Xiaolei Liu
HATS: High-Accuracy Triple-Set Watermarking for Large Language Models
Dec 22, 2025Abstract:Misuse of LLM-generated text can be curbed by watermarking techniques that embed implicit signals into the output. We propose a watermark that partitions the vocabulary at each decoding step into three sets (Green/Yellow/Red) with fixed ratios and restricts sampling to the Green and Yellow sets. At detection time, we replay the same partitions, compute Green-enrichment and Red-depletion statistics, convert them to one-sided z-scores, and aggregate their p-values via Fisher's method to decide whether a passage is watermarked. We implement generation, detection, and testing on Llama 2 7B, and evaluate true-positive rate, false-positive rate, and text quality. Results show that the triple-partition scheme achieves high detection accuracy at fixed FPR while preserving readability.
* Camera-ready version of the paper accepted for oral presentation at the 11th International Conference on Computer and Communications (ICCC 2025)
LoopLLM: Transferable Energy-Latency Attacks in LLMs via Repetitive Generation
Nov 11, 2025



Abstract:As large language models (LLMs) scale, their inference incurs substantial computational resources, exposing them to energy-latency attacks, where crafted prompts induce high energy and latency cost. Existing attack methods aim to prolong output by delaying the generation of termination symbols. However, as the output grows longer, controlling the termination symbols through input becomes difficult, making these methods less effective. Therefore, we propose LoopLLM, an energy-latency attack framework based on the observation that repetitive generation can trigger low-entropy decoding loops, reliably compelling LLMs to generate until their output limits. LoopLLM introduces (1) a repetition-inducing prompt optimization that exploits autoregressive vulnerabilities to induce repetitive generation, and (2) a token-aligned ensemble optimization that aggregates gradients to improve cross-model transferability. Extensive experiments on 12 open-source and 2 commercial LLMs show that LoopLLM significantly outperforms existing methods, achieving over 90% of the maximum output length, compared to 20% for baselines, and improving transferability by around 40% to DeepSeek-V3 and Gemini 2.5 Flash.
Unsupervised Domain Adaptation with Dynamic Clustering and Contrastive Refinement for Gait Recognition
Jan 28, 2025



Abstract:Gait recognition is an emerging identification technology that distinguishes individuals at long distances by analyzing individual walking patterns. Traditional techniques rely heavily on large-scale labeled datasets, which incurs high costs and significant labeling challenges. Recently, researchers have explored unsupervised gait recognition with clustering-based unsupervised domain adaptation methods and achieved notable success. However, these methods directly use pseudo-label generated by clustering and neglect pseudolabel noise caused by domain differences, which affects the effect of the model training process. To mitigate these issues, we proposed a novel model called GaitDCCR, which aims to reduce the influence of noisy pseudo labels on clustering and model training. Our approach can be divided into two main stages: clustering and training stage. In the clustering stage, we propose Dynamic Cluster Parameters (DCP) and Dynamic Weight Centroids (DWC) to improve the efficiency of clustering and obtain reliable cluster centroids. In the training stage, we employ the classical teacher-student structure and propose Confidence-based Pseudo-label Refinement (CPR) and Contrastive Teacher Module (CTM) to encourage noisy samples to converge towards clusters containing their true identities. Extensive experiments on public gait datasets have demonstrated that our simple and effective method significantly enhances the performance of unsupervised gait recognition, laying the foundation for its application in the real-world.The code is available at https://github.com/YanSun-github/GaitDCCR
Information Maximization via Variational Autoencoders for Cross-Domain Recommendation
May 31, 2024



Abstract:Cross-Domain Sequential Recommendation (CDSR) methods aim to address the data sparsity and cold-start problems present in Single-Domain Sequential Recommendation (SDSR). Existing CDSR methods typically rely on overlapping users, designing complex cross-domain modules to capture users' latent interests that can propagate across different domains. However, their propagated informative information is limited to the overlapping users and the users who have rich historical behavior records. As a result, these methods often underperform in real-world scenarios, where most users are non-overlapping (cold-start) and long-tailed. In this research, we introduce a new CDSR framework named Information Maximization Variational Autoencoder (\textbf{\texttt{IM-VAE}}). Here, we suggest using a Pseudo-Sequence Generator to enhance the user's interaction history input for downstream fine-grained CDSR models to alleviate the cold-start issues. We also propose a Generative Recommendation Framework combined with three regularizers inspired by the mutual information maximization (MIM) theory \cite{mcgill1954multivariate} to capture the semantic differences between a user's interests shared across domains and those specific to certain domains, as well as address the informational gap between a user's actual interaction sequences and the pseudo-sequences generated. To the best of our knowledge, this paper is the first CDSR work that considers the information disentanglement and denoising of pseudo-sequences in the open-world recommendation scenario. Empirical experiments illustrate that \texttt{IM-VAE} outperforms the state-of-the-art approaches on two real-world cross-domain datasets on all sorts of users, including cold-start and tailed users, demonstrating the effectiveness of \texttt{IM-VAE} in open-world recommendation.
An Embarrassingly Simple Approach to Enhance Transformer Performance in Genomic Selection for Crop Breeding
May 15, 2024Abstract:Genomic selection (GS), as a critical crop breeding strategy, plays a key role in enhancing food production and addressing the global hunger crisis. The predominant approaches in GS currently revolve around employing statistical methods for prediction. However, statistical methods often come with two main limitations: strong statistical priors and linear assumptions. A recent trend is to capture the non-linear relationships between markers by deep learning. However, as crop datasets are commonly long sequences with limited samples, the robustness of deep learning models, especially Transformers, remains a challenge. In this work, to unleash the unexplored potential of attention mechanism for the task of interest, we propose a simple yet effective Transformer-based framework that enables end-to-end training of the whole sequence. Via experiments on rice3k and wheat3k datasets, we show that, with simple tricks such as k-mer tokenization and random masking, Transformer can achieve overall superior performance against seminal methods on GS tasks of interest.
SUB-PLAY: Adversarial Policies against Partially Observed Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning Systems
Feb 06, 2024Abstract:Recent advances in multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL) have opened up vast application prospects, including swarm control of drones, collaborative manipulation by robotic arms, and multi-target encirclement. However, potential security threats during the MARL deployment need more attention and thorough investigation. Recent researches reveal that an attacker can rapidly exploit the victim's vulnerabilities and generate adversarial policies, leading to the victim's failure in specific tasks. For example, reducing the winning rate of a superhuman-level Go AI to around 20%. They predominantly focus on two-player competitive environments, assuming attackers possess complete global state observation. In this study, we unveil, for the first time, the capability of attackers to generate adversarial policies even when restricted to partial observations of the victims in multi-agent competitive environments. Specifically, we propose a novel black-box attack (SUB-PLAY), which incorporates the concept of constructing multiple subgames to mitigate the impact of partial observability and suggests the sharing of transitions among subpolicies to improve the exploitative ability of attackers. Extensive evaluations demonstrate the effectiveness of SUB-PLAY under three typical partial observability limitations. Visualization results indicate that adversarial policies induce significantly different activations of the victims' policy networks. Furthermore, we evaluate three potential defenses aimed at exploring ways to mitigate security threats posed by adversarial policies, providing constructive recommendations for deploying MARL in competitive environments.
Launching a Robust Backdoor Attack under Capability Constrained Scenarios
Apr 21, 2023Abstract:As deep neural networks continue to be used in critical domains, concerns over their security have emerged. Deep learning models are vulnerable to backdoor attacks due to the lack of transparency. A poisoned backdoor model may perform normally in routine environments, but exhibit malicious behavior when the input contains a trigger. Current research on backdoor attacks focuses on improving the stealthiness of triggers, and most approaches require strong attacker capabilities, such as knowledge of the model structure or control over the training process. These attacks are impractical since in most cases the attacker's capabilities are limited. Additionally, the issue of model robustness has not received adequate attention. For instance, model distillation is commonly used to streamline model size as the number of parameters grows exponentially, and most of previous backdoor attacks failed after model distillation; the image augmentation operations can destroy the trigger and thus disable the backdoor. This study explores the implementation of black-box backdoor attacks within capability constraints. An attacker can carry out such attacks by acting as either an image annotator or an image provider, without involvement in the training process or knowledge of the target model's structure. Through the design of a backdoor trigger, our attack remains effective after model distillation and image augmentation, making it more threatening and practical. Our experimental results demonstrate that our method achieves a high attack success rate in black-box scenarios and evades state-of-the-art backdoor defenses.
Neural Node Matching for Multi-Target Cross Domain Recommendation
Feb 12, 2023



Abstract:Multi-Target Cross Domain Recommendation(CDR) has attracted a surge of interest recently, which intends to improve the recommendation performance in multiple domains (or systems) simultaneously. Most existing multi-target CDR frameworks primarily rely on the existence of the majority of overlapped users across domains. However, general practical CDR scenarios cannot meet the strictly overlapping requirements and only share a small margin of common users across domains}. Additionally, the majority of users have quite a few historical behaviors in such small-overlapping CDR scenarios}. To tackle the aforementioned issues, we propose a simple-yet-effective neural node matching based framework for more general CDR settings, i.e., only (few) partially overlapped users exist across domains and most overlapped as well as non-overlapped users do have sparse interactions. The present framework} mainly contains two modules: (i) intra-to-inter node matching module, and (ii) intra node complementing module. Concretely, the first module conducts intra-knowledge fusion within each domain and subsequent inter-knowledge fusion across domains by fully connected user-user homogeneous graph information aggregating.
* 13pages
Semi-Supervised Heterogeneous Graph Learning with Multi-level Data Augmentation
Nov 30, 2022Abstract:In recent years, semi-supervised graph learning with data augmentation (DA) is currently the most commonly used and best-performing method to enhance model robustness in sparse scenarios with few labeled samples. Differing from homogeneous graph, DA in heterogeneous graph has greater challenges: heterogeneity of information requires DA strategies to effectively handle heterogeneous relations, which considers the information contribution of different types of neighbors and edges to the target nodes. Furthermore, over-squashing of information is caused by the negative curvature that formed by the non-uniformity distribution and strong clustering in complex graph. To address these challenges, this paper presents a novel method named Semi-Supervised Heterogeneous Graph Learning with Multi-level Data Augmentation (HG-MDA). For the problem of heterogeneity of information in DA, node and topology augmentation strategies are proposed for the characteristics of heterogeneous graph. And meta-relation-based attention is applied as one of the indexes for selecting augmented nodes and edges. For the problem of over-squashing of information, triangle based edge adding and removing are designed to alleviate the negative curvature and bring the gain of topology. Finally, the loss function consists of the cross-entropy loss for labeled data and the consistency regularization for unlabeled data. In order to effectively fuse the prediction results of various DA strategies, the sharpening is used. Existing experiments on public datasets, i.e., ACM, DBLP, OGB, and industry dataset MB show that HG-MDA outperforms current SOTA models. Additionly, HG-MDA is applied to user identification in internet finance scenarios, helping the business to add 30% key users, and increase loans and balances by 3.6%, 11.1%, and 9.8%.
Poincaré Heterogeneous Graph Neural Networks for Sequential Recommendation
May 16, 2022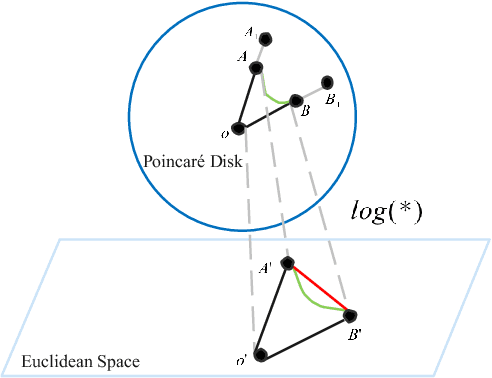
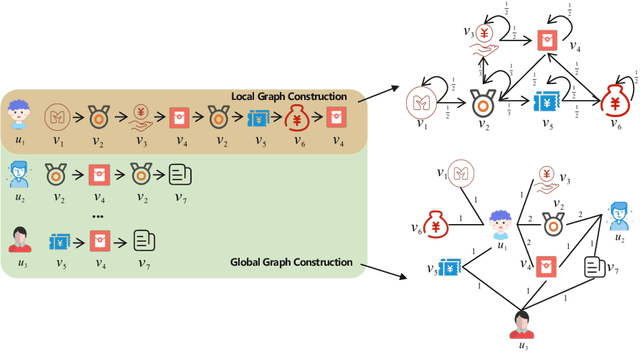
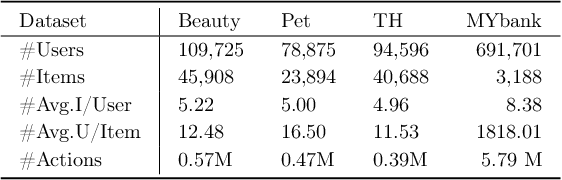
Abstract:Sequential recommendation (SR) learns users' preferences by capturing the sequential patterns from users' behaviors evolution. As discussed in many works, user-item interactions of SR generally present the intrinsic power-law distribution, which can be ascended to hierarchy-like structures. Previous methods usually handle such hierarchical information by making user-item sectionalization empirically under Euclidean space, which may cause distortion of user-item representation in real online scenarios. In this paper, we propose a Poincar\'{e}-based heterogeneous graph neural network named PHGR to model the sequential pattern information as well as hierarchical information contained in the data of SR scenarios simultaneously. Specifically, for the purpose of explicitly capturing the hierarchical information, we first construct a weighted user-item heterogeneous graph by aliening all the user-item interactions to improve the perception domain of each user from a global view. Then the output of the global representation would be used to complement the local directed item-item homogeneous graph convolution. By defining a novel hyperbolic inner product operator, the global and local graph representation learning are directly conducted in Poincar\'{e} ball instead of commonly used projection operation between Poincar\'{e} ball and Euclidean space, which could alleviate the cumulative error issue of general bidirectional translation process. Moreover, for the purpose of explicitly capturing the sequential dependency information, we design two types of temporal attention operations under Poincar\'{e} ball space. Empirical evaluations on datasets from the public and financial industry show that PHGR outperforms several comparison methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge