Chunyi Zhou
When Agents "Misremember" Collectively: Exploring the Mandela Effect in LLM-based Multi-Agent Systems
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:Recent advancements in large language models (LLMs) have significantly enhanced the capabilities of collaborative multi-agent systems, enabling them to address complex challenges. However, within these multi-agent systems, the susceptibility of agents to collective cognitive biases remains an underexplored issue. A compelling example is the Mandela effect, a phenomenon where groups collectively misremember past events as a result of false details reinforced through social influence and internalized misinformation. This vulnerability limits our understanding of memory bias in multi-agent systems and raises ethical concerns about the potential spread of misinformation. In this paper, we conduct a comprehensive study on the Mandela effect in LLM-based multi-agent systems, focusing on its existence, causing factors, and mitigation strategies. We propose MANBENCH, a novel benchmark designed to evaluate agent behaviors across four common task types that are susceptible to the Mandela effect, using five interaction protocols that vary in agent roles and memory timescales. We evaluate agents powered by several LLMs on MANBENCH to quantify the Mandela effect and analyze how different factors affect it. Moreover, we propose strategies to mitigate this effect, including prompt-level defenses (e.g., cognitive anchoring and source scrutiny) and model-level alignment-based defense, achieving an average 74.40% reduction in the Mandela effect compared to the baseline. Our findings provide valuable insights for developing more resilient and ethically aligned collaborative multi-agent systems.
FraudShield: Knowledge Graph Empowered Defense for LLMs against Fraud Attacks
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have been widely integrated into critical automated workflows, including contract review and job application processes. However, LLMs are susceptible to manipulation by fraudulent information, which can lead to harmful outcomes. Although advanced defense methods have been developed to address this issue, they often exhibit limitations in effectiveness, interpretability, and generalizability, particularly when applied to LLM-based applications. To address these challenges, we introduce FraudShield, a novel framework designed to protect LLMs from fraudulent content by leveraging a comprehensive analysis of fraud tactics. Specifically, FraudShield constructs and refines a fraud tactic-keyword knowledge graph to capture high-confidence associations between suspicious text and fraud techniques. The structured knowledge graph augments the original input by highlighting keywords and providing supporting evidence, guiding the LLM toward more secure responses. Extensive experiments show that FraudShield consistently outperforms state-of-the-art defenses across four mainstream LLMs and five representative fraud types, while also offering interpretable clues for the model's generations.
Bridging the Copyright Gap: Do Large Vision-Language Models Recognize and Respect Copyrighted Content?
Dec 26, 2025Abstract:Large vision-language models (LVLMs) have achieved remarkable advancements in multimodal reasoning tasks. However, their widespread accessibility raises critical concerns about potential copyright infringement. Will LVLMs accurately recognize and comply with copyright regulations when encountering copyrighted content (i.e., user input, retrieved documents) in the context? Failure to comply with copyright regulations may lead to serious legal and ethical consequences, particularly when LVLMs generate responses based on copyrighted materials (e.g., retrieved book experts, news reports). In this paper, we present a comprehensive evaluation of various LVLMs, examining how they handle copyrighted content -- such as book excerpts, news articles, music lyrics, and code documentation when they are presented as visual inputs. To systematically measure copyright compliance, we introduce a large-scale benchmark dataset comprising 50,000 multimodal query-content pairs designed to evaluate how effectively LVLMs handle queries that could lead to copyright infringement. Given that real-world copyrighted content may or may not include a copyright notice, the dataset includes query-content pairs in two distinct scenarios: with and without a copyright notice. For the former, we extensively cover four types of copyright notices to account for different cases. Our evaluation reveals that even state-of-the-art closed-source LVLMs exhibit significant deficiencies in recognizing and respecting the copyrighted content, even when presented with the copyright notice. To solve this limitation, we introduce a novel tool-augmented defense framework for copyright compliance, which reduces infringement risks in all scenarios. Our findings underscore the importance of developing copyright-aware LVLMs to ensure the responsible and lawful use of copyrighted content.
The Eminence in Shadow: Exploiting Feature Boundary Ambiguity for Robust Backdoor Attacks
Dec 17, 2025Abstract:Deep neural networks (DNNs) underpin critical applications yet remain vulnerable to backdoor attacks, typically reliant on heuristic brute-force methods. Despite significant empirical advancements in backdoor research, the lack of rigorous theoretical analysis limits understanding of underlying mechanisms, constraining attack predictability and adaptability. Therefore, we provide a theoretical analysis targeting backdoor attacks, focusing on how sparse decision boundaries enable disproportionate model manipulation. Based on this finding, we derive a closed-form, ambiguous boundary region, wherein negligible relabeled samples induce substantial misclassification. Influence function analysis further quantifies significant parameter shifts caused by these margin samples, with minimal impact on clean accuracy, formally grounding why such low poison rates suffice for efficacious attacks. Leveraging these insights, we propose Eminence, an explainable and robust black-box backdoor framework with provable theoretical guarantees and inherent stealth properties. Eminence optimizes a universal, visually subtle trigger that strategically exploits vulnerable decision boundaries and effectively achieves robust misclassification with exceptionally low poison rates (< 0.1%, compared to SOTA methods typically requiring > 1%). Comprehensive experiments validate our theoretical discussions and demonstrate the effectiveness of Eminence, confirming an exponential relationship between margin poisoning and adversarial boundary manipulation. Eminence maintains > 90% attack success rate, exhibits negligible clean-accuracy loss, and demonstrates high transferability across diverse models, datasets and scenarios.
Poison in the Well: Feature Embedding Disruption in Backdoor Attacks
May 26, 2025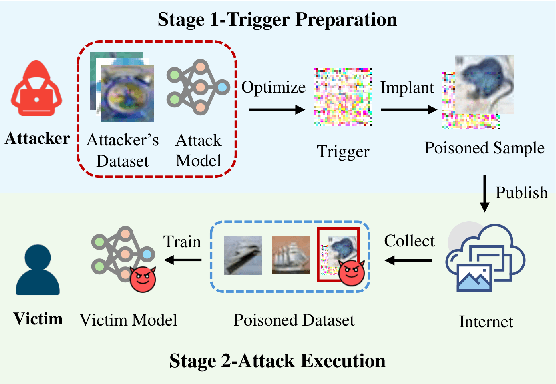
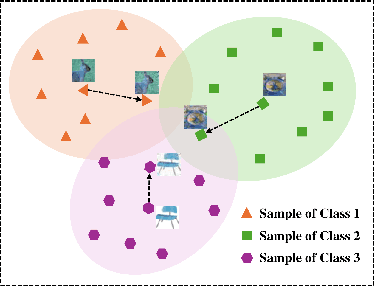
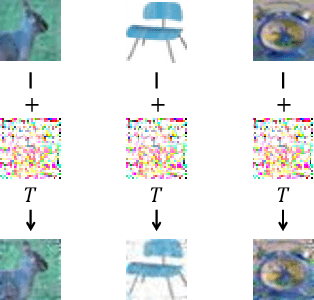
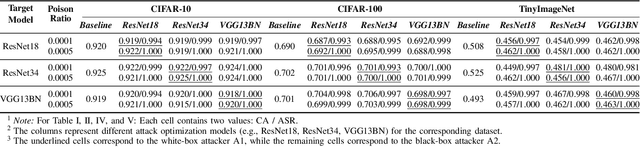
Abstract:Backdoor attacks embed malicious triggers into training data, enabling attackers to manipulate neural network behavior during inference while maintaining high accuracy on benign inputs. However, existing backdoor attacks face limitations manifesting in excessive reliance on training data, poor stealth, and instability, which hinder their effectiveness in real-world applications. Therefore, this paper introduces ShadowPrint, a versatile backdoor attack that targets feature embeddings within neural networks to achieve high ASRs and stealthiness. Unlike traditional approaches, ShadowPrint reduces reliance on training data access and operates effectively with exceedingly low poison rates (as low as 0.01%). It leverages a clustering-based optimization strategy to align feature embeddings, ensuring robust performance across diverse scenarios while maintaining stability and stealth. Extensive evaluations demonstrate that ShadowPrint achieves superior ASR (up to 100%), steady CA (with decay no more than 1% in most cases), and low DDR (averaging below 5%) across both clean-label and dirty-label settings, and with poison rates ranging from as low as 0.01% to 0.05%, setting a new standard for backdoor attack capabilities and emphasizing the need for advanced defense strategies focused on feature space manipulations.
UNIDOOR: A Universal Framework for Action-Level Backdoor Attacks in Deep Reinforcement Learning
Jan 26, 2025



Abstract:Deep reinforcement learning (DRL) is widely applied to safety-critical decision-making scenarios. However, DRL is vulnerable to backdoor attacks, especially action-level backdoors, which pose significant threats through precise manipulation and flexible activation, risking outcomes like vehicle collisions or drone crashes. The key distinction of action-level backdoors lies in the utilization of the backdoor reward function to associate triggers with target actions. Nevertheless, existing studies typically rely on backdoor reward functions with fixed values or conditional flipping, which lack universality across diverse DRL tasks and backdoor designs, resulting in fluctuations or even failure in practice. This paper proposes the first universal action-level backdoor attack framework, called UNIDOOR, which enables adaptive exploration of backdoor reward functions through performance monitoring, eliminating the reliance on expert knowledge and grid search. We highlight that action tampering serves as a crucial component of action-level backdoor attacks in continuous action scenarios, as it addresses attack failures caused by low-frequency target actions. Extensive evaluations demonstrate that UNIDOOR significantly enhances the attack performance of action-level backdoors, showcasing its universality across diverse attack scenarios, including single/multiple agents, single/multiple backdoors, discrete/continuous action spaces, and sparse/dense reward signals. Furthermore, visualization results encompassing state distribution, neuron activation, and animations demonstrate the stealthiness of UNIDOOR. The source code of UNIDOOR can be found at https://github.com/maoubo/UNIDOOR.
Navigating the Risks: A Survey of Security, Privacy, and Ethics Threats in LLM-Based Agents
Nov 14, 2024



Abstract:With the continuous development of large language models (LLMs), transformer-based models have made groundbreaking advances in numerous natural language processing (NLP) tasks, leading to the emergence of a series of agents that use LLMs as their control hub. While LLMs have achieved success in various tasks, they face numerous security and privacy threats, which become even more severe in the agent scenarios. To enhance the reliability of LLM-based applications, a range of research has emerged to assess and mitigate these risks from different perspectives. To help researchers gain a comprehensive understanding of various risks, this survey collects and analyzes the different threats faced by these agents. To address the challenges posed by previous taxonomies in handling cross-module and cross-stage threats, we propose a novel taxonomy framework based on the sources and impacts. Additionally, we identify six key features of LLM-based agents, based on which we summarize the current research progress and analyze their limitations. Subsequently, we select four representative agents as case studies to analyze the risks they may face in practical use. Finally, based on the aforementioned analyses, we propose future research directions from the perspectives of data, methodology, and policy, respectively.
Intellectual Property Protection for Deep Learning Model and Dataset Intelligence
Nov 07, 2024
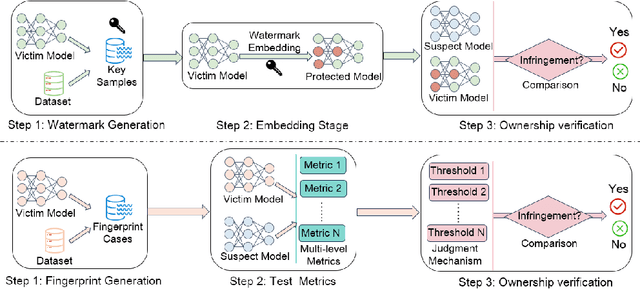


Abstract:With the growing applications of Deep Learning (DL), especially recent spectacular achievements of Large Language Models (LLMs) such as ChatGPT and LLaMA, the commercial significance of these remarkable models has soared. However, acquiring well-trained models is costly and resource-intensive. It requires a considerable high-quality dataset, substantial investment in dedicated architecture design, expensive computational resources, and efforts to develop technical expertise. Consequently, safeguarding the Intellectual Property (IP) of well-trained models is attracting increasing attention. In contrast to existing surveys overwhelmingly focusing on model IPP mainly, this survey not only encompasses the protection on model level intelligence but also valuable dataset intelligence. Firstly, according to the requirements for effective IPP design, this work systematically summarizes the general and scheme-specific performance evaluation metrics. Secondly, from proactive IP infringement prevention and reactive IP ownership verification perspectives, it comprehensively investigates and analyzes the existing IPP methods for both dataset and model intelligence. Additionally, from the standpoint of training settings, it delves into the unique challenges that distributed settings pose to IPP compared to centralized settings. Furthermore, this work examines various attacks faced by deep IPP techniques. Finally, we outline prospects for promising future directions that may act as a guide for innovative research.
"No Matter What You Do!": Mitigating Backdoor Attacks in Graph Neural Networks
Oct 02, 2024



Abstract:Recent studies have exposed that GNNs are vulnerable to several adversarial attacks, among which backdoor attack is one of the toughest. Similar to Deep Neural Networks (DNNs), backdoor attacks in GNNs lie in the fact that the attacker modifies a portion of graph data by embedding triggers and enforces the model to learn the trigger feature during the model training process. Despite the massive prior backdoor defense works on DNNs, defending against backdoor attacks in GNNs is largely unexplored, severely hindering the widespread application of GNNs in real-world tasks. To bridge this gap, we present GCleaner, the first backdoor mitigation method on GNNs. GCleaner can mitigate the presence of the backdoor logic within backdoored GNNs by reversing the backdoor learning procedure, aiming to restore the model performance to a level similar to that is directly trained on the original clean dataset. To achieve this objective, we ask: How to recover universal and hard backdoor triggers in GNNs? How to unlearn the backdoor trigger feature while maintaining the model performance? We conduct the graph trigger recovery via the explanation method to identify optimal trigger locations, facilitating the search of universal and hard backdoor triggers in the feature space of the backdoored model through maximal similarity. Subsequently, we introduce the backdoor unlearning mechanism, which combines knowledge distillation and gradient-based explainable knowledge for fine-grained backdoor erasure. Extensive experimental evaluations on four benchmark datasets demonstrate that GCleaner can reduce the backdoor attack success rate to 10% with only 1% of clean data, and has almost negligible degradation in model performance, which far outperforms the state-of-the-art (SOTA) defense methods.
TruVRF: Towards Triple-Granularity Verification on Machine Unlearning
Aug 12, 2024Abstract:The concept of the right to be forgotten has led to growing interest in machine unlearning, but reliable validation methods are lacking, creating opportunities for dishonest model providers to mislead data contributors. Traditional invasive methods like backdoor injection are not feasible for legacy data. To address this, we introduce TruVRF, a non-invasive unlearning verification framework operating at class-, volume-, and sample-level granularities. TruVRF includes three Unlearning-Metrics designed to detect different types of dishonest servers: Neglecting, Lazy, and Deceiving. Unlearning-Metric-I checks class alignment, Unlearning-Metric-II verifies sample count, and Unlearning-Metric-III confirms specific sample deletion. Evaluations on three datasets show TruVRF's robust performance, with over 90% accuracy for Metrics I and III, and a 4.8% to 8.2% inference deviation for Metric II. TruVRF also demonstrates generalizability and practicality across various conditions and with state-of-the-art unlearning frameworks like SISA and Amnesiac Unlearning.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge