Liefeng Bo
University of Washington
iFSQ: Improving FSQ for Image Generation with 1 Line of Code
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:The field of image generation is currently bifurcated into autoregressive (AR) models operating on discrete tokens and diffusion models utilizing continuous latents. This divide, rooted in the distinction between VQ-VAEs and VAEs, hinders unified modeling and fair benchmarking. Finite Scalar Quantization (FSQ) offers a theoretical bridge, yet vanilla FSQ suffers from a critical flaw: its equal-interval quantization can cause activation collapse. This mismatch forces a trade-off between reconstruction fidelity and information efficiency. In this work, we resolve this dilemma by simply replacing the activation function in original FSQ with a distribution-matching mapping to enforce a uniform prior. Termed iFSQ, this simple strategy requires just one line of code yet mathematically guarantees both optimal bin utilization and reconstruction precision. Leveraging iFSQ as a controlled benchmark, we uncover two key insights: (1) The optimal equilibrium between discrete and continuous representations lies at approximately 4 bits per dimension. (2) Under identical reconstruction constraints, AR models exhibit rapid initial convergence, whereas diffusion models achieve a superior performance ceiling, suggesting that strict sequential ordering may limit the upper bounds of generation quality. Finally, we extend our analysis by adapting Representation Alignment (REPA) to AR models, yielding LlamaGen-REPA. Codes is available at https://github.com/Tencent-Hunyuan/iFSQ
ShortFT: Diffusion Model Alignment via Shortcut-based Fine-Tuning
Jul 30, 2025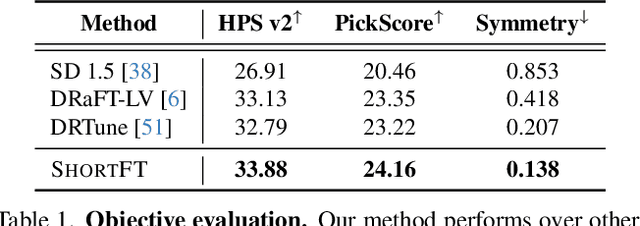
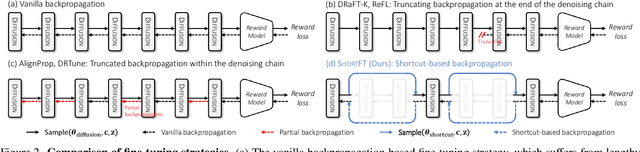


Abstract:Backpropagation-based approaches aim to align diffusion models with reward functions through end-to-end backpropagation of the reward gradient within the denoising chain, offering a promising perspective. However, due to the computational costs and the risk of gradient explosion associated with the lengthy denoising chain, existing approaches struggle to achieve complete gradient backpropagation, leading to suboptimal results. In this paper, we introduce Shortcut-based Fine-Tuning (ShortFT), an efficient fine-tuning strategy that utilizes the shorter denoising chain. More specifically, we employ the recently researched trajectory-preserving few-step diffusion model, which enables a shortcut over the original denoising chain, and construct a shortcut-based denoising chain of shorter length. The optimization on this chain notably enhances the efficiency and effectiveness of fine-tuning the foundational model. Our method has been rigorously tested and can be effectively applied to various reward functions, significantly improving alignment performance and surpassing state-of-the-art alternatives.
Exploring Timeline Control for Facial Motion Generation
May 27, 2025Abstract:This paper introduces a new control signal for facial motion generation: timeline control. Compared to audio and text signals, timelines provide more fine-grained control, such as generating specific facial motions with precise timing. Users can specify a multi-track timeline of facial actions arranged in temporal intervals, allowing precise control over the timing of each action. To model the timeline control capability, We first annotate the time intervals of facial actions in natural facial motion sequences at a frame-level granularity. This process is facilitated by Toeplitz Inverse Covariance-based Clustering to minimize human labor. Based on the annotations, we propose a diffusion-based generation model capable of generating facial motions that are natural and accurately aligned with input timelines. Our method supports text-guided motion generation by using ChatGPT to convert text into timelines. Experimental results show that our method can annotate facial action intervals with satisfactory accuracy, and produces natural facial motions accurately aligned with timelines.
CoGenAV: Versatile Audio-Visual Representation Learning via Contrastive-Generative Synchronization
May 06, 2025Abstract:The inherent synchronization between a speaker's lip movements, voice, and the underlying linguistic content offers a rich source of information for improving speech processing tasks, especially in challenging conditions where traditional audio-only systems falter. We introduce CoGenAV, a powerful and data-efficient model designed to learn versatile audio-visual representations applicable across a wide range of speech and audio-visual tasks. CoGenAV is trained by optimizing a dual objective derived from natural audio-visual synchrony, contrastive feature alignment and generative text prediction, using only 223 hours of labeled data from the LRS2 dataset. This contrastive-generative synchronization strategy effectively captures fundamental cross-modal correlations. We showcase the effectiveness and versatility of the learned CoGenAV representations on multiple benchmarks. When utilized for Audio-Visual Speech Recognition (AVSR) on LRS2, these representations contribute to achieving a state-of-the-art Word Error Rate (WER) of 1.27. They also enable strong performance in Visual Speech Recognition (VSR) with a WER of 22.0 on LRS2, and significantly improve performance in noisy environments by over 70%. Furthermore, CoGenAV representations benefit speech reconstruction tasks, boosting performance in Speech Enhancement and Separation, and achieve competitive results in audio-visual synchronization tasks like Active Speaker Detection (ASD). Our model will be open-sourced to facilitate further development and collaboration within both academia and industry.
MoSAM: Motion-Guided Segment Anything Model with Spatial-Temporal Memory Selection
Apr 30, 2025



Abstract:The recent Segment Anything Model 2 (SAM2) has demonstrated exceptional capabilities in interactive object segmentation for both images and videos. However, as a foundational model on interactive segmentation, SAM2 performs segmentation directly based on mask memory from the past six frames, leading to two significant challenges. Firstly, during inference in videos, objects may disappear since SAM2 relies solely on memory without accounting for object motion information, which limits its long-range object tracking capabilities. Secondly, its memory is constructed from fixed past frames, making it susceptible to challenges associated with object disappearance or occlusion, due to potentially inaccurate segmentation results in memory. To address these problems, we present MoSAM, incorporating two key strategies to integrate object motion cues into the model and establish more reliable feature memory. Firstly, we propose Motion-Guided Prompting (MGP), which represents the object motion in both sparse and dense manners, then injects them into SAM2 through a set of motion-guided prompts. MGP enables the model to adjust its focus towards the direction of motion, thereby enhancing the object tracking capabilities. Furthermore, acknowledging that past segmentation results may be inaccurate, we devise a Spatial-Temporal Memory Selection (ST-MS) mechanism that dynamically identifies frames likely to contain accurate segmentation in both pixel- and frame-level. By eliminating potentially inaccurate mask predictions from memory, we can leverage more reliable memory features to exploit similar regions for improving segmentation results. Extensive experiments on various benchmarks of video object segmentation and video instance segmentation demonstrate that our MoSAM achieves state-of-the-art results compared to other competitors.
EchoMask: Speech-Queried Attention-based Mask Modeling for Holistic Co-Speech Motion Generation
Apr 15, 2025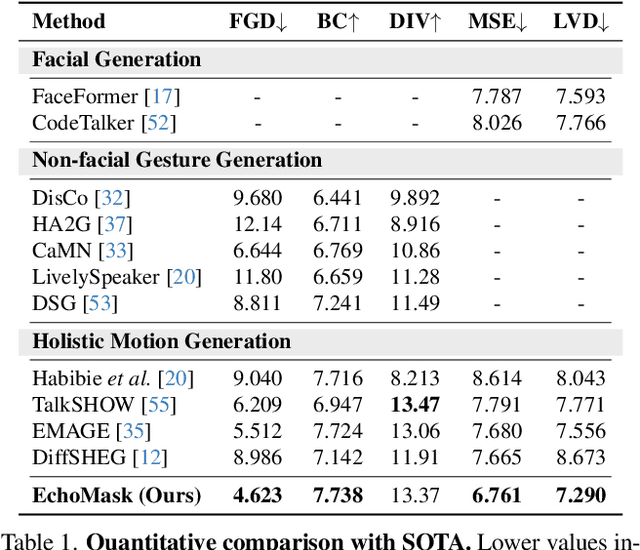
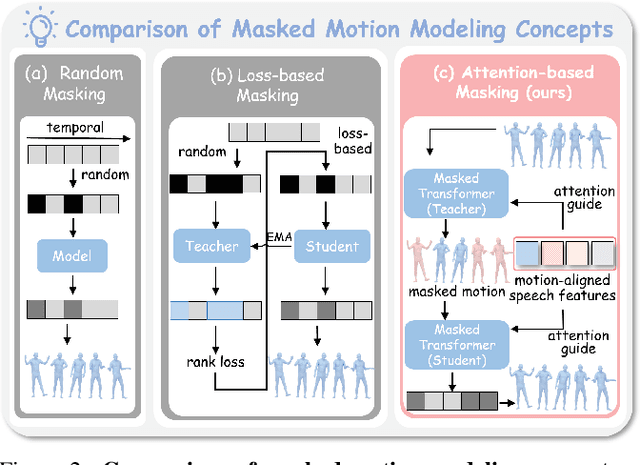
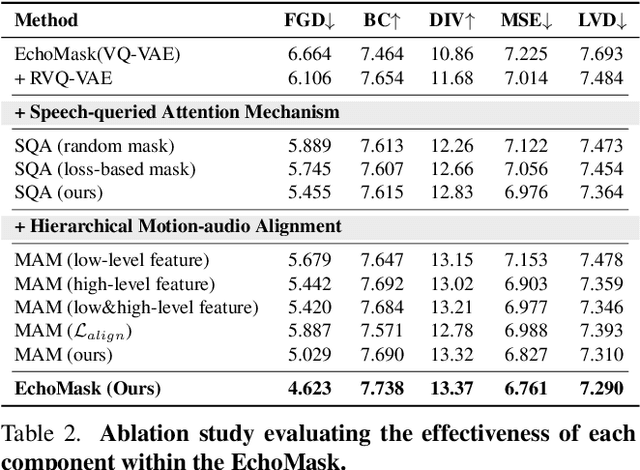
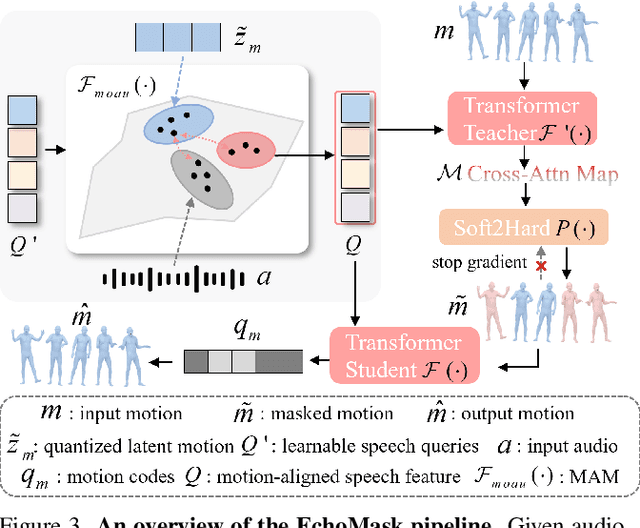
Abstract:Masked modeling framework has shown promise in co-speech motion generation. However, it struggles to identify semantically significant frames for effective motion masking. In this work, we propose a speech-queried attention-based mask modeling framework for co-speech motion generation. Our key insight is to leverage motion-aligned speech features to guide the masked motion modeling process, selectively masking rhythm-related and semantically expressive motion frames. Specifically, we first propose a motion-audio alignment module (MAM) to construct a latent motion-audio joint space. In this space, both low-level and high-level speech features are projected, enabling motion-aligned speech representation using learnable speech queries. Then, a speech-queried attention mechanism (SQA) is introduced to compute frame-level attention scores through interactions between motion keys and speech queries, guiding selective masking toward motion frames with high attention scores. Finally, the motion-aligned speech features are also injected into the generation network to facilitate co-speech motion generation. Qualitative and quantitative evaluations confirm that our method outperforms existing state-of-the-art approaches, successfully producing high-quality co-speech motion.
OmniTalker: Real-Time Text-Driven Talking Head Generation with In-Context Audio-Visual Style Replication
Apr 03, 2025Abstract:Recent years have witnessed remarkable advances in talking head generation, owing to its potential to revolutionize the human-AI interaction from text interfaces into realistic video chats. However, research on text-driven talking heads remains underexplored, with existing methods predominantly adopting a cascaded pipeline that combines TTS systems with audio-driven talking head models. This conventional pipeline not only introduces system complexity and latency overhead but also fundamentally suffers from asynchronous audiovisual output and stylistic discrepancies between generated speech and visual expressions. To address these limitations, we introduce OmniTalker, an end-to-end unified framework that simultaneously generates synchronized speech and talking head videos from text and reference video in real-time zero-shot scenarios, while preserving both speech style and facial styles. The framework employs a dual-branch diffusion transformer architecture: the audio branch synthesizes mel-spectrograms from text, while the visual branch predicts fine-grained head poses and facial dynamics. To bridge modalities, we introduce a novel audio-visual fusion module that integrates cross-modal information to ensure temporal synchronization and stylistic coherence between audio and visual outputs. Furthermore, our in-context reference learning module effectively captures both speech and facial style characteristics from a single reference video without introducing an extra style extracting module. To the best of our knowledge, OmniTalker presents the first unified framework that jointly models speech style and facial style in a zero-shot setting, achieving real-time inference speed of 25 FPS. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method surpasses existing approaches in generation quality, particularly excelling in style preservation and audio-video synchronization.
ChatAnyone: Stylized Real-time Portrait Video Generation with Hierarchical Motion Diffusion Model
Mar 27, 2025Abstract:Real-time interactive video-chat portraits have been increasingly recognized as the future trend, particularly due to the remarkable progress made in text and voice chat technologies. However, existing methods primarily focus on real-time generation of head movements, but struggle to produce synchronized body motions that match these head actions. Additionally, achieving fine-grained control over the speaking style and nuances of facial expressions remains a challenge. To address these limitations, we introduce a novel framework for stylized real-time portrait video generation, enabling expressive and flexible video chat that extends from talking head to upper-body interaction. Our approach consists of the following two stages. The first stage involves efficient hierarchical motion diffusion models, that take both explicit and implicit motion representations into account based on audio inputs, which can generate a diverse range of facial expressions with stylistic control and synchronization between head and body movements. The second stage aims to generate portrait video featuring upper-body movements, including hand gestures. We inject explicit hand control signals into the generator to produce more detailed hand movements, and further perform face refinement to enhance the overall realism and expressiveness of the portrait video. Additionally, our approach supports efficient and continuous generation of upper-body portrait video in maximum 512 * 768 resolution at up to 30fps on 4090 GPU, supporting interactive video-chat in real-time. Experimental results demonstrate the capability of our approach to produce portrait videos with rich expressiveness and natural upper-body movements.
GaussianIP: Identity-Preserving Realistic 3D Human Generation via Human-Centric Diffusion Prior
Mar 14, 2025Abstract:Text-guided 3D human generation has advanced with the development of efficient 3D representations and 2D-lifting methods like Score Distillation Sampling (SDS). However, current methods suffer from prolonged training times and often produce results that lack fine facial and garment details. In this paper, we propose GaussianIP, an effective two-stage framework for generating identity-preserving realistic 3D humans from text and image prompts. Our core insight is to leverage human-centric knowledge to facilitate the generation process. In stage 1, we propose a novel Adaptive Human Distillation Sampling (AHDS) method to rapidly generate a 3D human that maintains high identity consistency with the image prompt and achieves a realistic appearance. Compared to traditional SDS methods, AHDS better aligns with the human-centric generation process, enhancing visual quality with notably fewer training steps. To further improve the visual quality of the face and clothes regions, we design a View-Consistent Refinement (VCR) strategy in stage 2. Specifically, it produces detail-enhanced results of the multi-view images from stage 1 iteratively, ensuring the 3D texture consistency across views via mutual attention and distance-guided attention fusion. Then a polished version of the 3D human can be achieved by directly perform reconstruction with the refined images. Extensive experiments demonstrate that GaussianIP outperforms existing methods in both visual quality and training efficiency, particularly in generating identity-preserving results. Our code is available at: https://github.com/silence-tang/GaussianIP.
LHM: Large Animatable Human Reconstruction Model from a Single Image in Seconds
Mar 13, 2025Abstract:Animatable 3D human reconstruction from a single image is a challenging problem due to the ambiguity in decoupling geometry, appearance, and deformation. Recent advances in 3D human reconstruction mainly focus on static human modeling, and the reliance of using synthetic 3D scans for training limits their generalization ability. Conversely, optimization-based video methods achieve higher fidelity but demand controlled capture conditions and computationally intensive refinement processes. Motivated by the emergence of large reconstruction models for efficient static reconstruction, we propose LHM (Large Animatable Human Reconstruction Model) to infer high-fidelity avatars represented as 3D Gaussian splatting in a feed-forward pass. Our model leverages a multimodal transformer architecture to effectively encode the human body positional features and image features with attention mechanism, enabling detailed preservation of clothing geometry and texture. To further boost the face identity preservation and fine detail recovery, we propose a head feature pyramid encoding scheme to aggregate multi-scale features of the head regions. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our LHM generates plausible animatable human in seconds without post-processing for face and hands, outperforming existing methods in both reconstruction accuracy and generalization ability.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge