Bin Qin
All-in-One Image Restoration via Causal-Deconfounding Wavelet-Disentangled Prompt Network
Mar 04, 2026Abstract:Image restoration represents a promising approach for addressing the inherent defects of image content distortion. Standard image restoration approaches suffer from high storage cost and the requirement towards the known degradation pattern, including type and degree, which can barely be satisfied in dynamic practical scenarios. In contrast, all-in-one image restoration (AiOIR) eliminates multiple degradations within a unified model to circumvent the aforementioned issues. However, according to our causal analysis, we disclose that two significant defects still exacerbate the effectiveness and generalization of AiOIR models: 1) the spurious correlation between non-degradation semantic features and degradation patterns; 2) the biased estimation of degradation patterns. To obtain the true causation between degraded images and restored images, we propose Causal-deconfounding Wavelet-disentangled Prompt Network (CWP-Net) to perform effective AiOIR. CWP-Net introduces two modules for decoupling, i.e., wavelet attention module of encoder and wavelet attention module of decoder. These modules explicitly disentangle the degradation and semantic features to tackle the issue of spurious correlation. To address the issue stemming from the biased estimation of degradation patterns, CWP-Net leverages a wavelet prompt block to generate the alternative variable for causal deconfounding. Extensive experiments on two all-in-one settings prove the effectiveness and superior performance of our proposed CWP-Net over the state-of-the-art AiOIR methods.
OneVision-Encoder: Codec-Aligned Sparsity as a Foundational Principle for Multimodal Intelligence
Feb 09, 2026Abstract:Hypothesis. Artificial general intelligence is, at its core, a compression problem. Effective compression demands resonance: deep learning scales best when its architecture aligns with the fundamental structure of the data. These are the fundamental principles. Yet, modern vision architectures have strayed from these truths: visual signals are highly redundant, while discriminative information, the surprise, is sparse. Current models process dense pixel grids uniformly, wasting vast compute on static background rather than focusing on the predictive residuals that define motion and meaning. We argue that to solve visual understanding, we must align our architectures with the information-theoretic principles of video, i.e., Codecs. Method. OneVision-Encoder encodes video by compressing predictive visual structure into semantic meaning. By adopting Codec Patchification, OV-Encoder abandons uniform computation to focus exclusively on the 3.1%-25% of regions rich in signal entropy. To unify spatial and temporal reasoning under irregular token layouts, OneVision-Encoder employs a shared 3D RoPE and is trained with a large-scale cluster discrimination objective over more than one million semantic concepts, jointly capturing object permanence and motion dynamics. Evidence. The results validate our core hypothesis: efficiency and accuracy are not a trade-off; they are positively correlated. When integrated into LLM, it consistently outperforms strong vision backbones such as Qwen3-ViT and SigLIP2 across 16 image, video, and document understanding benchmarks, despite using substantially fewer visual tokens and pretraining data. Notably, on video understanding tasks, OV-Encoder achieves an average improvement of 4.1% over Qwen3-ViT. Codec-aligned, patch-level sparsity is a foundational principle, enabling OV-Encoder as a scalable engine for next-generation visual generalists.
GAIA: A Data Flywheel System for Training GUI Test-Time Scaling Critic Models
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:While Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) have significantly advanced GUI agents' capabilities in parsing textual instructions, interpreting screen content, and executing tasks, a critical challenge persists: the irreversibility of agent operations, where a single erroneous action can trigger catastrophic deviations. To address this, we propose the GUI Action Critic's Data Flywheel System (GAIA), a training framework that enables the models to have iterative critic capabilities, which are used to improve the Test-Time Scaling (TTS) of basic GUI agents' performance. Specifically, we train an Intuitive Critic Model (ICM) using positive and negative action examples from a base agent first. This critic evaluates the immediate correctness of the agent's intended actions, thereby selecting operations with higher success probability. Then, the initial critic guides agent actions to collect refined positive/negative samples, initiating the self-improving cycle. The augmented data then trains a second-round critic with enhanced discernment capability. We conduct experiments on various datasets and demonstrate that the proposed ICM can improve the test-time performance of various closed-source and open-source models, and the performance can be gradually improved as the data is recycled. The code and dataset will be publicly released.
DanQing: An Up-to-Date Large-Scale Chinese Vision-Language Pre-training Dataset
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:Vision-Language Pre-training (VLP) models demonstrate strong performance across various downstream tasks by learning from large-scale image-text pairs through contrastive pretraining. The release of extensive English image-text datasets (e.g., COYO-700M and LAION-400M) has enabled widespread adoption of models such as CLIP and SigLIP in tasks including cross-modal retrieval and image captioning. However, the advancement of Chinese vision-language pretraining has substantially lagged behind, due to the scarcity of high-quality Chinese image-text data. To address this gap, we develop a comprehensive pipeline for constructing a high-quality Chinese cross-modal dataset. As a result, we propose DanQing, which contains 100 million image-text pairs collected from Common Crawl. Different from existing datasets, DanQing is curated through a more rigorous selection process, yielding superior data quality. Moreover, DanQing is primarily built from 2024-2025 web data, enabling models to better capture evolving semantic trends and thus offering greater practical utility. We compare DanQing with existing datasets by continual pre-training of the SigLIP2 model. Experimental results show that DanQing consistently achieves superior performance across a range of Chinese downstream tasks, including zero-shot classification, cross-modal retrieval, and LMM-based evaluations. To facilitate further research in Chinese vision-language pre-training, we will open-source the DanQing dataset under the Creative Common CC-BY 4.0 license.
MCGA: A Multi-task Classical Chinese Literary Genre Audio Corpus
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:With the rapid advancement of Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs), their potential has garnered significant attention in Chinese Classical Studies (CCS). While existing research has primarily focused on text and visual modalities, the audio corpus within this domain remains largely underexplored. To bridge this gap, we propose the Multi-task Classical Chinese Literary Genre Audio Corpus (MCGA). It encompasses a diverse range of literary genres across six tasks: Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR), Speech-to-Text Translation (S2TT), Speech Emotion Captioning (SEC), Spoken Question Answering (SQA), Speech Understanding (SU), and Speech Reasoning (SR). Through the evaluation of ten MLLMs, our experimental results demonstrate that current models still face substantial challenges when processed on the MCGA test set. Furthermore, we introduce an evaluation metric for SEC and a metric to measure the consistency between the speech and text capabilities of MLLMs. We release MCGA and our code to the public to facilitate the development of MLLMs with more robust multidimensional audio capabilities in CCS. MCGA Corpus: https://github.com/yxduir/MCGA
IMSE: Efficient U-Net-based Speech Enhancement using Inception Depthwise Convolution and Amplitude-Aware Linear Attention
Nov 18, 2025Abstract:Achieving a balance between lightweight design and high performance remains a significant challenge for speech enhancement (SE) tasks on resource-constrained devices. Existing state-of-the-art methods, such as MUSE, have established a strong baseline with only 0.51M parameters by introducing a Multi-path Enhanced Taylor (MET) transformer and Deformable Embedding (DE). However, an in-depth analysis reveals that MUSE still suffers from efficiency bottlenecks: the MET module relies on a complex "approximate-compensate" mechanism to mitigate the limitations of Taylor-expansion-based attention, while the offset calculation for deformable embedding introduces additional computational burden. This paper proposes IMSE, a systematically optimized and ultra-lightweight network. We introduce two core innovations: 1) Replacing the MET module with Amplitude-Aware Linear Attention (MALA). MALA fundamentally rectifies the "amplitude-ignoring" problem in linear attention by explicitly preserving the norm information of query vectors in the attention calculation, achieving efficient global modeling without an auxiliary compensation branch. 2) Replacing the DE module with Inception Depthwise Convolution (IDConv). IDConv borrows the Inception concept, decomposing large-kernel operations into efficient parallel branches (square, horizontal, and vertical strips), thereby capturing spectrogram features with extremely low parameter redundancy. Extensive experiments on the VoiceBank+DEMAND dataset demonstrate that, compared to the MUSE baseline, IMSE significantly reduces the parameter count by 16.8\% (from 0.513M to 0.427M) while achieving competitive performance comparable to the state-of-the-art on the PESQ metric (3.373). This study sets a new benchmark for the trade-off between model size and speech quality in ultra-lightweight speech enhancement.
DevPiolt: Operation Recommendation for IoT Devices at Xiaomi Home
Nov 18, 2025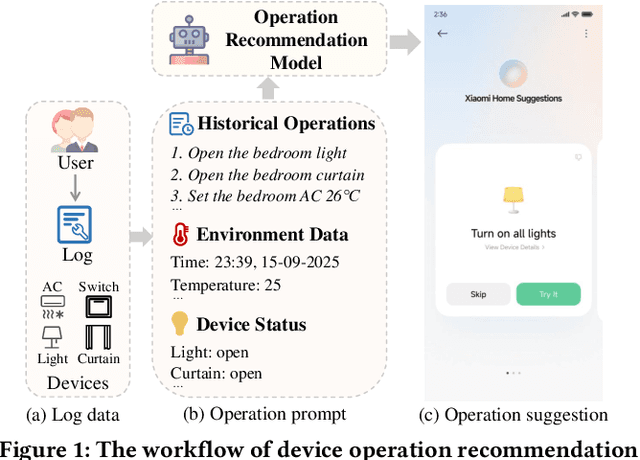
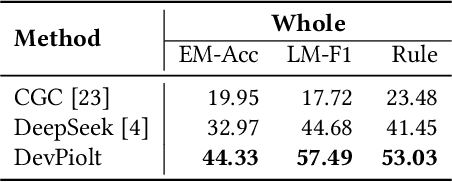
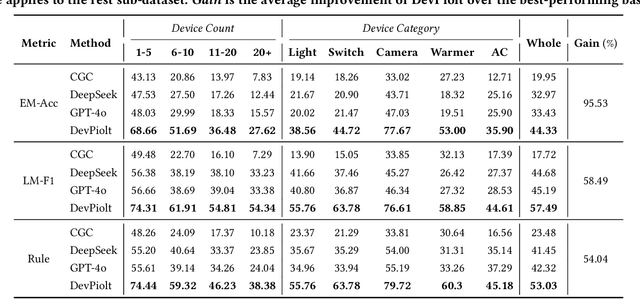
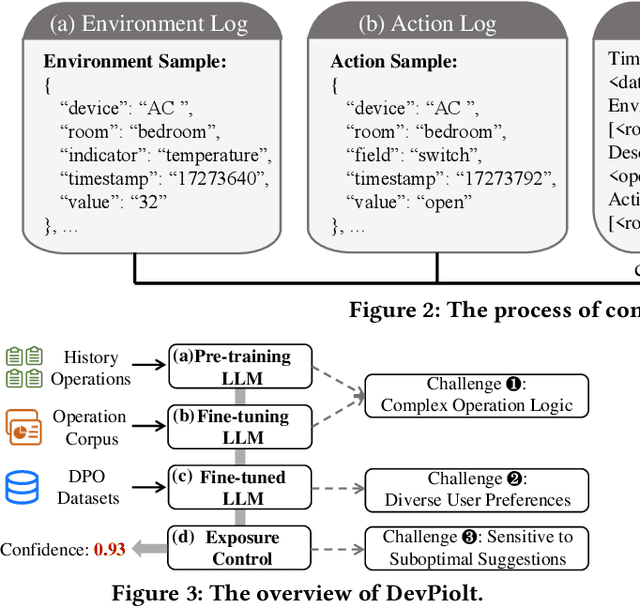
Abstract:Operation recommendation for IoT devices refers to generating personalized device operations for users based on their context, such as historical operations, environment information, and device status. This task is crucial for enhancing user satisfaction and corporate profits. Existing recommendation models struggle with complex operation logic, diverse user preferences, and sensitive to suboptimal suggestions, limiting their applicability to IoT device operations. To address these issues, we propose DevPiolt, a LLM-based recommendation model for IoT device operations. Specifically, we first equip the LLM with fundamental domain knowledge of IoT operations via continual pre-training and multi-task fine-tuning. Then, we employ direct preference optimization to align the fine-tuned LLM with specific user preferences. Finally, we design a confidence-based exposure control mechanism to avoid negative user experiences from low-quality recommendations. Extensive experiments show that DevPiolt significantly outperforms baselines on all datasets, with an average improvement of 69.5% across all metrics. DevPiolt has been practically deployed in Xiaomi Home app for one quarter, providing daily operation recommendations to 255,000 users. Online experiment results indicate a 21.6% increase in unique visitor device coverage and a 29.1% increase in page view acceptance rates.
HyperClick: Advancing Reliable GUI Grounding via Uncertainty Calibration
Oct 31, 2025Abstract:Autonomous Graphical User Interface (GUI) agents rely on accurate GUI grounding, which maps language instructions to on-screen coordinates, to execute user commands. However, current models, whether trained via supervised fine-tuning (SFT) or reinforcement fine-tuning (RFT), lack self-awareness of their capability boundaries, leading to overconfidence and unreliable predictions. We first systematically evaluate probabilistic and verbalized confidence in general and GUI-specific models, revealing a misalignment between confidence and actual accuracy, which is particularly critical in dynamic GUI automation tasks, where single errors can cause task failure. To address this, we propose HyperClick, a novel framework that enhances reliable GUI grounding through uncertainty calibration. HyperClick introduces a dual reward mechanism, combining a binary reward for correct actions with a truncated Gaussian-based spatial confidence modeling, calibrated using the Brier score. This approach jointly optimizes grounding accuracy and confidence reliability, fostering introspective self-criticism. Extensive experiments on seven challenge benchmarks show that HyperClick achieves state-of-the-art performance while providing well-calibrated confidence. By enabling explicit confidence calibration and introspective self-criticism, HyperClick reduces overconfidence and supports more reliable GUI automation.
ACPO: Adaptive Curriculum Policy Optimization for Aligning Vision-Language Models in Complex Reasoning
Oct 01, 2025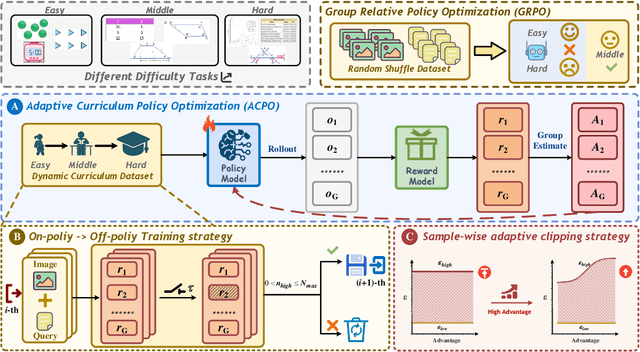
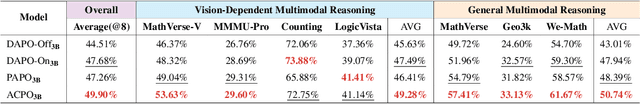
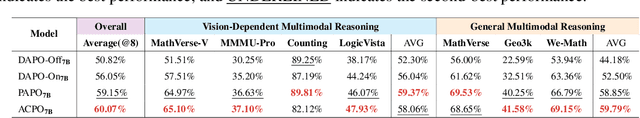
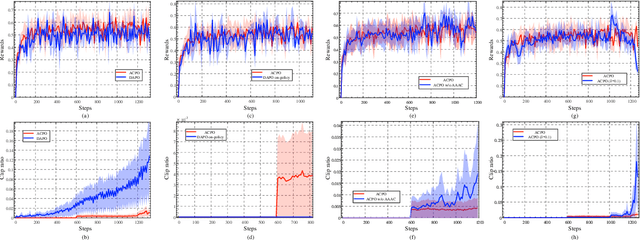
Abstract:Aligning large-scale vision-language models (VLMs) for complex reasoning via reinforcement learning is often hampered by the limitations of existing policy optimization algorithms, such as static training schedules and the rigid, uniform clipping mechanism in Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO). In this work, we introduce Adaptive Curriculum Policy Optimization (ACPO), a novel framework that addresses these challenges through a dual-component adaptive learning strategy. First, ACPO employs a dynamic curriculum that orchestrates a principled transition from a stable, near on-policy exploration phase to an efficient, off-policy exploitation phase by progressively increasing sample reuse. Second, we propose an Advantage-Aware Adaptive Clipping (AAAC) mechanism that replaces the fixed clipping hyperparameter with dynamic, sample-wise bounds modulated by the normalized advantage of each token. This allows for more granular and robust policy updates, enabling larger gradients for high-potential samples while safeguarding against destructive ones. We conduct extensive experiments on a suite of challenging multimodal reasoning benchmarks, including MathVista, LogicVista, and MMMU-Pro. Results demonstrate that ACPO consistently outperforms strong baselines such as DAPO and PAPO, achieving state-of-the-art performance, accelerated convergence, and superior training stability.
BTL-UI: Blink-Think-Link Reasoning Model for GUI Agent
Sep 19, 2025Abstract:In the field of AI-driven human-GUI interaction automation, while rapid advances in multimodal large language models and reinforcement fine-tuning techniques have yielded remarkable progress, a fundamental challenge persists: their interaction logic significantly deviates from natural human-GUI communication patterns. To fill this gap, we propose "Blink-Think-Link" (BTL), a brain-inspired framework for human-GUI interaction that mimics the human cognitive process between users and graphical interfaces. The system decomposes interactions into three biologically plausible phases: (1) Blink - rapid detection and attention to relevant screen areas, analogous to saccadic eye movements; (2) Think - higher-level reasoning and decision-making, mirroring cognitive planning; and (3) Link - generation of executable commands for precise motor control, emulating human action selection mechanisms. Additionally, we introduce two key technical innovations for the BTL framework: (1) Blink Data Generation - an automated annotation pipeline specifically optimized for blink data, and (2) BTL Reward -- the first rule-based reward mechanism that enables reinforcement learning driven by both process and outcome. Building upon this framework, we develop a GUI agent model named BTL-UI, which demonstrates consistent state-of-the-art performance across both static GUI understanding and dynamic interaction tasks in comprehensive benchmarks. These results provide conclusive empirical validation of the framework's efficacy in developing advanced GUI Agents.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge