Oubo Ma
TrojanTO: Action-Level Backdoor Attacks against Trajectory Optimization Models
Jun 15, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in Trajectory Optimization (TO) models have achieved remarkable success in offline reinforcement learning. However, their vulnerabilities against backdoor attacks are poorly understood. We find that existing backdoor attacks in reinforcement learning are based on reward manipulation, which are largely ineffective against the TO model due to its inherent sequence modeling nature. Moreover, the complexities introduced by high-dimensional action spaces further compound the challenge of action manipulation. To address these gaps, we propose TrojanTO, the first action-level backdoor attack against TO models. TrojanTO employs alternating training to enhance the connection between triggers and target actions for attack effectiveness. To improve attack stealth, it utilizes precise poisoning via trajectory filtering for normal performance and batch poisoning for trigger consistency. Extensive evaluations demonstrate that TrojanTO effectively implants backdoor attacks across diverse tasks and attack objectives with a low attack budget (0.3\% of trajectories). Furthermore, TrojanTO exhibits broad applicability to DT, GDT, and DC, underscoring its scalability across diverse TO model architectures.
UNIDOOR: A Universal Framework for Action-Level Backdoor Attacks in Deep Reinforcement Learning
Jan 26, 2025



Abstract:Deep reinforcement learning (DRL) is widely applied to safety-critical decision-making scenarios. However, DRL is vulnerable to backdoor attacks, especially action-level backdoors, which pose significant threats through precise manipulation and flexible activation, risking outcomes like vehicle collisions or drone crashes. The key distinction of action-level backdoors lies in the utilization of the backdoor reward function to associate triggers with target actions. Nevertheless, existing studies typically rely on backdoor reward functions with fixed values or conditional flipping, which lack universality across diverse DRL tasks and backdoor designs, resulting in fluctuations or even failure in practice. This paper proposes the first universal action-level backdoor attack framework, called UNIDOOR, which enables adaptive exploration of backdoor reward functions through performance monitoring, eliminating the reliance on expert knowledge and grid search. We highlight that action tampering serves as a crucial component of action-level backdoor attacks in continuous action scenarios, as it addresses attack failures caused by low-frequency target actions. Extensive evaluations demonstrate that UNIDOOR significantly enhances the attack performance of action-level backdoors, showcasing its universality across diverse attack scenarios, including single/multiple agents, single/multiple backdoors, discrete/continuous action spaces, and sparse/dense reward signals. Furthermore, visualization results encompassing state distribution, neuron activation, and animations demonstrate the stealthiness of UNIDOOR. The source code of UNIDOOR can be found at https://github.com/maoubo/UNIDOOR.
Is Mamba Compatible with Trajectory Optimization in Offline Reinforcement Learning?
May 20, 2024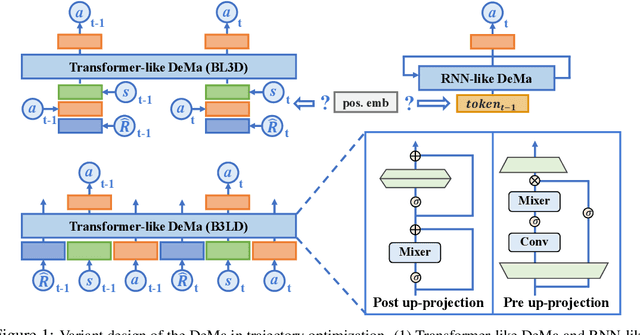
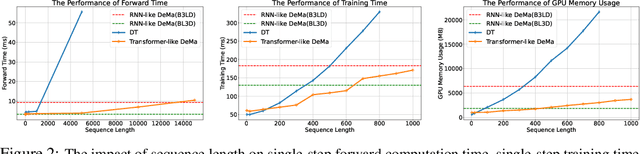
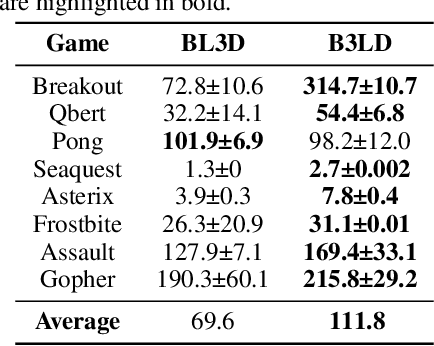
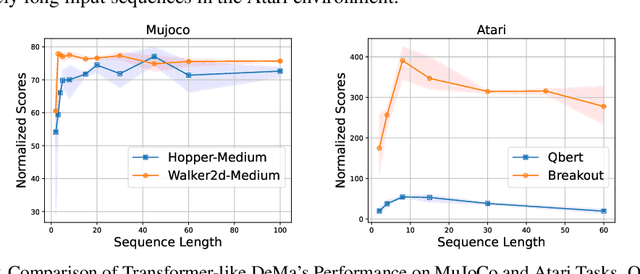
Abstract:Transformer-based trajectory optimization methods have demonstrated exceptional performance in offline Reinforcement Learning (offline RL), yet it poses challenges due to substantial parameter size and limited scalability, which is particularly critical in sequential decision-making scenarios where resources are constrained such as in robots and drones with limited computational power. Mamba, a promising new linear-time sequence model, offers performance on par with transformers while delivering substantially fewer parameters on long sequences. As it remains unclear whether Mamba is compatible with trajectory optimization, this work aims to conduct comprehensive experiments to explore the potential of Decision Mamba in offline RL (dubbed DeMa) from the aspect of data structures and network architectures with the following insights: (1) Long sequences impose a significant computational burden without contributing to performance improvements due to the fact that DeMa's focus on sequences diminishes approximately exponentially. Consequently, we introduce a Transformer-like DeMa as opposed to an RNN-like DeMa. (2) For the components of DeMa, we identify that the hidden attention mechanism is key to its success, which can also work well with other residual structures and does not require position embedding. Extensive evaluations from eight Atari games demonstrate that our specially designed DeMa is compatible with trajectory optimization and surpasses previous state-of-the-art methods, outdoing Decision Transformer (DT) by 80\% with 30\% fewer parameters, and exceeds DT in MuJoCo with only a quarter of the parameters.
SUB-PLAY: Adversarial Policies against Partially Observed Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning Systems
Feb 06, 2024Abstract:Recent advances in multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL) have opened up vast application prospects, including swarm control of drones, collaborative manipulation by robotic arms, and multi-target encirclement. However, potential security threats during the MARL deployment need more attention and thorough investigation. Recent researches reveal that an attacker can rapidly exploit the victim's vulnerabilities and generate adversarial policies, leading to the victim's failure in specific tasks. For example, reducing the winning rate of a superhuman-level Go AI to around 20%. They predominantly focus on two-player competitive environments, assuming attackers possess complete global state observation. In this study, we unveil, for the first time, the capability of attackers to generate adversarial policies even when restricted to partial observations of the victims in multi-agent competitive environments. Specifically, we propose a novel black-box attack (SUB-PLAY), which incorporates the concept of constructing multiple subgames to mitigate the impact of partial observability and suggests the sharing of transitions among subpolicies to improve the exploitative ability of attackers. Extensive evaluations demonstrate the effectiveness of SUB-PLAY under three typical partial observability limitations. Visualization results indicate that adversarial policies induce significantly different activations of the victims' policy networks. Furthermore, we evaluate three potential defenses aimed at exploring ways to mitigate security threats posed by adversarial policies, providing constructive recommendations for deploying MARL in competitive environments.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge