Peihao Li
Large Video Planner Enables Generalizable Robot Control
Dec 17, 2025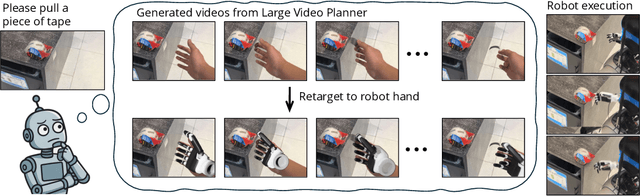
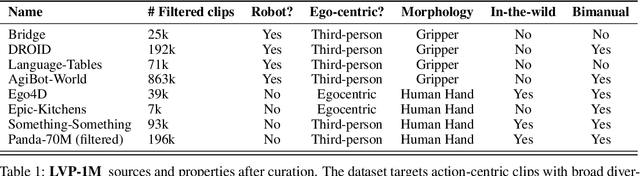
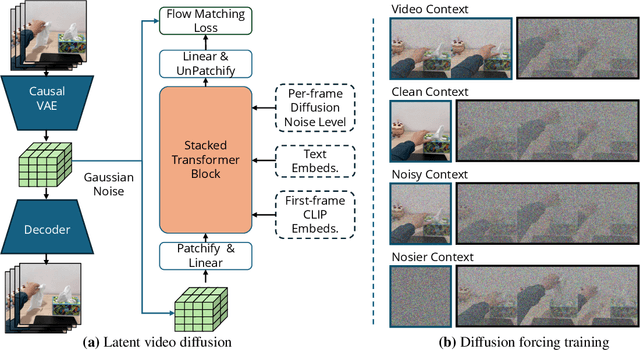
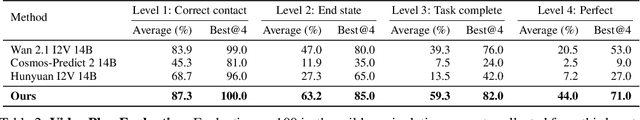
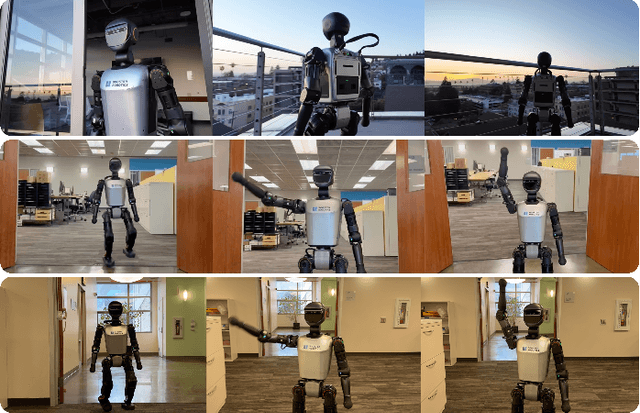
Abstract:General-purpose robots require decision-making models that generalize across diverse tasks and environments. Recent works build robot foundation models by extending multimodal large language models (MLLMs) with action outputs, creating vision-language-action (VLA) systems. These efforts are motivated by the intuition that MLLMs' large-scale language and image pretraining can be effectively transferred to the action output modality. In this work, we explore an alternative paradigm of using large-scale video pretraining as a primary modality for building robot foundation models. Unlike static images and language, videos capture spatio-temporal sequences of states and actions in the physical world that are naturally aligned with robotic behavior. We curate an internet-scale video dataset of human activities and task demonstrations, and train, for the first time at a foundation-model scale, an open video model for generative robotics planning. The model produces zero-shot video plans for novel scenes and tasks, which we post-process to extract executable robot actions. We evaluate task-level generalization through third-party selected tasks in the wild and real-robot experiments, demonstrating successful physical execution. Together, these results show robust instruction following, strong generalization, and real-world feasibility. We release both the model and dataset to support open, reproducible video-based robot learning. Our website is available at https://www.boyuan.space/large-video-planner/.
ViSA: 3D-Aware Video Shading for Real-Time Upper-Body Avatar Creation
Dec 09, 2025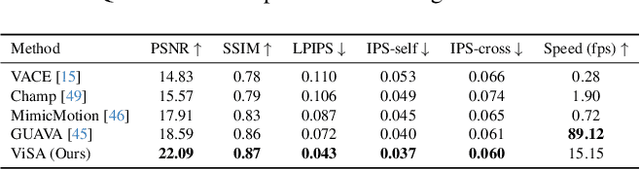
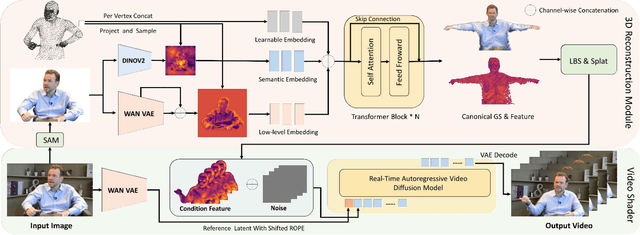
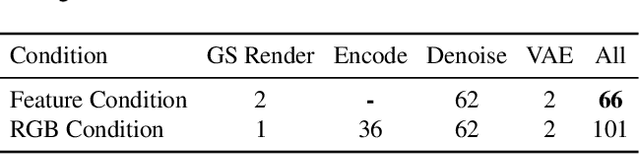
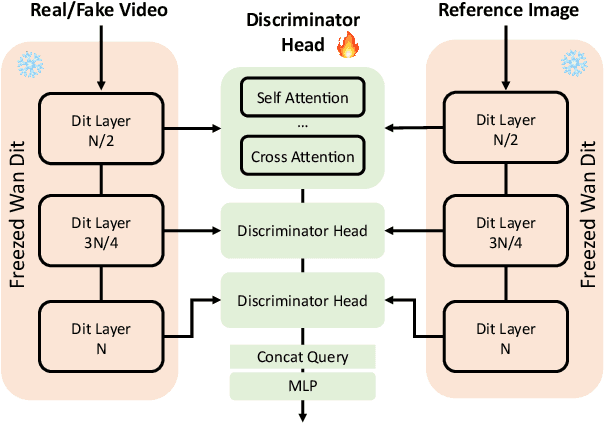
Abstract:Generating high-fidelity upper-body 3D avatars from one-shot input image remains a significant challenge. Current 3D avatar generation methods, which rely on large reconstruction models, are fast and capable of producing stable body structures, but they often suffer from artifacts such as blurry textures and stiff, unnatural motion. In contrast, generative video models show promising performance by synthesizing photorealistic and dynamic results, but they frequently struggle with unstable behavior, including body structural errors and identity drift. To address these limitations, we propose a novel approach that combines the strengths of both paradigms. Our framework employs a 3D reconstruction model to provide robust structural and appearance priors, which in turn guides a real-time autoregressive video diffusion model for rendering. This process enables the model to synthesize high-frequency, photorealistic details and fluid dynamics in real time, effectively reducing texture blur and motion stiffness while preventing the structural inconsistencies common in video generation methods. By uniting the geometric stability of 3D reconstruction with the generative capabilities of video models, our method produces high-fidelity digital avatars with realistic appearance and dynamic, temporally coherent motion. Experiments demonstrate that our approach significantly reduces artifacts and achieves substantial improvements in visual quality over leading methods, providing a robust and efficient solution for real-time applications such as gaming and virtual reality. Project page: https://lhyfst.github.io/visa
PF-LHM: 3D Animatable Avatar Reconstruction from Pose-free Articulated Human Images
Jun 16, 2025Abstract:Reconstructing an animatable 3D human from casually captured images of an articulated subject without camera or human pose information is a practical yet challenging task due to view misalignment, occlusions, and the absence of structural priors. While optimization-based methods can produce high-fidelity results from monocular or multi-view videos, they require accurate pose estimation and slow iterative optimization, limiting scalability in unconstrained scenarios. Recent feed-forward approaches enable efficient single-image reconstruction but struggle to effectively leverage multiple input images to reduce ambiguity and improve reconstruction accuracy. To address these challenges, we propose PF-LHM, a large human reconstruction model that generates high-quality 3D avatars in seconds from one or multiple casually captured pose-free images. Our approach introduces an efficient Encoder-Decoder Point-Image Transformer architecture, which fuses hierarchical geometric point features and multi-view image features through multimodal attention. The fused features are decoded to recover detailed geometry and appearance, represented using 3D Gaussian splats. Extensive experiments on both real and synthetic datasets demonstrate that our method unifies single- and multi-image 3D human reconstruction, achieving high-fidelity and animatable 3D human avatars without requiring camera and human pose annotations. Code and models will be released to the public.
NOVA3D: Normal Aligned Video Diffusion Model for Single Image to 3D Generation
Jun 09, 2025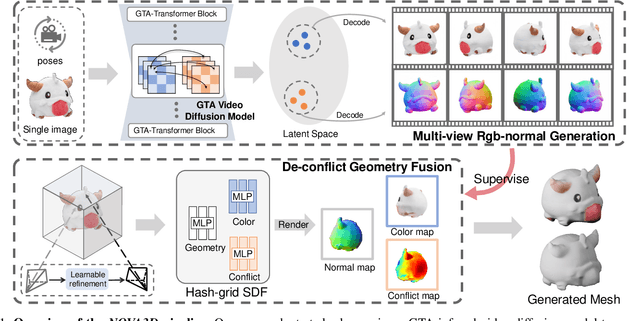
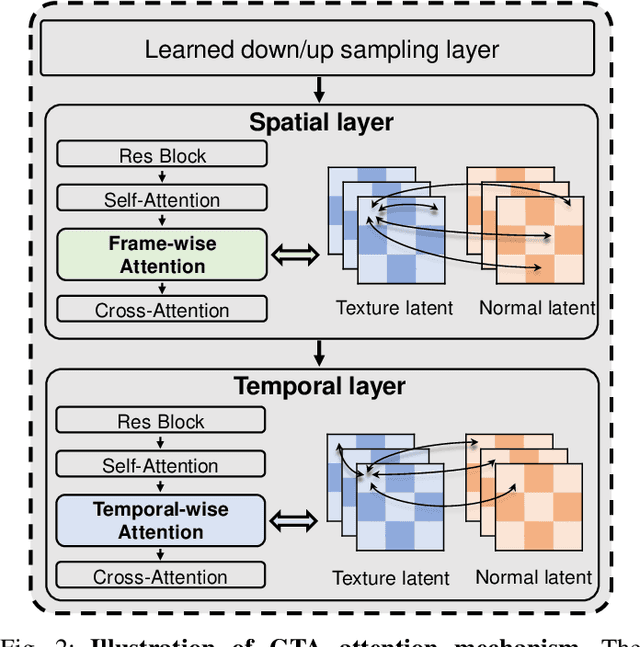


Abstract:3D AI-generated content (AIGC) has made it increasingly accessible for anyone to become a 3D content creator. While recent methods leverage Score Distillation Sampling to distill 3D objects from pretrained image diffusion models, they often suffer from inadequate 3D priors, leading to insufficient multi-view consistency. In this work, we introduce NOVA3D, an innovative single-image-to-3D generation framework. Our key insight lies in leveraging strong 3D priors from a pretrained video diffusion model and integrating geometric information during multi-view video fine-tuning. To facilitate information exchange between color and geometric domains, we propose the Geometry-Temporal Alignment (GTA) attention mechanism, thereby improving generalization and multi-view consistency. Moreover, we introduce the de-conflict geometry fusion algorithm, which improves texture fidelity by addressing multi-view inaccuracies and resolving discrepancies in pose alignment. Extensive experiments validate the superiority of NOVA3D over existing baselines.
AlphaOne: Reasoning Models Thinking Slow and Fast at Test Time
May 30, 2025Abstract:This paper presents AlphaOne ($\alpha$1), a universal framework for modulating reasoning progress in large reasoning models (LRMs) at test time. $\alpha$1 first introduces $\alpha$ moment, which represents the scaled thinking phase with a universal parameter $\alpha$. Within this scaled pre-$\alpha$ moment phase, it dynamically schedules slow thinking transitions by modeling the insertion of reasoning transition tokens as a Bernoulli stochastic process. After the $\alpha$ moment, $\alpha$1 deterministically terminates slow thinking with the end-of-thinking token, thereby fostering fast reasoning and efficient answer generation. This approach unifies and generalizes existing monotonic scaling methods by enabling flexible and dense slow-to-fast reasoning modulation. Extensive empirical studies on various challenging benchmarks across mathematical, coding, and scientific domains demonstrate $\alpha$1's superior reasoning capability and efficiency. Project page: https://alphaone-project.github.io/
RoboVerse: Towards a Unified Platform, Dataset and Benchmark for Scalable and Generalizable Robot Learning
Apr 26, 2025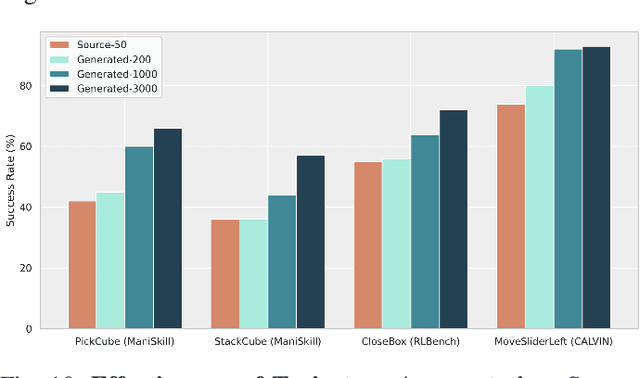
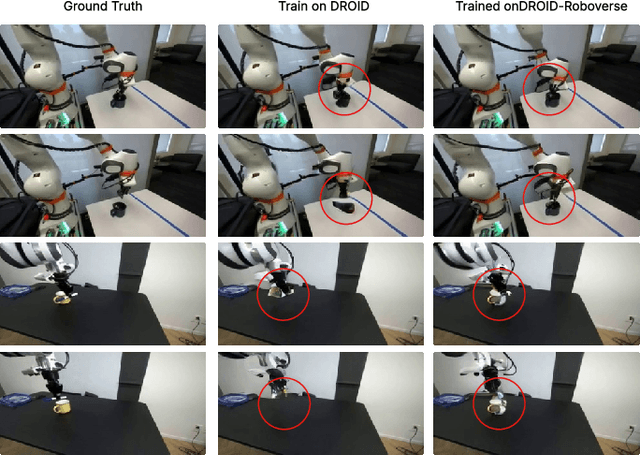

Abstract:Data scaling and standardized evaluation benchmarks have driven significant advances in natural language processing and computer vision. However, robotics faces unique challenges in scaling data and establishing evaluation protocols. Collecting real-world data is resource-intensive and inefficient, while benchmarking in real-world scenarios remains highly complex. Synthetic data and simulation offer promising alternatives, yet existing efforts often fall short in data quality, diversity, and benchmark standardization. To address these challenges, we introduce RoboVerse, a comprehensive framework comprising a simulation platform, a synthetic dataset, and unified benchmarks. Our simulation platform supports multiple simulators and robotic embodiments, enabling seamless transitions between different environments. The synthetic dataset, featuring high-fidelity physics and photorealistic rendering, is constructed through multiple approaches. Additionally, we propose unified benchmarks for imitation learning and reinforcement learning, enabling evaluation across different levels of generalization. At the core of the simulation platform is MetaSim, an infrastructure that abstracts diverse simulation environments into a universal interface. It restructures existing simulation environments into a simulator-agnostic configuration system, as well as an API aligning different simulator functionalities, such as launching simulation environments, loading assets with initial states, stepping the physics engine, etc. This abstraction ensures interoperability and extensibility. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate that RoboVerse enhances the performance of imitation learning, reinforcement learning, world model learning, and sim-to-real transfer. These results validate the reliability of our dataset and benchmarks, establishing RoboVerse as a robust solution for advancing robot learning.
LHM: Large Animatable Human Reconstruction Model from a Single Image in Seconds
Mar 13, 2025Abstract:Animatable 3D human reconstruction from a single image is a challenging problem due to the ambiguity in decoupling geometry, appearance, and deformation. Recent advances in 3D human reconstruction mainly focus on static human modeling, and the reliance of using synthetic 3D scans for training limits their generalization ability. Conversely, optimization-based video methods achieve higher fidelity but demand controlled capture conditions and computationally intensive refinement processes. Motivated by the emergence of large reconstruction models for efficient static reconstruction, we propose LHM (Large Animatable Human Reconstruction Model) to infer high-fidelity avatars represented as 3D Gaussian splatting in a feed-forward pass. Our model leverages a multimodal transformer architecture to effectively encode the human body positional features and image features with attention mechanism, enabling detailed preservation of clothing geometry and texture. To further boost the face identity preservation and fine detail recovery, we propose a head feature pyramid encoding scheme to aggregate multi-scale features of the head regions. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our LHM generates plausible animatable human in seconds without post-processing for face and hands, outperforming existing methods in both reconstruction accuracy and generalization ability.
SLGaussian: Fast Language Gaussian Splatting in Sparse Views
Dec 11, 2024Abstract:3D semantic field learning is crucial for applications like autonomous navigation, AR/VR, and robotics, where accurate comprehension of 3D scenes from limited viewpoints is essential. Existing methods struggle under sparse view conditions, relying on inefficient per-scene multi-view optimizations, which are impractical for many real-world tasks. To address this, we propose SLGaussian, a feed-forward method for constructing 3D semantic fields from sparse viewpoints, allowing direct inference of 3DGS-based scenes. By ensuring consistent SAM segmentations through video tracking and using low-dimensional indexing for high-dimensional CLIP features, SLGaussian efficiently embeds language information in 3D space, offering a robust solution for accurate 3D scene understanding under sparse view conditions. In experiments on two-view sparse 3D object querying and segmentation in the LERF and 3D-OVS datasets, SLGaussian outperforms existing methods in chosen IoU, Localization Accuracy, and mIoU. Moreover, our model achieves scene inference in under 30 seconds and open-vocabulary querying in just 0.011 seconds per query.
A Novel Access Control and Privacy-Enhancing Approach for Models in Edge Computing
Nov 06, 2024Abstract:With the widespread adoption of edge computing technologies and the increasing prevalence of deep learning models in these environments, the security risks and privacy threats to models and data have grown more acute. Attackers can exploit various techniques to illegally obtain models or misuse data, leading to serious issues such as intellectual property infringement and privacy breaches. Existing model access control technologies primarily rely on traditional encryption and authentication methods; however, these approaches exhibit significant limitations in terms of flexibility and adaptability in dynamic environments. Although there have been advancements in model watermarking techniques for marking model ownership, they remain limited in their ability to proactively protect intellectual property and prevent unauthorized access. To address these challenges, we propose a novel model access control method tailored for edge computing environments. This method leverages image style as a licensing mechanism, embedding style recognition into the model's operational framework to enable intrinsic access control. Consequently, models deployed on edge platforms are designed to correctly infer only on license data with specific style, rendering them ineffective on any other data. By restricting the input data to the edge model, this approach not only prevents attackers from gaining unauthorized access to the model but also enhances the privacy of data on terminal devices. We conducted extensive experiments on benchmark datasets, including MNIST, CIFAR-10, and FACESCRUB, and the results demonstrate that our method effectively prevents unauthorized access to the model while maintaining accuracy. Additionally, the model shows strong resistance against attacks such as forged licenses and fine-tuning. These results underscore the method's usability, security, and robustness.
Gaussian in the Wild: 3D Gaussian Splatting for Unconstrained Image Collections
Mar 23, 2024Abstract:Novel view synthesis from unconstrained in-the-wild images remains a meaningful but challenging task. The photometric variation and transient occluders in those unconstrained images make it difficult to reconstruct the original scene accurately. Previous approaches tackle the problem by introducing a global appearance feature in Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF). However, in the real world, the unique appearance of each tiny point in a scene is determined by its independent intrinsic material attributes and the varying environmental impacts it receives. Inspired by this fact, we propose Gaussian in the wild (GS-W), a method that uses 3D Gaussian points to reconstruct the scene and introduces separated intrinsic and dynamic appearance feature for each point, capturing the unchanged scene appearance along with dynamic variation like illumination and weather. Additionally, an adaptive sampling strategy is presented to allow each Gaussian point to focus on the local and detailed information more effectively. We also reduce the impact of transient occluders using a 2D visibility map. More experiments have demonstrated better reconstruction quality and details of GS-W compared to previous methods, with a $1000\times$ increase in rendering speed.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge