Junnan Wu
Lightweight speech enhancement guided target speech extraction in noisy multi-speaker scenarios
Aug 27, 2025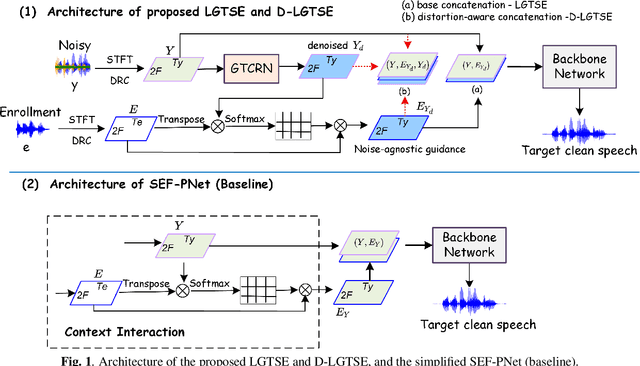
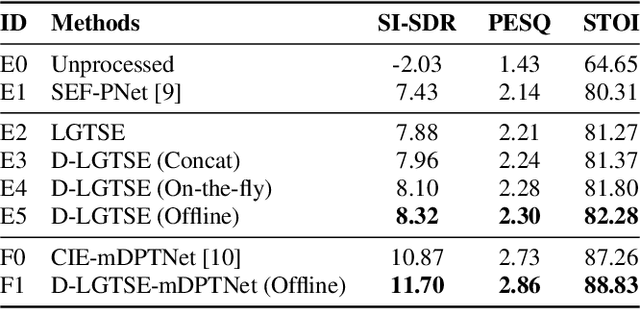
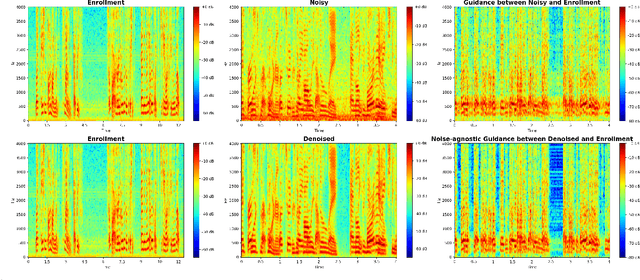
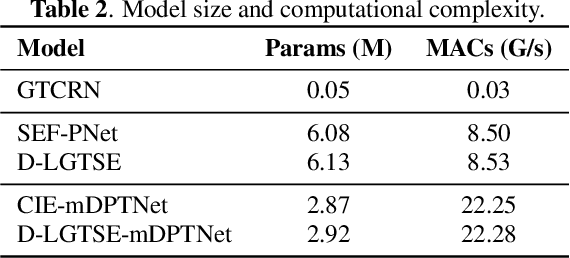
Abstract:Target speech extraction (TSE) has achieved strong performance in relatively simple conditions such as one-speaker-plus-noise and two-speaker mixtures, but its performance remains unsatisfactory in noisy multi-speaker scenarios. To address this issue, we introduce a lightweight speech enhancement model, GTCRN, to better guide TSE in noisy environments. Building on our competitive previous speaker embedding/encoder-free framework SEF-PNet, we propose two extensions: LGTSE and D-LGTSE. LGTSE incorporates noise-agnostic enrollment guidance by denoising the input noisy speech before context interaction with enrollment speech, thereby reducing noise interference. D-LGTSE further improves system robustness against speech distortion by leveraging denoised speech as an additional noisy input during training, expanding the dynamic range of noisy conditions and enabling the model to directly learn from distorted signals. Furthermore, we propose a two-stage training strategy, first with GTCRN enhancement-guided pre-training and then joint fine-tuning, to fully exploit model potential.Experiments on the Libri2Mix dataset demonstrate significant improvements of 0.89 dB in SISDR, 0.16 in PESQ, and 1.97% in STOI, validating the effectiveness of our approach. Our code is publicly available at https://github.com/isHuangZiling/D-LGTSE.
The Tenth NTIRE 2025 Efficient Super-Resolution Challenge Report
Apr 14, 2025Abstract:This paper presents a comprehensive review of the NTIRE 2025 Challenge on Single-Image Efficient Super-Resolution (ESR). The challenge aimed to advance the development of deep models that optimize key computational metrics, i.e., runtime, parameters, and FLOPs, while achieving a PSNR of at least 26.90 dB on the $\operatorname{DIV2K\_LSDIR\_valid}$ dataset and 26.99 dB on the $\operatorname{DIV2K\_LSDIR\_test}$ dataset. A robust participation saw \textbf{244} registered entrants, with \textbf{43} teams submitting valid entries. This report meticulously analyzes these methods and results, emphasizing groundbreaking advancements in state-of-the-art single-image ESR techniques. The analysis highlights innovative approaches and establishes benchmarks for future research in the field.
Enhanced Neural Beamformer with Spatial Information for Target Speech Extraction
Jun 28, 2023Abstract:Recently, deep learning-based beamforming algorithms have shown promising performance in target speech extraction tasks. However, most systems do not fully utilize spatial information. In this paper, we propose a target speech extraction network that utilizes spatial information to enhance the performance of neural beamformer. To achieve this, we first use the UNet-TCN structure to model input features and improve the estimation accuracy of the speech pre-separation module by avoiding information loss caused by direct dimensionality reduction in other models. Furthermore, we introduce a multi-head cross-attention mechanism that enhances the neural beamformer's perception of spatial information by making full use of the spatial information received by the array. Experimental results demonstrate that our approach, which incorporates a more reasonable target mask estimation network and a spatial information-based cross-attention mechanism into the neural beamformer, effectively improves speech separation performance.
Multi-channel Speech Enhancement with 2-D Convolutional Time-frequency Domain Features and a Pre-trained Acoustic Model
Jul 26, 2021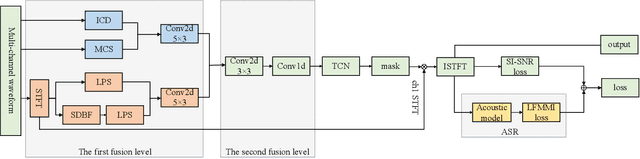
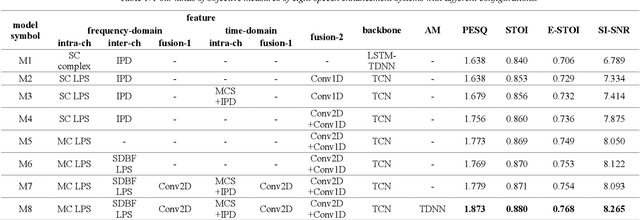
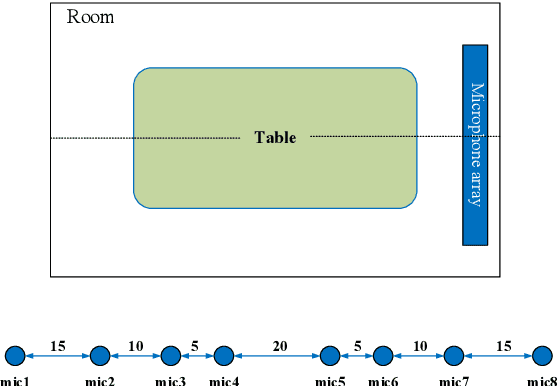
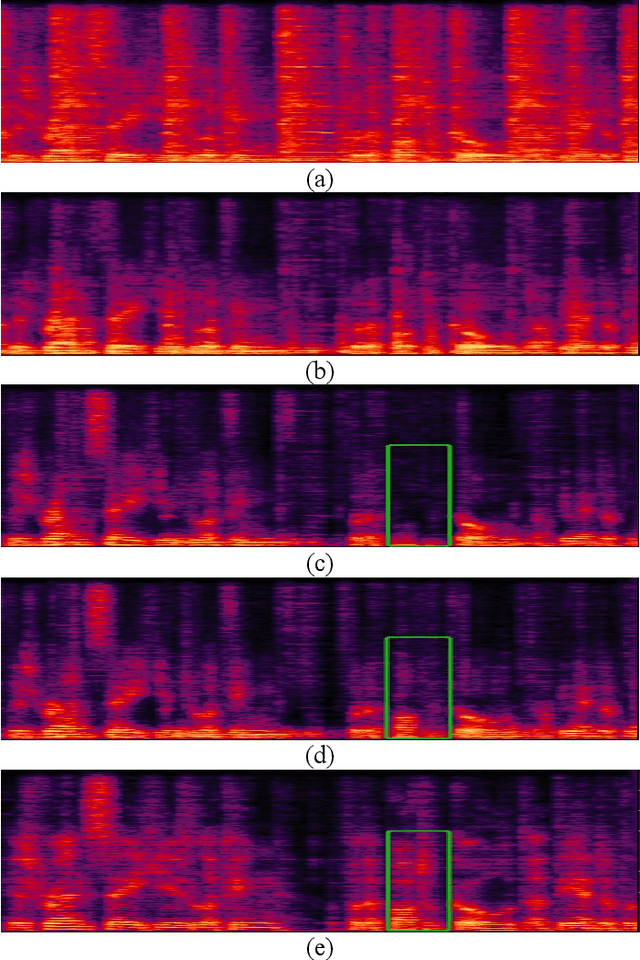
Abstract:We propose a multi-channel speech enhancement approach with a novel two-stage feature fusion method and a pre-trained acoustic model in a multi-task learning paradigm. In the first fusion stage, the time-domain and frequency-domain features are extracted separately. In the time domain, the multi-channel convolution sum (MCS) and the inter-channel convolution differences (ICDs) features are computed and then integrated with a 2-D convolutional layer, while in the frequency domain, the log-power spectra (LPS) features from both original channels and super-directive beamforming outputs are combined with another 2-D convolutional layer. To fully integrate the rich information of multi-channel speech, i.e. time-frequency domain features and the array geometry, we apply a third 2-D convolutional layer in the second stage of fusion to obtain the final convolutional features. Furthermore, we propose to use a fixed clean acoustic model trained with the end-to-end lattice-free maximum mutual information criterion to enforce the enhanced output to have the same distribution as the clean waveform to alleviate the over-estimation problem of the enhancement task and constrain distortion. On the Task1 development dataset of the ConferencingSpeech 2021 challenge, a PESQ improvement of 0.24 and 0.19 is attained compared to the official baseline and a recently proposed multi-channel separation method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge