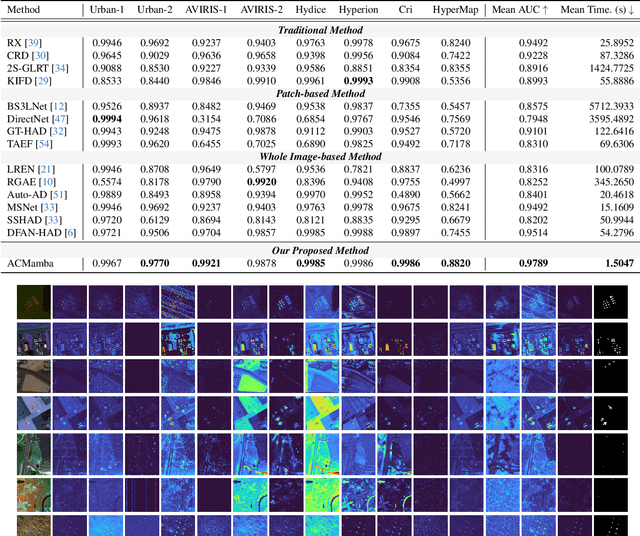
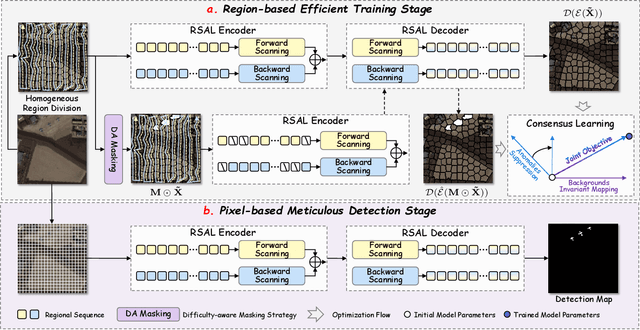
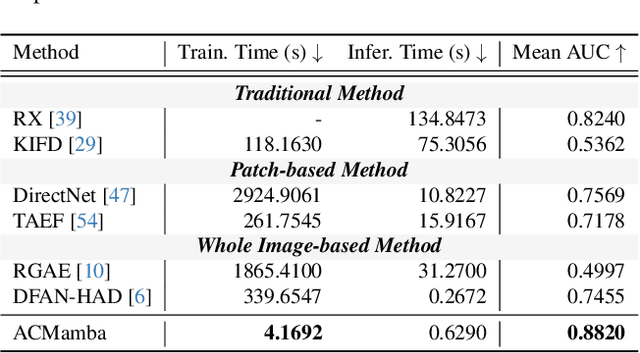
Abstract:Unsupervised anomaly detection in hyperspectral images (HSI), aiming to detect unknown targets from backgrounds, is challenging for earth surface monitoring. However, current studies are hindered by steep computational costs due to the high-dimensional property of HSI and dense sampling-based training paradigm, constraining their rapid deployment. Our key observation is that, during training, not all samples within the same homogeneous area are indispensable, whereas ingenious sampling can provide a powerful substitute for reducing costs. Motivated by this, we propose an Asymmetrical Consensus State Space Model (ACMamba) to significantly reduce computational costs without compromising accuracy. Specifically, we design an asymmetrical anomaly detection paradigm that utilizes region-level instances as an efficient alternative to dense pixel-level samples. In this paradigm, a low-cost Mamba-based module is introduced to discover global contextual attributes of regions that are essential for HSI reconstruction. Additionally, we develop a consensus learning strategy from the optimization perspective to simultaneously facilitate background reconstruction and anomaly compression, further alleviating the negative impact of anomaly reconstruction. Theoretical analysis and extensive experiments across eight benchmarks verify the superiority of ACMamba, demonstrating a faster speed and stronger performance over the state-of-the-art.
DiffMOD: Progressive Diffusion Point Denoising for Moving Object Detection in Remote Sensing
Apr 14, 2025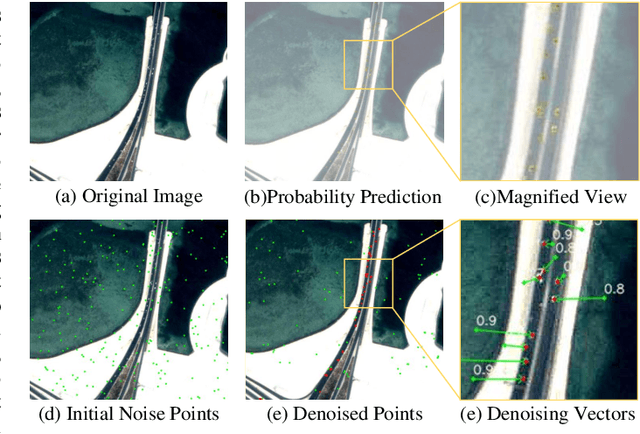
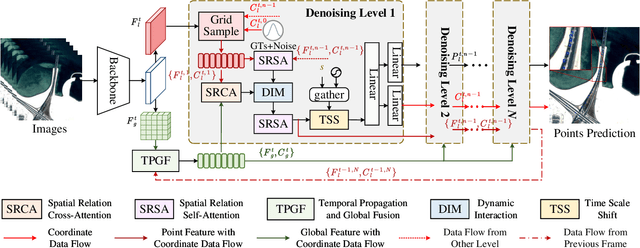
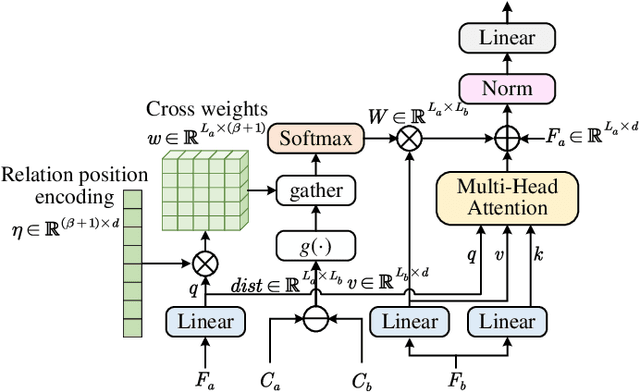
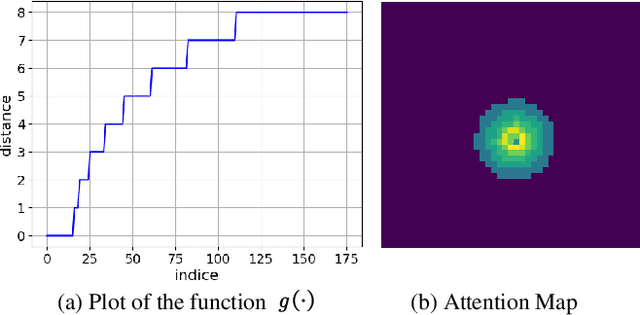
Abstract:Moving object detection (MOD) in remote sensing is significantly challenged by low resolution, extremely small object sizes, and complex noise interference. Current deep learning-based MOD methods rely on probability density estimation, which restricts flexible information interaction between objects and across temporal frames. To flexibly capture high-order inter-object and temporal relationships, we propose a point-based MOD in remote sensing. Inspired by diffusion models, the network optimization is formulated as a progressive denoising process that iteratively recovers moving object centers from sparse noisy points. Specifically, we sample scattered features from the backbone outputs as atomic units for subsequent processing, while global feature embeddings are aggregated to compensate for the limited coverage of sparse point features. By modeling spatial relative positions and semantic affinities, Spatial Relation Aggregation Attention is designed to enable high-order interactions among point-level features for enhanced object representation. To enhance temporal consistency, the Temporal Propagation and Global Fusion module is designed, which leverages an implicit memory reasoning mechanism for robust cross-frame feature integration. To align with the progressive denoising process, we propose a progressive MinK optimal transport assignment strategy that establishes specialized learning objectives at each denoising level. Additionally, we introduce a missing loss function to counteract the clustering tendency of denoised points around salient objects. Experiments on the RsData remote sensing MOD dataset show that our MOD method based on scattered point denoising can more effectively explore potential relationships between sparse moving objects and improve the detection capability and temporal consistency.
DeProPose: Deficiency-Proof 3D Human Pose Estimation via Adaptive Multi-View Fusion
Feb 23, 2025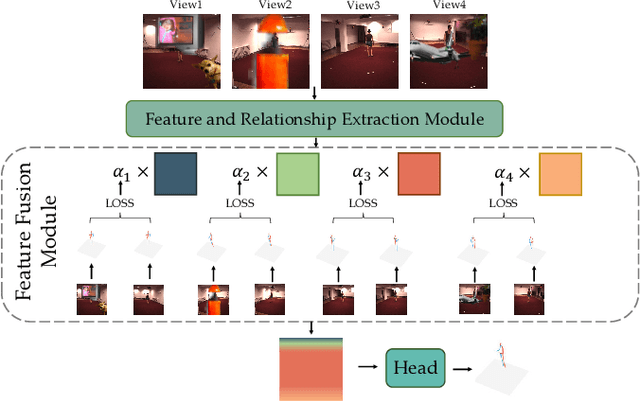
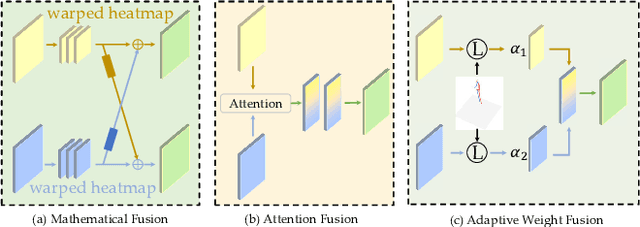
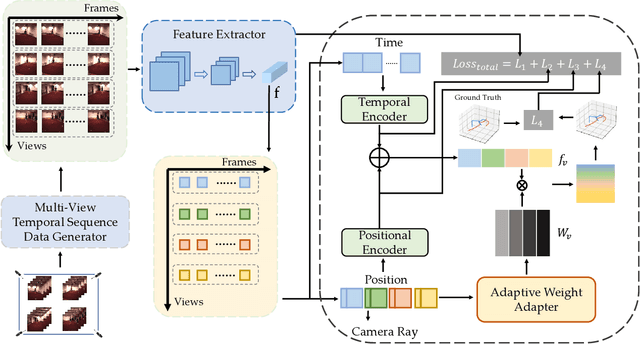
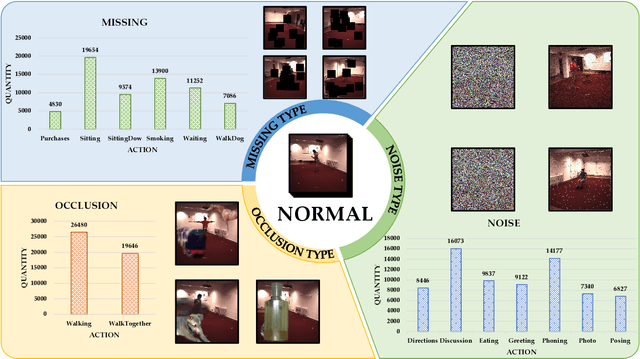
Abstract:3D human pose estimation has wide applications in fields such as intelligent surveillance, motion capture, and virtual reality. However, in real-world scenarios, issues such as occlusion, noise interference, and missing viewpoints can severely affect pose estimation. To address these challenges, we introduce the task of Deficiency-Aware 3D Pose Estimation. Traditional 3D pose estimation methods often rely on multi-stage networks and modular combinations, which can lead to cumulative errors and increased training complexity, making them unable to effectively address deficiency-aware estimation. To this end, we propose DeProPose, a flexible method that simplifies the network architecture to reduce training complexity and avoid information loss in multi-stage designs. Additionally, the model innovatively introduces a multi-view feature fusion mechanism based on relative projection error, which effectively utilizes information from multiple viewpoints and dynamically assigns weights, enabling efficient integration and enhanced robustness to overcome deficiency-aware 3D Pose Estimation challenges. Furthermore, to thoroughly evaluate this end-to-end multi-view 3D human pose estimation model and to advance research on occlusion-related challenges, we have developed a novel 3D human pose estimation dataset, termed the Deficiency-Aware 3D Pose Estimation (DA-3DPE) dataset. This dataset encompasses a wide range of deficiency scenarios, including noise interference, missing viewpoints, and occlusion challenges. Compared to state-of-the-art methods, DeProPose not only excels in addressing the deficiency-aware problem but also shows improvement in conventional scenarios, providing a powerful and user-friendly solution for 3D human pose estimation. The source code will be available at https://github.com/WUJINHUAN/DeProPose.
S$^2$Mamba: A Spatial-spectral State Space Model for Hyperspectral Image Classification
Apr 28, 2024



Abstract:Land cover analysis using hyperspectral images (HSI) remains an open problem due to their low spatial resolution and complex spectral information. Recent studies are primarily dedicated to designing Transformer-based architectures for spatial-spectral long-range dependencies modeling, which is computationally expensive with quadratic complexity. Selective structured state space model (Mamba), which is efficient for modeling long-range dependencies with linear complexity, has recently shown promising progress. However, its potential in hyperspectral image processing that requires handling numerous spectral bands has not yet been explored. In this paper, we innovatively propose S$^2$Mamba, a spatial-spectral state space model for hyperspectral image classification, to excavate spatial-spectral contextual features, resulting in more efficient and accurate land cover analysis. In S$^2$Mamba, two selective structured state space models through different dimensions are designed for feature extraction, one for spatial, and the other for spectral, along with a spatial-spectral mixture gate for optimal fusion. More specifically, S$^2$Mamba first captures spatial contextual relations by interacting each pixel with its adjacent through a Patch Cross Scanning module and then explores semantic information from continuous spectral bands through a Bi-directional Spectral Scanning module. Considering the distinct expertise of the two attributes in homogenous and complicated texture scenes, we realize the Spatial-spectral Mixture Gate by a group of learnable matrices, allowing for the adaptive incorporation of representations learned across different dimensions. Extensive experiments conducted on HSI classification benchmarks demonstrate the superiority and prospect of S$^2$Mamba. The code will be available at: https://github.com/PURE-melo/S2Mamba.
Remote Sensing Object Detection Meets Deep Learning: A Meta-review of Challenges and Advances
Sep 13, 2023



Abstract:Remote sensing object detection (RSOD), one of the most fundamental and challenging tasks in the remote sensing field, has received longstanding attention. In recent years, deep learning techniques have demonstrated robust feature representation capabilities and led to a big leap in the development of RSOD techniques. In this era of rapid technical evolution, this review aims to present a comprehensive review of the recent achievements in deep learning based RSOD methods. More than 300 papers are covered in this review. We identify five main challenges in RSOD, including multi-scale object detection, rotated object detection, weak object detection, tiny object detection, and object detection with limited supervision, and systematically review the corresponding methods developed in a hierarchical division manner. We also review the widely used benchmark datasets and evaluation metrics within the field of RSOD, as well as the application scenarios for RSOD. Future research directions are provided for further promoting the research in RSOD.
DiffUCD:Unsupervised Hyperspectral Image Change Detection with Semantic Correlation Diffusion Model
May 21, 2023



Abstract:Hyperspectral image change detection (HSI-CD) has emerged as a crucial research area in remote sensing due to its ability to detect subtle changes on the earth's surface. Recently, diffusional denoising probabilistic models (DDPM) have demonstrated remarkable performance in the generative domain. Apart from their image generation capability, the denoising process in diffusion models can comprehensively account for the semantic correlation of spectral-spatial features in HSI, resulting in the retrieval of semantically relevant features in the original image. In this work, we extend the diffusion model's application to the HSI-CD field and propose a novel unsupervised HSI-CD with semantic correlation diffusion model (DiffUCD). Specifically, the semantic correlation diffusion model (SCDM) leverages abundant unlabeled samples and fully accounts for the semantic correlation of spectral-spatial features, which mitigates pseudo change between multi-temporal images arising from inconsistent imaging conditions. Besides, objects with the same semantic concept at the same spatial location may exhibit inconsistent spectral signatures at different times, resulting in pseudo change. To address this problem, we propose a cross-temporal contrastive learning (CTCL) mechanism that aligns the spectral feature representations of unchanged samples. By doing so, the spectral difference invariant features caused by environmental changes can be obtained. Experiments conducted on three publicly available datasets demonstrate that the proposed method outperforms the other state-of-the-art unsupervised methods in terms of Overall Accuracy (OA), Kappa Coefficient (KC), and F1 scores, achieving improvements of approximately 3.95%, 8.13%, and 4.45%, respectively. Notably, our method can achieve comparable results to those fully supervised methods requiring numerous annotated samples.
SoftMatch Distance: A Novel Distance for Weakly-Supervised Trend Change Detection in Bi-Temporal Images
Mar 08, 2023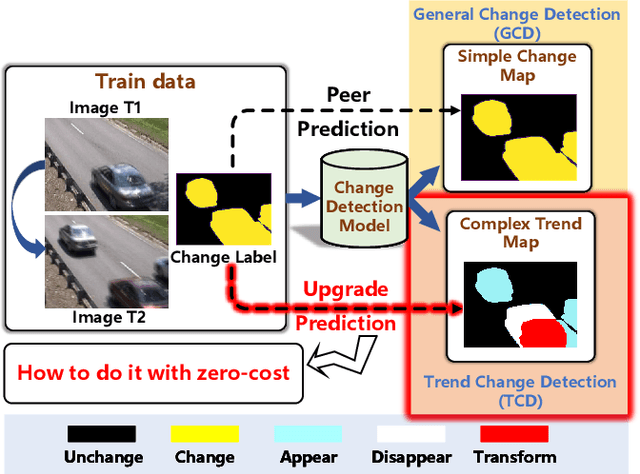
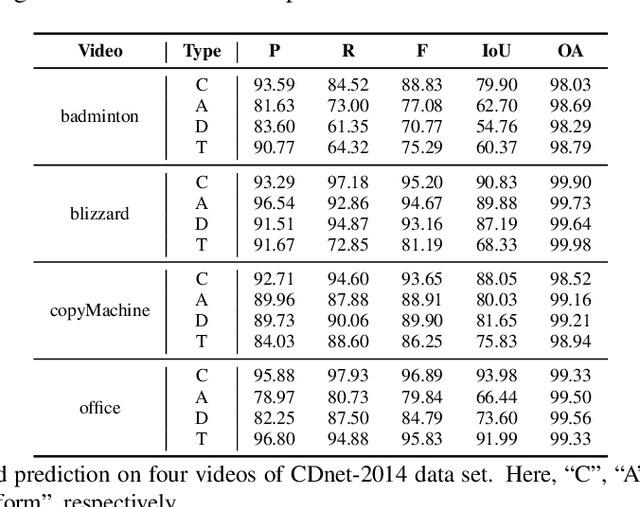
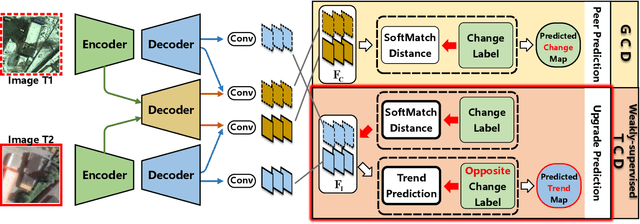
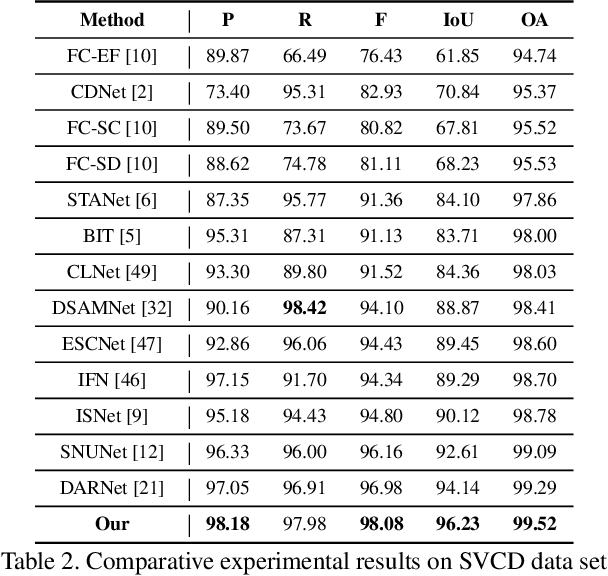
Abstract:General change detection (GCD) and semantic change detection (SCD) are common methods for identifying changes and distinguishing object categories involved in those changes, respectively. However, the binary changes provided by GCD is often not practical enough, while annotating semantic labels for training SCD models is very expensive. Therefore, there is a novel solution that intuitively dividing changes into three trends (``appear'', ``disappear'' and ``transform'') instead of semantic categories, named it trend change detection (TCD) in this paper. It offers more detailed change information than GCD, while requiring less manual annotation cost than SCD. However, there are limited public data sets with specific trend labels to support TCD application. To address this issue, we propose a softmatch distance which is used to construct a weakly-supervised TCD branch in a simple GCD model, using GCD labels instead of TCD label for training. Furthermore, a strategic approach is presented to successfully explore and extract background information, which is crucial for the weakly-supervised TCD task. The experiment results on four public data sets are highly encouraging, which demonstrates the effectiveness of our proposed model.
Absolute Wrong Makes Better: Boosting Weakly Supervised Object Detection via Negative Deterministic Information
Apr 21, 2022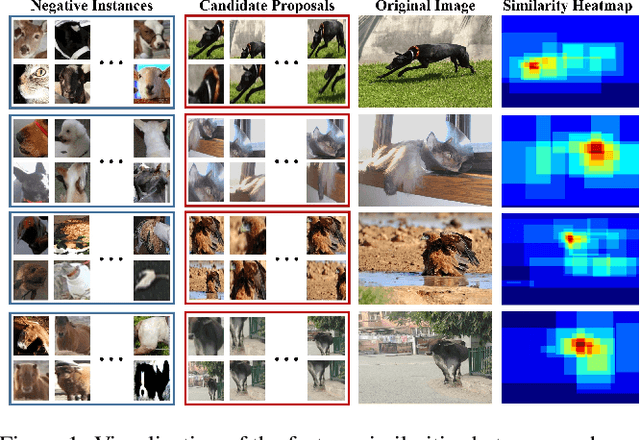
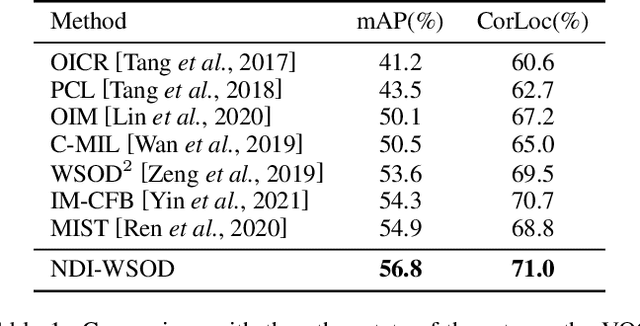
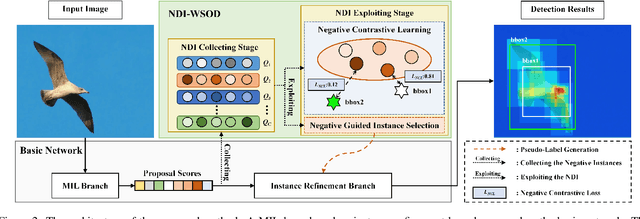
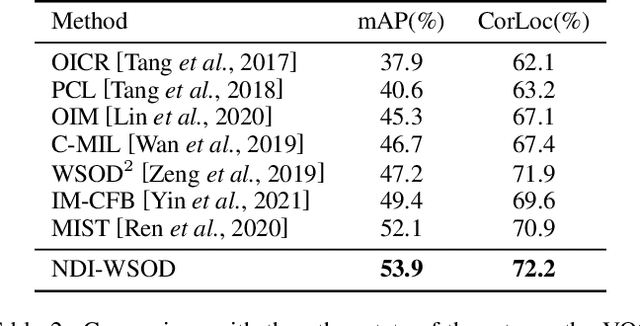
Abstract:Weakly supervised object detection (WSOD) is a challenging task, in which image-level labels (e.g., categories of the instances in the whole image) are used to train an object detector. Many existing methods follow the standard multiple instance learning (MIL) paradigm and have achieved promising performance. However, the lack of deterministic information leads to part domination and missing instances. To address these issues, this paper focuses on identifying and fully exploiting the deterministic information in WSOD. We discover that negative instances (i.e. absolutely wrong instances), ignored in most of the previous studies, normally contain valuable deterministic information. Based on this observation, we here propose a negative deterministic information (NDI) based method for improving WSOD, namely NDI-WSOD. Specifically, our method consists of two stages: NDI collecting and exploiting. In the collecting stage, we design several processes to identify and distill the NDI from negative instances online. In the exploiting stage, we utilize the extracted NDI to construct a novel negative contrastive learning mechanism and a negative guided instance selection strategy for dealing with the issues of part domination and missing instances, respectively. Experimental results on several public benchmarks including VOC 2007, VOC 2012 and MS COCO show that our method achieves satisfactory performance.
MidNet: An Anchor-and-Angle-Free Detector for Oriented Ship Detection in Aerial Images
Nov 22, 2021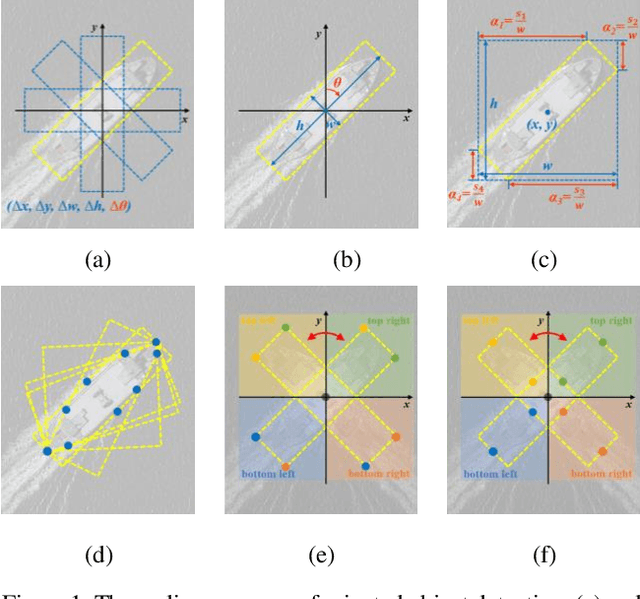
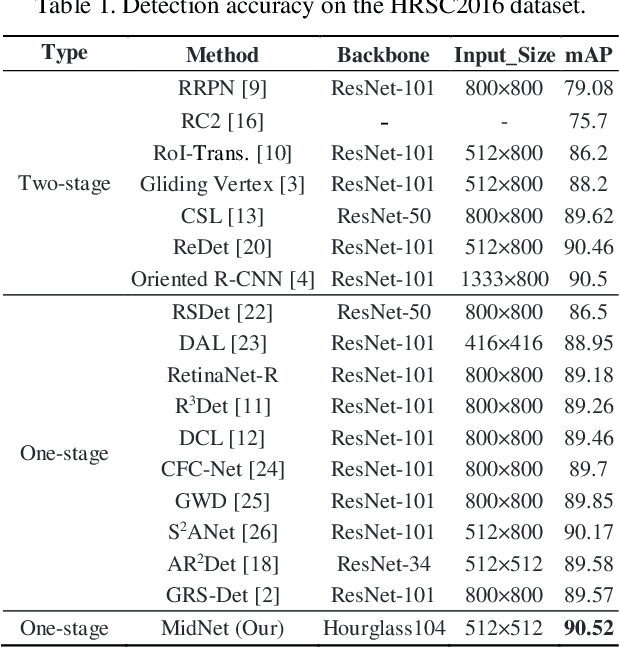
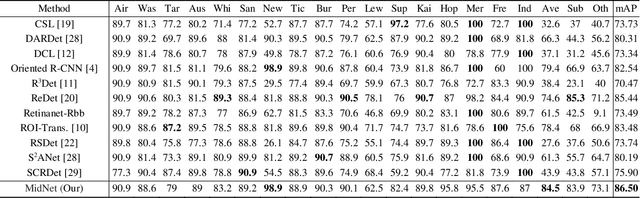
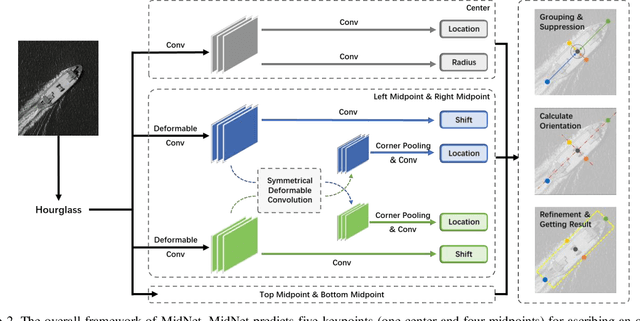
Abstract:Ship detection in aerial images remains an active yet challenging task due to arbitrary object orientation and complex background from a bird's-eye perspective. Most of the existing methods rely on angular prediction or predefined anchor boxes, making these methods highly sensitive to unstable angular regression and excessive hyper-parameter setting. To address these issues, we replace the angular-based object encoding with an anchor-and-angle-free paradigm, and propose a novel detector deploying a center and four midpoints for encoding each oriented object, namely MidNet. MidNet designs a symmetrical deformable convolution customized for enhancing the midpoints of ships, then the center and midpoints for an identical ship are adaptively matched by predicting corresponding centripetal shift and matching radius. Finally, a concise analytical geometry algorithm is proposed to refine the centers and midpoints step-wisely for building precise oriented bounding boxes. On two public ship detection datasets, HRSC2016 and FGSD2021, MidNet outperforms the state-of-the-art detectors by achieving APs of 90.52% and 86.50%. Additionally, MidNet obtains competitive results in the ship detection of DOTA.
Adaptive Affinity Loss and Erroneous Pseudo-Label Refinement for Weakly Supervised Semantic Segmentation
Aug 03, 2021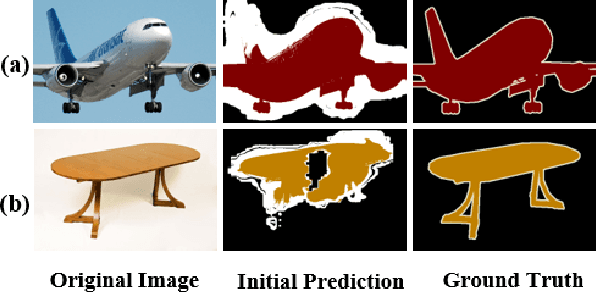
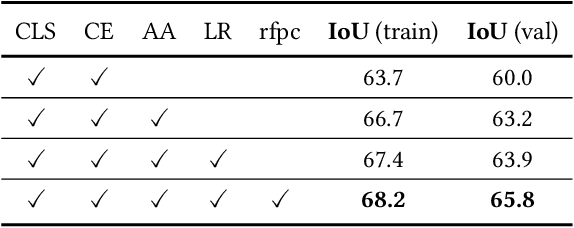
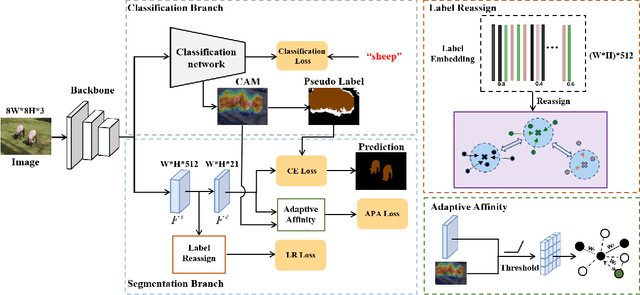
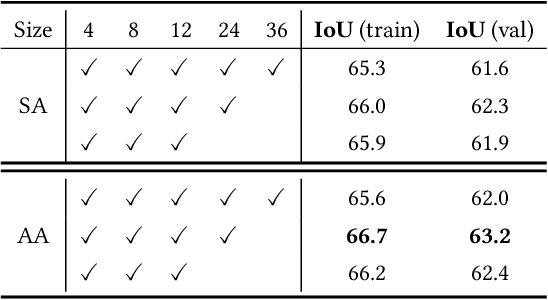
Abstract:Semantic segmentation has been continuously investigated in the last ten years, and majority of the established technologies are based on supervised models. In recent years, image-level weakly supervised semantic segmentation (WSSS), including single- and multi-stage process, has attracted large attention due to data labeling efficiency. In this paper, we propose to embed affinity learning of multi-stage approaches in a single-stage model. To be specific, we introduce an adaptive affinity loss to thoroughly learn the local pairwise affinity. As such, a deep neural network is used to deliver comprehensive semantic information in the training phase, whilst improving the performance of the final prediction module. On the other hand, considering the existence of errors in the pseudo labels, we propose a novel label reassign loss to mitigate over-fitting. Extensive experiments are conducted on the PASCAL VOC 2012 dataset to evaluate the effectiveness of our proposed approach that outperforms other standard single-stage methods and achieves comparable performance against several multi-stage methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge