Liyong Guo
Flow2GAN: Hybrid Flow Matching and GAN with Multi-Resolution Network for Few-step High-Fidelity Audio Generation
Dec 29, 2025Abstract:Existing dominant methods for audio generation include Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and diffusion-based methods like Flow Matching. GANs suffer from slow convergence and potential mode collapse during training, while diffusion methods require multi-step inference that introduces considerable computational overhead. In this work, we introduce Flow2GAN, a two-stage framework that combines Flow Matching training for learning generative capabilities with GAN fine-tuning for efficient few-step inference. Specifically, given audio's unique properties, we first improve Flow Matching for audio modeling through: 1) reformulating the objective as endpoint estimation, avoiding velocity estimation difficulties when involving empty regions; 2) applying spectral energy-based loss scaling to emphasize perceptually salient quieter regions. Building on these Flow Matching adaptations, we demonstrate that a further stage of lightweight GAN fine-tuning enables us to obtain one-step generator that produces high-quality audio. In addition, we develop a multi-branch network architecture that processes Fourier coefficients at different time-frequency resolutions, which improves the modeling capabilities compared to prior single-resolution designs. Experimental results indicate that our Flow2GAN delivers high-fidelity audio generation from Mel-spectrograms or discrete audio tokens, achieving better quality-efficiency trade-offs than existing state-of-the-art GAN-based and Flow Matching-based methods. Online demo samples are available at https://flow2gan.github.io, and the source code is released at https://github.com/k2-fsa/Flow2GAN.
ZipVoice: Fast and High-Quality Zero-Shot Text-to-Speech with Flow Matching
Jun 16, 2025Abstract:Existing large-scale zero-shot text-to-speech (TTS) models deliver high speech quality but suffer from slow inference speeds due to massive parameters. To address this issue, this paper introduces ZipVoice, a high-quality flow-matching-based zero-shot TTS model with a compact model size and fast inference speed. Key designs include: 1) a Zipformer-based flow-matching decoder to maintain adequate modeling capabilities under constrained size; 2) Average upsampling-based initial speech-text alignment and Zipformer-based text encoder to improve speech intelligibility; 3) A flow distillation method to reduce sampling steps and eliminate the inference overhead associated with classifier-free guidance. Experiments on 100k hours multilingual datasets show that ZipVoice matches state-of-the-art models in speech quality, while being 3 times smaller and up to 30 times faster than a DiT-based flow-matching baseline. Codes, model checkpoints and demo samples are publicly available.
k2SSL: A Faster and Better Framework for Self-Supervised Speech Representation Learning
Nov 26, 2024Abstract:Self-supervised learning (SSL) has achieved great success in speech-related tasks, driven by advancements in speech encoder architectures and the expansion of datasets. While Transformer and Conformer architectures have dominated SSL backbones, encoders like Zipformer, which excel in automatic speech recognition (ASR), remain unexplored in SSL. Concurrently, inefficiencies in data processing within existing SSL training frameworks, such as fairseq, pose challenges in managing the growing volumes of training data. To address these issues, we propose k2SSL, an open-source framework that offers faster, more memory-efficient, and better-performing self-supervised speech representation learning, with a focus on downstream ASR tasks. The optimized HuBERT and proposed Zipformer-based SSL systems exhibit substantial reductions in both training time and memory usage during SSL training. Experiments on LibriSpeech and Libri-Light demonstrate that Zipformer-based SSL systems significantly outperform comparable HuBERT and WavLM systems, achieving a relative WER reduction on dev-other/test-other of up to 34.8%/32.4% compared to HuBERT Base after supervised fine-tuning, along with a 3.5x pre-training speedup in total GPU hours.
CR-CTC: Consistency regularization on CTC for improved speech recognition
Oct 07, 2024



Abstract:Connectionist Temporal Classification (CTC) is a widely used method for automatic speech recognition (ASR), renowned for its simplicity and computational efficiency. However, it often falls short in recognition performance compared to transducer or systems combining CTC and attention-based encoder-decoder (CTC/AED). In this work, we propose the Consistency-Regularized CTC (CR-CTC), which enforces consistency between two CTC distributions obtained from different augmented views of the input speech mel-spectrogram. We provide in-depth insights into its essential behaviors from three perspectives: 1) it conducts self-distillation between random pairs of sub-models that process different augmented views; 2) it learns contextual representation through masked prediction for positions within time-masked regions, especially when we increase the amount of time masking; 3) it suppresses the extremely peaky CTC distributions, thereby reducing overfitting and improving the generalization ability. Extensive experiments on LibriSpeech, Aishell-1, and GigaSpeech datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our CR-CTC, which achieves performance comparable to, or even slightly better than, that of transducer and CTC/AED.
LibriheavyMix: A 20,000-Hour Dataset for Single-Channel Reverberant Multi-Talker Speech Separation, ASR and Speaker Diarization
Sep 01, 2024



Abstract:The evolving speech processing landscape is increasingly focused on complex scenarios like meetings or cocktail parties with multiple simultaneous speakers and far-field conditions. Existing methodologies for addressing these challenges fall into two categories: multi-channel and single-channel solutions. Single-channel approaches, notable for their generality and convenience, do not require specific information about microphone arrays. This paper presents a large-scale far-field overlapping speech dataset, crafted to advance research in speech separation, recognition, and speaker diarization. This dataset is a critical resource for decoding ``Who said What and When'' in multi-talker, reverberant environments, a daunting challenge in the field. Additionally, we introduce a pipeline system encompassing speech separation, recognition, and diarization as a foundational benchmark. Evaluations on the WHAMR! dataset validate the broad applicability of the proposed data.
Zipformer: A faster and better encoder for automatic speech recognition
Oct 17, 2023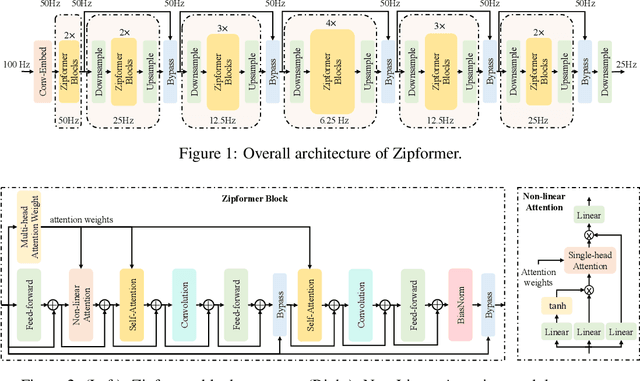

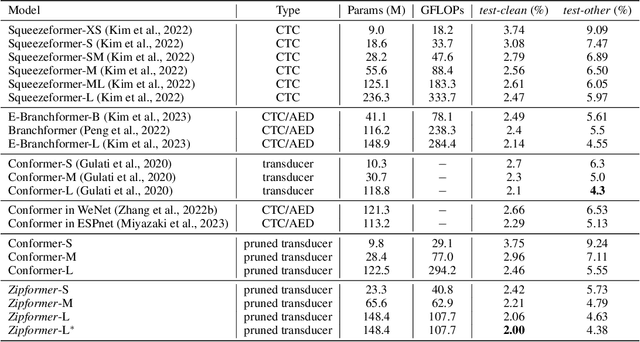
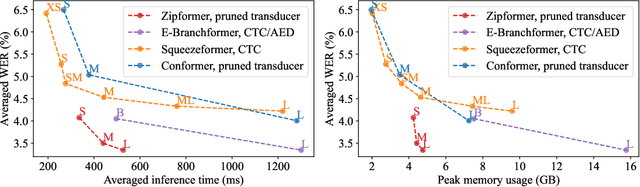
Abstract:The Conformer has become the most popular encoder model for automatic speech recognition (ASR). It adds convolution modules to a transformer to learn both local and global dependencies. In this work we describe a faster, more memory-efficient, and better-performing transformer, called Zipformer. Modeling changes include: 1) a U-Net-like encoder structure where middle stacks operate at lower frame rates; 2) reorganized block structure with more modules, within which we re-use attention weights for efficiency; 3) a modified form of LayerNorm called BiasNorm allows us to retain some length information; 4) new activation functions SwooshR and SwooshL work better than Swish. We also propose a new optimizer, called ScaledAdam, which scales the update by each tensor's current scale to keep the relative change about the same, and also explictly learns the parameter scale. It achieves faster convergence and better performance than Adam. Extensive experiments on LibriSpeech, Aishell-1, and WenetSpeech datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed Zipformer over other state-of-the-art ASR models. Our code is publicly available at https://github.com/k2-fsa/icefall.
PromptASR for contextualized ASR with controllable style
Sep 20, 2023Abstract:Prompts are crucial to large language models as they provide context information such as topic or logical relationships. Inspired by this, we propose PromptASR, a framework that integrates prompts in end-to-end automatic speech recognition (E2E ASR) systems to achieve contextualized ASR with controllable style of transcriptions. Specifically, a dedicated text encoder encodes the text prompts and the encodings are injected into the speech encoder by cross-attending the features from two modalities. When using the ground truth text from preceding utterances as content prompt, the proposed system achieves 21.9% and 6.8% relative word error rate reductions on a book reading dataset and an in-house dataset compared to a baseline ASR system. The system can also take word-level biasing lists as prompt to improve recognition accuracy on rare words. An additional style prompt can be given to the text encoder and guide the ASR system to output different styles of transcriptions. The code is available at icefall.
Libriheavy: a 50,000 hours ASR corpus with punctuation casing and context
Sep 15, 2023



Abstract:In this paper, we introduce Libriheavy, a large-scale ASR corpus consisting of 50,000 hours of read English speech derived from LibriVox. To the best of our knowledge, Libriheavy is the largest freely-available corpus of speech with supervisions. Different from other open-sourced datasets that only provide normalized transcriptions, Libriheavy contains richer information such as punctuation, casing and text context, which brings more flexibility for system building. Specifically, we propose a general and efficient pipeline to locate, align and segment the audios in previously published Librilight to its corresponding texts. The same as Librilight, Libriheavy also has three training subsets small, medium, large of the sizes 500h, 5000h, 50000h respectively. We also extract the dev and test evaluation sets from the aligned audios and guarantee there is no overlapping speakers and books in training sets. Baseline systems are built on the popular CTC-Attention and transducer models. Additionally, we open-source our dataset creatation pipeline which can also be used to other audio alignment tasks.
Delay-penalized CTC implemented based on Finite State Transducer
May 19, 2023



Abstract:Connectionist Temporal Classification (CTC) suffers from the latency problem when applied to streaming models. We argue that in CTC lattice, the alignments that can access more future context are preferred during training, thereby leading to higher symbol delay. In this work we propose the delay-penalized CTC which is augmented with latency penalty regularization. We devise a flexible and efficient implementation based on the differentiable Finite State Transducer (FST). Specifically, by attaching a binary attribute to CTC topology, we can locate the frames that firstly emit non-blank tokens on the resulting CTC lattice, and add the frame offsets to the log-probabilities. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed delay-penalized CTC, which is able to balance the delay-accuracy trade-off. Furthermore, combining the delay-penalized transducer enables the CTC model to achieve better performance and lower latency. Our work is open-sourced and publicly available https://github.com/k2-fsa/k2.
Blank-regularized CTC for Frame Skipping in Neural Transducer
May 19, 2023



Abstract:Neural Transducer and connectionist temporal classification (CTC) are popular end-to-end automatic speech recognition systems. Due to their frame-synchronous design, blank symbols are introduced to address the length mismatch between acoustic frames and output tokens, which might bring redundant computation. Previous studies managed to accelerate the training and inference of neural Transducers by discarding frames based on the blank symbols predicted by a co-trained CTC. However, there is no guarantee that the co-trained CTC can maximize the ratio of blank symbols. This paper proposes two novel regularization methods to explicitly encourage more blanks by constraining the self-loop of non-blank symbols in the CTC. It is interesting to find that the frame reduction ratio of the neural Transducer can approach the theoretical boundary. Experiments on LibriSpeech corpus show that our proposed method accelerates the inference of neural Transducer by 4 times without sacrificing performance. Our work is open-sourced and publicly available https://github.com/k2-fsa/icefall.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge