Cheng Hu
School of Software Engineering, Sun Yat-sen University
CRAFT: Calibrated Reasoning with Answer-Faithful Traces via Reinforcement Learning for Multi-Hop Question Answering
Feb 01, 2026Abstract:Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) is widely used to ground Large Language Models (LLMs) for multi-hop question answering. Recent work mainly focused on improving answer accuracy via fine-tuning and structured or reinforcement-based optimization. However, reliable reasoning in response generation faces three challenges: 1) Reasoning Collapse. Reasoning in multi-hop QA is inherently complex due to multi-hop composition and is further destabilized by noisy retrieval. 2) Reasoning-answer inconsistency. Due to the intrinsic uncertainty of LLM generation and exposure to evidence--distractor mixtures, models may produce correct answers that are not faithfully supported by their intermediate reasoning or evidence. 3) Loss of format control. Traditional chain-of-thought generation often deviates from required structured output formats, leading to incomplete or malformed structured content. To address these challenges, we propose CRAFT (Calibrated Reasoning with Answer-Faithful Traces), a Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) based reinforcement learning framework that trains models to perform faithful reasoning during response generation. CRAFT employs dual reward mechanisms to optimize multi-hop reasoning: deterministic rewards ensure structural correctness while judge-based rewards verify semantic faithfulness. This optimization framework supports controllable trace variants that enable systematic analysis of how structure and scale affect reasoning performance and faithfulness. Experiments on three multi-hop QA benchmarks show that CRAFT improves both answer accuracy and reasoning faithfulness across model scales, with the CRAFT 7B model achieving competitive performance with closed-source LLMs across multiple reasoning trace settings.
A Rapid Iterative Trajectory Planning Method for Automated Parking through Differential Flatness
Aug 23, 2025Abstract:As autonomous driving continues to advance, automated parking is becoming increasingly essential. However, significant challenges arise when implementing path velocity decomposition (PVD) trajectory planning for automated parking. The primary challenge is ensuring rapid and precise collision-free trajectory planning, which is often in conflict. The secondary challenge involves maintaining sufficient control feasibility of the planned trajectory, particularly at gear shifting points (GSP). This paper proposes a PVD-based rapid iterative trajectory planning (RITP) method to solve the above challenges. The proposed method effectively balances the necessity for time efficiency and precise collision avoidance through a novel collision avoidance framework. Moreover, it enhances the overall control feasibility of the planned trajectory by incorporating the vehicle kinematics model and including terminal smoothing constraints (TSC) at GSP during path planning. Specifically, the proposed method leverages differential flatness to ensure the planned path adheres to the vehicle kinematic model. Additionally, it utilizes TSC to maintain curvature continuity at GSP, thereby enhancing the control feasibility of the overall trajectory. The simulation results demonstrate superior time efficiency and tracking errors compared to model-integrated and other iteration-based trajectory planning methods. In the real-world experiment, the proposed method was implemented and validated on a ROS-based vehicle, demonstrating the applicability of the RITP method for real vehicles.
* Published in the journal Robotics and Autonomous Systems
Efficient and Real-Time Motion Planning for Robotics Using Projection-Based Optimization
Jun 17, 2025Abstract:Generating motions for robots interacting with objects of various shapes is a complex challenge, further complicated by the robot geometry and multiple desired behaviors. While current robot programming tools (such as inverse kinematics, collision avoidance, and manipulation planning) often treat these problems as constrained optimization, many existing solvers focus on specific problem domains or do not exploit geometric constraints effectively. We propose an efficient first-order method, Augmented Lagrangian Spectral Projected Gradient Descent (ALSPG), which leverages geometric projections via Euclidean projections, Minkowski sums, and basis functions. We show that by using geometric constraints rather than full constraints and gradients, ALSPG significantly improves real-time performance. Compared to second-order methods like iLQR, ALSPG remains competitive in the unconstrained case. We validate our method through toy examples and extensive simulations, and demonstrate its effectiveness on a 7-axis Franka robot, a 6-axis P-Rob robot and a 1:10 scale car in real-world experiments. Source codes, experimental data and videos are available on the project webpage: https://sites.google.com/view/alspg-oc
Event-Priori-Based Vision-Language Model for Efficient Visual Understanding
Jun 09, 2025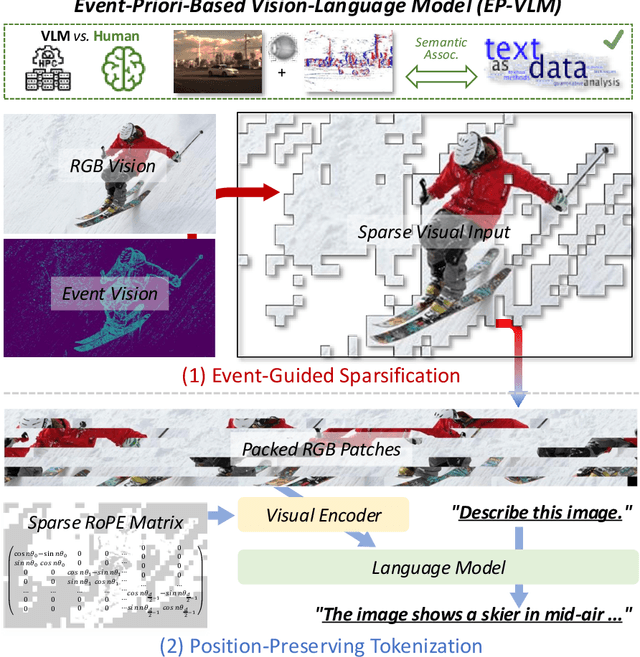
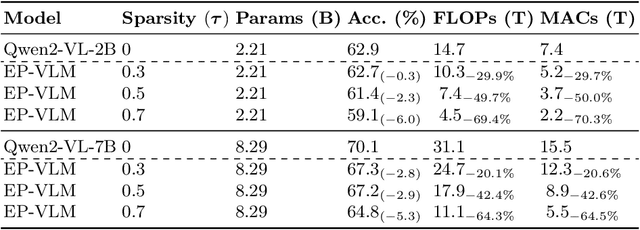


Abstract:Large Language Model (LLM)-based Vision-Language Models (VLMs) have substantially extended the boundaries of visual understanding capabilities. However, their high computational demands hinder deployment on resource-constrained edge devices. A key source of inefficiency stems from the VLM's need to process dense and redundant visual information. Visual inputs contain significant regions irrelevant to text semantics, rendering the associated computations ineffective for inference. This paper introduces a novel Event-Priori-Based Vision-Language Model, termed EP-VLM. Its core contribution is a novel mechanism leveraging motion priors derived from dynamic event vision to enhance VLM efficiency. Inspired by human visual cognition, EP-VLM first employs event data to guide the patch-wise sparsification of RGB visual inputs, progressively concentrating VLM computation on salient regions of the visual input. Subsequently, we construct a position-preserving tokenization strategy for the visual encoder within the VLM architecture. This strategy processes the event-guided, unstructured, sparse visual input while accurately preserving positional understanding within the visual input. Experimental results demonstrate that EP-VLM achieves significant efficiency improvements while maintaining nearly lossless accuracy compared to baseline models from the Qwen2-VL series. For instance, against the original Qwen2-VL-2B, EP-VLM achieves 50% FLOPs savings while retaining 98% of the original accuracy on the RealWorldQA dataset. This work demonstrates the potential of event-based vision priors for improving VLM inference efficiency, paving the way for creating more efficient and deployable VLMs for sustainable visual understanding at the edge.
Drive Fast, Learn Faster: On-Board RL for High Performance Autonomous Racing
May 12, 2025Abstract:Autonomous racing presents unique challenges due to its non-linear dynamics, the high speed involved, and the critical need for real-time decision-making under dynamic and unpredictable conditions. Most traditional Reinforcement Learning (RL) approaches rely on extensive simulation-based pre-training, which faces crucial challenges in transfer effectively to real-world environments. This paper introduces a robust on-board RL framework for autonomous racing, designed to eliminate the dependency on simulation-based pre-training enabling direct real-world adaptation. The proposed system introduces a refined Soft Actor-Critic (SAC) algorithm, leveraging a residual RL structure to enhance classical controllers in real-time by integrating multi-step Temporal-Difference (TD) learning, an asynchronous training pipeline, and Heuristic Delayed Reward Adjustment (HDRA) to improve sample efficiency and training stability. The framework is validated through extensive experiments on the F1TENTH racing platform, where the residual RL controller consistently outperforms the baseline controllers and achieves up to an 11.5 % reduction in lap times compared to the State-of-the-Art (SotA) with only 20 min of training. Additionally, an End-to-End (E2E) RL controller trained without a baseline controller surpasses the previous best results with sustained on-track learning. These findings position the framework as a robust solution for high-performance autonomous racing and a promising direction for other real-time, dynamic autonomous systems.
Towards Intelligent Edge Sensing for ISCC Network: Joint Multi-Tier DNN Partitioning and Beamforming Design
Apr 30, 2025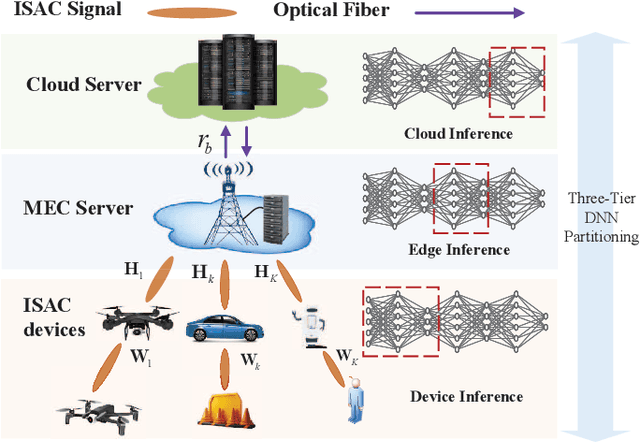
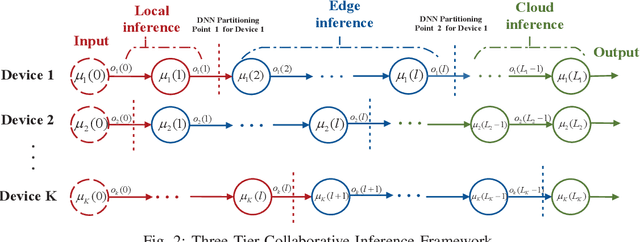
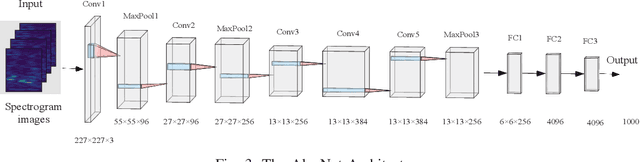
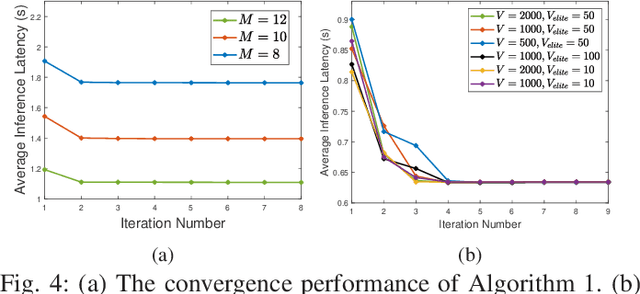
Abstract:The combination of Integrated Sensing and Communication (ISAC) and Mobile Edge Computing (MEC) enables devices to simultaneously sense the environment and offload data to the base stations (BS) for intelligent processing, thereby reducing local computational burdens. However, transmitting raw sensing data from ISAC devices to the BS often incurs substantial fronthaul overhead and latency. This paper investigates a three-tier collaborative inference framework enabled by Integrated Sensing, Communication, and Computing (ISCC), where cloud servers, MEC servers, and ISAC devices cooperatively execute different segments of a pre-trained deep neural network (DNN) for intelligent sensing. By offloading intermediate DNN features, the proposed framework can significantly reduce fronthaul transmission load. Furthermore, multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) technology is employed to enhance both sensing quality and offloading efficiency. To minimize the overall sensing task inference latency across all ISAC devices, we jointly optimize the DNN partitioning strategy, ISAC beamforming, and computational resource allocation at the MEC servers and devices, subject to sensing beampattern constraints. We also propose an efficient two-layer optimization algorithm. In the inner layer, we derive closed-form solutions for computational resource allocation using the Karush-Kuhn-Tucker conditions. Moreover, we design the ISAC beamforming vectors via an iterative method based on the majorization-minimization and weighted minimum mean square error techniques. In the outer layer, we develop a cross-entropy based probabilistic learning algorithm to determine an optimal DNN partitioning strategy. Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed framework substantially outperforms existing two-tier schemes in inference latency.
Enhancing Autonomous Driving Systems with On-Board Deployed Large Language Models
Apr 15, 2025Abstract:Neural Networks (NNs) trained through supervised learning struggle with managing edge-case scenarios common in real-world driving due to the intractability of exhaustive datasets covering all edge-cases, making knowledge-driven approaches, akin to how humans intuitively detect unexpected driving behavior, a suitable complement to data-driven methods. This work proposes a hybrid architecture combining low-level Model Predictive Controller (MPC) with locally deployed Large Language Models (LLMs) to enhance decision-making and Human Machine Interaction (HMI). The DecisionxLLM module evaluates robotic state information against natural language instructions to ensure adherence to desired driving behavior. The MPCxLLM module then adjusts MPC parameters based on LLM-generated insights, achieving control adaptability while preserving the safety and constraint guarantees of traditional MPC systems. Further, to enable efficient on-board deployment and to eliminate dependency on cloud connectivity, we shift processing to the on-board computing platform: We propose an approach that exploits Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG), Low Rank Adaptation (LoRA) fine-tuning, and quantization. Experimental results demonstrate that these enhancements yield significant improvements in reasoning accuracy by up to 10.45%, control adaptability by as much as 52.2%, and up to 10.5x increase in computational efficiency (tokens/s), validating the proposed framework's practicality for real-time deployment even on down-scaled robotic platforms. This work bridges high-level decision-making with low-level control adaptability, offering a synergistic framework for knowledge-driven and adaptive Autonomous Driving Systems (ADS).
GP-enhanced Autonomous Drifting Framework using ADMM-based iLQR
Mar 14, 2025Abstract:Autonomous drifting is a complex challenge due to the highly nonlinear dynamics and the need for precise real-time control, especially in uncertain environments. To address these limitations, this paper presents a hierarchical control framework for autonomous vehicles drifting along general paths, primarily focusing on addressing model inaccuracies and mitigating computational challenges in real-time control. The framework integrates Gaussian Process (GP) regression with an Alternating Direction Method of Multipliers (ADMM)-based iterative Linear Quadratic Regulator (iLQR). GP regression effectively compensates for model residuals, improving accuracy in dynamic conditions. ADMM-based iLQR not only combines the rapid trajectory optimization of iLQR but also utilizes ADMM's strength in decomposing the problem into simpler sub-problems. Simulation results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed framework, with significant improvements in both drift trajectory tracking and computational efficiency. Our approach resulted in a 38$\%$ reduction in RMSE lateral error and achieved an average computation time that is 75$\%$ lower than that of the Interior Point OPTimizer (IPOPT).
FSDP: Fast and Safe Data-Driven Overtaking Trajectory Planning for Head-to-Head Autonomous Racing Competitions
Mar 08, 2025Abstract:Generating overtaking trajectories in autonomous racing is a challenging task, as the trajectory must satisfy the vehicle's dynamics and ensure safety and real-time performance running on resource-constrained hardware. This work proposes the Fast and Safe Data-Driven Planner to address this challenge. Sparse Gaussian predictions are introduced to improve both the computational efficiency and accuracy of opponent predictions. Furthermore, the proposed approach employs a bi-level quadratic programming framework to generate an overtaking trajectory leveraging the opponent predictions. The first level uses polynomial fitting to generate a rough trajectory, from which reference states and control inputs are derived for the second level. The second level formulates a model predictive control optimization problem in the Frenet frame, generating a trajectory that satisfies both kinematic feasibility and safety. Experimental results on the F1TENTH platform show that our method outperforms the State-of-the-Art, achieving an 8.93% higher overtaking success rate, allowing the maximum opponent speed, ensuring a smoother ego trajectory, and reducing 74.04% computational time compared to the Predictive Spliner method. The code is available at: https://github.com/ZJU-DDRX/FSDP.
Separated Contrastive Learning for Matching in Cross-domain Recommendation with Curriculum Scheduling
Feb 22, 2025



Abstract:Cross-domain recommendation (CDR) is a task that aims to improve the recommendation performance in a target domain by leveraging the information from source domains. Contrastive learning methods have been widely adopted among intra-domain (intra-CL) and inter-domain (inter-CL) users/items for their representation learning and knowledge transfer during the matching stage of CDR. However, we observe that directly employing contrastive learning on mixed-up intra-CL and inter-CL tasks ignores the difficulty of learning from inter-domain over learning from intra-domain, and thus could cause severe training instability. Therefore, this instability deteriorates the representation learning process and hurts the quality of generated embeddings. To this end, we propose a novel framework named SCCDR built up on a separated intra-CL and inter-CL paradigm and a stop-gradient operation to handle the drawback. Specifically, SCCDR comprises two specialized curriculum stages: intra-inter separation and inter-domain curriculum scheduling. The former stage explicitly uses two distinct contrastive views for the intra-CL task in the source and target domains, respectively. Meanwhile, the latter stage deliberately tackles the inter-CL tasks with a curriculum scheduling strategy that derives effective curricula by accounting for the difficulty of negative samples anchored by overlapping users. Empirical experiments on various open-source datasets and an offline proprietary industrial dataset extracted from a real-world recommender system, and an online A/B test verify that SCCDR achieves state-of-the-art performance over multiple baselines.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge