Qiongxu Ma
Information Maximization via Variational Autoencoders for Cross-Domain Recommendation
May 31, 2024



Abstract:Cross-Domain Sequential Recommendation (CDSR) methods aim to address the data sparsity and cold-start problems present in Single-Domain Sequential Recommendation (SDSR). Existing CDSR methods typically rely on overlapping users, designing complex cross-domain modules to capture users' latent interests that can propagate across different domains. However, their propagated informative information is limited to the overlapping users and the users who have rich historical behavior records. As a result, these methods often underperform in real-world scenarios, where most users are non-overlapping (cold-start) and long-tailed. In this research, we introduce a new CDSR framework named Information Maximization Variational Autoencoder (\textbf{\texttt{IM-VAE}}). Here, we suggest using a Pseudo-Sequence Generator to enhance the user's interaction history input for downstream fine-grained CDSR models to alleviate the cold-start issues. We also propose a Generative Recommendation Framework combined with three regularizers inspired by the mutual information maximization (MIM) theory \cite{mcgill1954multivariate} to capture the semantic differences between a user's interests shared across domains and those specific to certain domains, as well as address the informational gap between a user's actual interaction sequences and the pseudo-sequences generated. To the best of our knowledge, this paper is the first CDSR work that considers the information disentanglement and denoising of pseudo-sequences in the open-world recommendation scenario. Empirical experiments illustrate that \texttt{IM-VAE} outperforms the state-of-the-art approaches on two real-world cross-domain datasets on all sorts of users, including cold-start and tailed users, demonstrating the effectiveness of \texttt{IM-VAE} in open-world recommendation.
Towards Open-world Cross-Domain Sequential Recommendation: A Model-Agnostic Contrastive Denoising Approach
Nov 23, 2023



Abstract:Cross-domain sequential recommendation (CDSR) aims to address the data sparsity problems that exist in traditional sequential recommendation (SR) systems. The existing approaches aim to design a specific cross-domain unit that can transfer and propagate information across multiple domains by relying on overlapping users with abundant behaviors. However, in real-world recommender systems, CDSR scenarios usually consist of a majority of long-tailed users with sparse behaviors and cold-start users who only exist in one domain. This leads to a drop in the performance of existing CDSR methods in the real-world industry platform. Therefore, improving the consistency and effectiveness of models in open-world CDSR scenarios is crucial for constructing CDSR models (\textit{1st} CH). Recently, some SR approaches have utilized auxiliary behaviors to complement the information for long-tailed users. However, these multi-behavior SR methods cannot deliver promising performance in CDSR, as they overlook the semantic gap between target and auxiliary behaviors, as well as user interest deviation across domains (\textit{2nd} CH).
Rethinking Cross-Domain Sequential Recommendation under Open-World Assumptions
Nov 08, 2023Abstract:Cross-Domain Sequential Recommendation (CDSR) methods aim to tackle the data sparsity and cold-start problems present in Single-Domain Sequential Recommendation (SDSR). Existing CDSR works design their elaborate structures relying on overlapping users to propagate the cross-domain information. However, current CDSR methods make closed-world assumptions, assuming fully overlapping users across multiple domains and that the data distribution remains unchanged from the training environment to the test environment. As a result, these methods typically result in lower performance on online real-world platforms due to the data distribution shifts. To address these challenges under open-world assumptions, we design an \textbf{A}daptive \textbf{M}ulti-\textbf{I}nterest \textbf{D}ebiasing framework for cross-domain sequential recommendation (\textbf{AMID}), which consists of a multi-interest information module (\textbf{MIM}) and a doubly robust estimator (\textbf{DRE}). Our framework is adaptive for open-world environments and can improve the model of most off-the-shelf single-domain sequential backbone models for CDSR. Our MIM establishes interest groups that consider both overlapping and non-overlapping users, allowing us to effectively explore user intent and explicit interest. To alleviate biases across multiple domains, we developed the DRE for the CDSR methods. We also provide a theoretical analysis that demonstrates the superiority of our proposed estimator in terms of bias and tail bound, compared to the IPS estimator used in previous work.
Neural Node Matching for Multi-Target Cross Domain Recommendation
Feb 12, 2023



Abstract:Multi-Target Cross Domain Recommendation(CDR) has attracted a surge of interest recently, which intends to improve the recommendation performance in multiple domains (or systems) simultaneously. Most existing multi-target CDR frameworks primarily rely on the existence of the majority of overlapped users across domains. However, general practical CDR scenarios cannot meet the strictly overlapping requirements and only share a small margin of common users across domains}. Additionally, the majority of users have quite a few historical behaviors in such small-overlapping CDR scenarios}. To tackle the aforementioned issues, we propose a simple-yet-effective neural node matching based framework for more general CDR settings, i.e., only (few) partially overlapped users exist across domains and most overlapped as well as non-overlapped users do have sparse interactions. The present framework} mainly contains two modules: (i) intra-to-inter node matching module, and (ii) intra node complementing module. Concretely, the first module conducts intra-knowledge fusion within each domain and subsequent inter-knowledge fusion across domains by fully connected user-user homogeneous graph information aggregating.
* 13pages
Adaptive Pattern Extraction Multi-Task Learning for Multi-Step Conversion Estimations
Jan 23, 2023Abstract:Multi-task learning (MTL) has been successfully used in many real-world applications, which aims to simultaneously solve multiple tasks with a single model. The general idea of multi-task learning is designing kinds of global parameter sharing mechanism and task-specific feature extractor to improve the performance of all tasks. However, challenge still remains in balancing the trade-off of various tasks since model performance is sensitive to the relationships between them. Less correlated or even conflict tasks will deteriorate the performance by introducing unhelpful or negative information. Therefore, it is important to efficiently exploit and learn fine-grained feature representation corresponding to each task. In this paper, we propose an Adaptive Pattern Extraction Multi-task (APEM) framework, which is adaptive and flexible for large-scale industrial application. APEM is able to fully utilize the feature information by learning the interactions between the input feature fields and extracted corresponding tasks-specific information. We first introduce a DeepAuto Group Transformer module to automatically and efficiently enhance the feature expressivity with a modified set attention mechanism and a Squeeze-and-Excitation operation. Second, explicit Pattern Selector is introduced to further enable selectively feature representation learning by adaptive task-indicator vectors. Empirical evaluations show that APEM outperforms the state-of-the-art MTL methods on public and real-world financial services datasets. More importantly, we explore the online performance of APEM in a real industrial-level recommendation scenario.
Poincaré Heterogeneous Graph Neural Networks for Sequential Recommendation
May 16, 2022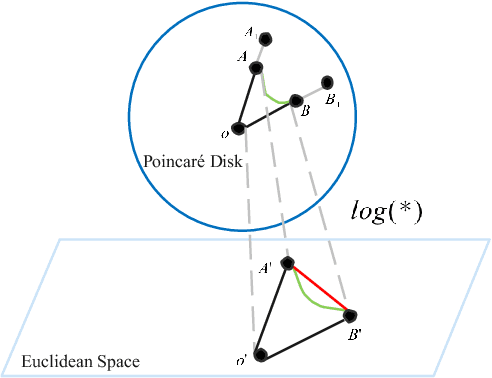
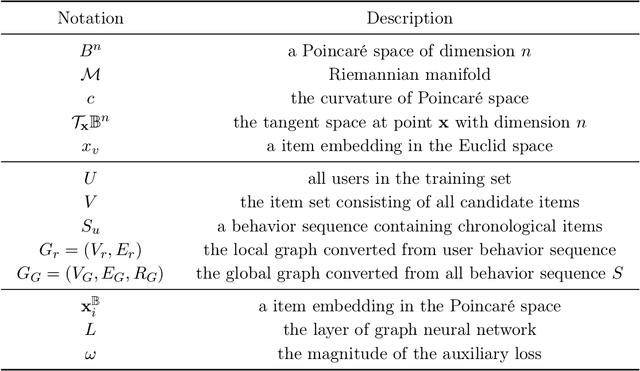
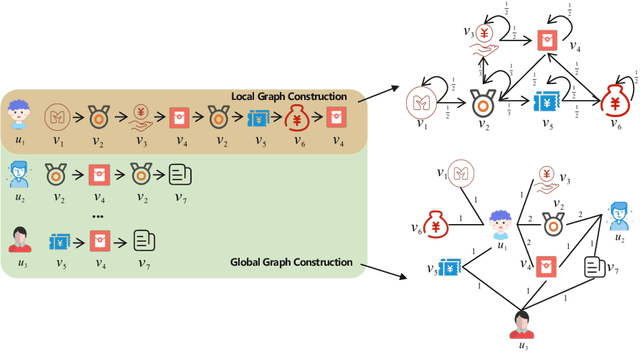
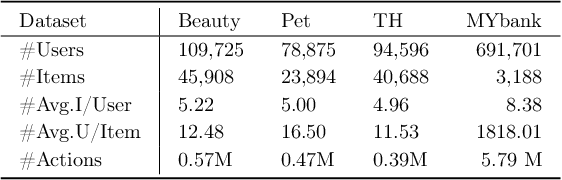
Abstract:Sequential recommendation (SR) learns users' preferences by capturing the sequential patterns from users' behaviors evolution. As discussed in many works, user-item interactions of SR generally present the intrinsic power-law distribution, which can be ascended to hierarchy-like structures. Previous methods usually handle such hierarchical information by making user-item sectionalization empirically under Euclidean space, which may cause distortion of user-item representation in real online scenarios. In this paper, we propose a Poincar\'{e}-based heterogeneous graph neural network named PHGR to model the sequential pattern information as well as hierarchical information contained in the data of SR scenarios simultaneously. Specifically, for the purpose of explicitly capturing the hierarchical information, we first construct a weighted user-item heterogeneous graph by aliening all the user-item interactions to improve the perception domain of each user from a global view. Then the output of the global representation would be used to complement the local directed item-item homogeneous graph convolution. By defining a novel hyperbolic inner product operator, the global and local graph representation learning are directly conducted in Poincar\'{e} ball instead of commonly used projection operation between Poincar\'{e} ball and Euclidean space, which could alleviate the cumulative error issue of general bidirectional translation process. Moreover, for the purpose of explicitly capturing the sequential dependency information, we design two types of temporal attention operations under Poincar\'{e} ball space. Empirical evaluations on datasets from the public and financial industry show that PHGR outperforms several comparison methods.
MHSCNet: A Multimodal Hierarchical Shot-aware Convolutional Network for Video Summarization
Apr 19, 2022



Abstract:Video summarization intends to produce a concise video summary by effectively capturing and combining the most informative parts of the whole content. Existing approaches for video summarization regard the task as a frame-wise keyframe selection problem and generally construct the frame-wise representation by combining the long-range temporal dependency with the unimodal or bimodal information. However, the optimal video summaries need to reflect the most valuable keyframe with its own information, and one with semantic power of the whole content. Thus, it is critical to construct a more powerful and robust frame-wise representation and predict the frame-level importance score in a fair and comprehensive manner. To tackle the above issues, we propose a multimodal hierarchical shot-aware convolutional network, denoted as MHSCNet, to enhance the frame-wise representation via combining the comprehensive available multimodal information. Specifically, we design a hierarchical ShotConv network to incorporate the adaptive shot-aware frame-level representation by considering the short-range and long-range temporal dependency. Based on the learned shot-aware representations, MHSCNet can predict the frame-level importance score in the local and global view of the video. Extensive experiments on two standard video summarization datasets demonstrate that our proposed method consistently outperforms state-of-the-art baselines. Source code will be made publicly available.
HCGR: Hyperbolic Contrastive Graph Representation Learning for Session-based Recommendation
Jul 06, 2021
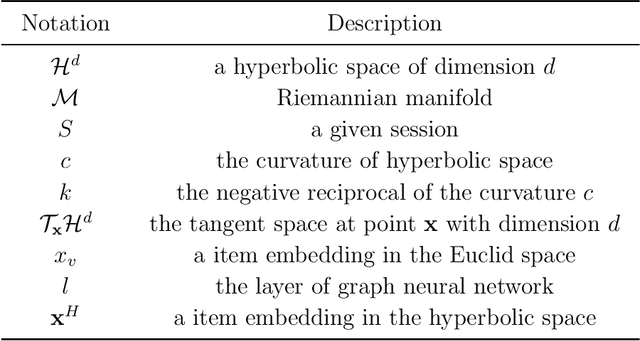
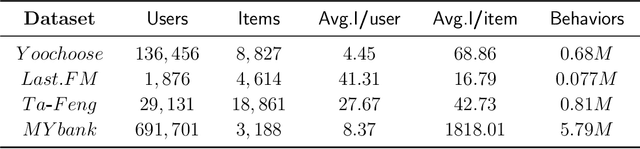
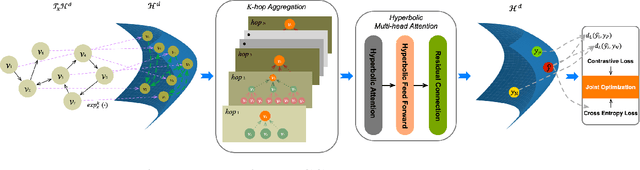
Abstract:Session-based recommendation (SBR) learns users' preferences by capturing the short-term and sequential patterns from the evolution of user behaviors. Among the studies in the SBR field, graph-based approaches are a relatively powerful kind of way, which generally extract item information by message aggregation under Euclidean space. However, such methods can't effectively extract the hierarchical information contained among consecutive items in a session, which is critical to represent users' preferences. In this paper, we present a hyperbolic contrastive graph recommender (HCGR), a principled session-based recommendation framework involving Lorentz hyperbolic space to adequately capture the coherence and hierarchical representations of the items. Within this framework, we design a novel adaptive hyperbolic attention computation to aggregate the graph message of each user's preference in a session-based behavior sequence. In addition, contrastive learning is leveraged to optimize the item representation by considering the geodesic distance between positive and negative samples in hyperbolic space. Extensive experiments on four real-world datasets demonstrate that HCGR consistently outperforms state-of-the-art baselines by 0.43$\%$-28.84$\%$ in terms of $HitRate$, $NDCG$ and $MRR$.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge