Xiongfei Su
Unfolding Framework with Complex-Valued Deformable Attention for High-Quality Computer-Generated Hologram Generation
Aug 29, 2025Abstract:Computer-generated holography (CGH) has gained wide attention with deep learning-based algorithms. However, due to its nonlinear and ill-posed nature, challenges remain in achieving accurate and stable reconstruction. Specifically, ($i$) the widely used end-to-end networks treat the reconstruction model as a black box, ignoring underlying physical relationships, which reduces interpretability and flexibility. ($ii$) CNN-based CGH algorithms have limited receptive fields, hindering their ability to capture long-range dependencies and global context. ($iii$) Angular spectrum method (ASM)-based models are constrained to finite near-fields.In this paper, we propose a Deep Unfolding Network (DUN) that decomposes gradient descent into two modules: an adaptive bandwidth-preserving model (ABPM) and a phase-domain complex-valued denoiser (PCD), providing more flexibility. ABPM allows for wider working distances compared to ASM-based methods. At the same time, PCD leverages its complex-valued deformable self-attention module to capture global features and enhance performance, achieving a PSNR over 35 dB. Experiments on simulated and real data show state-of-the-art results.
DOVE: Efficient One-Step Diffusion Model for Real-World Video Super-Resolution
May 22, 2025Abstract:Diffusion models have demonstrated promising performance in real-world video super-resolution (VSR). However, the dozens of sampling steps they require, make inference extremely slow. Sampling acceleration techniques, particularly single-step, provide a potential solution. Nonetheless, achieving one step in VSR remains challenging, due to the high training overhead on video data and stringent fidelity demands. To tackle the above issues, we propose DOVE, an efficient one-step diffusion model for real-world VSR. DOVE is obtained by fine-tuning a pretrained video diffusion model (*i.e.*, CogVideoX). To effectively train DOVE, we introduce the latent-pixel training strategy. The strategy employs a two-stage scheme to gradually adapt the model to the video super-resolution task. Meanwhile, we design a video processing pipeline to construct a high-quality dataset tailored for VSR, termed HQ-VSR. Fine-tuning on this dataset further enhances the restoration capability of DOVE. Extensive experiments show that DOVE exhibits comparable or superior performance to multi-step diffusion-based VSR methods. It also offers outstanding inference efficiency, achieving up to a **28$\times$** speed-up over existing methods such as MGLD-VSR. Code is available at: https://github.com/zhengchen1999/DOVE.
Prior-guided Hierarchical Harmonization Network for Efficient Image Dehazing
Mar 03, 2025Abstract:Image dehazing is a crucial task that involves the enhancement of degraded images to recover their sharpness and textures. While vision Transformers have exhibited impressive results in diverse dehazing tasks, their quadratic complexity and lack of dehazing priors pose significant drawbacks for real-world applications. In this paper, guided by triple priors, Bright Channel Prior (BCP), Dark Channel Prior (DCP), and Histogram Equalization (HE), we propose a \textit{P}rior-\textit{g}uided Hierarchical \textit{H}armonization Network (PGH$^2$Net) for image dehazing. PGH$^2$Net is built upon the UNet-like architecture with an efficient encoder and decoder, consisting of two module types: (1) Prior aggregation module that injects B/DCP and selects diverse contexts with gating attention. (2) Feature harmonization modules that subtract low-frequency components from spatial and channel aspects and learn more informative feature distributions to equalize the feature maps.
Dual-branch Graph Feature Learning for NLOS Imaging
Feb 27, 2025Abstract:The domain of non-line-of-sight (NLOS) imaging is advancing rapidly, offering the capability to reveal occluded scenes that are not directly visible. However, contemporary NLOS systems face several significant challenges: (1) The computational and storage requirements are profound due to the inherent three-dimensional grid data structure, which restricts practical application. (2) The simultaneous reconstruction of albedo and depth information requires a delicate balance using hyperparameters in the loss function, rendering the concurrent reconstruction of texture and depth information difficult. This paper introduces the innovative methodology, \xnet, which integrates an albedo-focused reconstruction branch dedicated to albedo information recovery and a depth-focused reconstruction branch that extracts geometrical structure, to overcome these obstacles. The dual-branch framework segregates content delivery to the respective reconstructions, thereby enhancing the quality of the retrieved data. To our knowledge, we are the first to employ the GNN as a fundamental component to transform dense NLOS grid data into sparse structural features for efficient reconstruction. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate that our method attains the highest level of performance among existing methods across synthetic and real data. https://github.com/Nicholassu/DG-NLOS.
Distillation-Free One-Step Diffusion for Real-World Image Super-Resolution
Oct 05, 2024Abstract:Diffusion models have been achieving excellent performance for real-world image super-resolution (Real-ISR) with considerable computational costs. Current approaches are trying to derive one-step diffusion models from multi-step counterparts through knowledge distillation. However, these methods incur substantial training costs and may constrain the performance of the student model by the teacher's limitations. To tackle these issues, we propose DFOSD, a Distillation-Free One-Step Diffusion model. Specifically, we propose a noise-aware discriminator (NAD) to participate in adversarial training, further enhancing the authenticity of the generated content. Additionally, we improve the perceptual loss with edge-aware DISTS (EA-DISTS) to enhance the model's ability to generate fine details. Our experiments demonstrate that, compared with previous diffusion-based methods requiring dozens or even hundreds of steps, our DFOSD attains comparable or even superior results in both quantitative metrics and qualitative evaluations. Our DFOSD also abtains higher performance and efficiency compared with other one-step diffusion methods. We will release code and models at \url{https://github.com/JianzeLi-114/DFOSD}.
Binarized Diffusion Model for Image Super-Resolution
Jun 09, 2024



Abstract:Advanced diffusion models (DMs) perform impressively in image super-resolution (SR), but the high memory and computational costs hinder their deployment. Binarization, an ultra-compression algorithm, offers the potential for effectively accelerating DMs. Nonetheless, due to the model structure and the multi-step iterative attribute of DMs, existing binarization methods result in significant performance degradation. In this paper, we introduce a novel binarized diffusion model, BI-DiffSR, for image SR. First, for the model structure, we design a UNet architecture optimized for binarization. We propose the consistent-pixel-downsample (CP-Down) and consistent-pixel-upsample (CP-Up) to maintain dimension consistent and facilitate the full-precision information transfer. Meanwhile, we design the channel-shuffle-fusion (CS-Fusion) to enhance feature fusion in skip connection. Second, for the activation difference across timestep, we design the timestep-aware redistribution (TaR) and activation function (TaA). The TaR and TaA dynamically adjust the distribution of activations based on different timesteps, improving the flexibility and representation alability of the binarized module. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate that our BI-DiffSR outperforms existing binarization methods. Code is available at https://github.com/zhengchen1999/BI-DiffSR.
Adaptive Deep PnP Algorithm for Video Snapshot Compressive Imaging
Jan 28, 2022
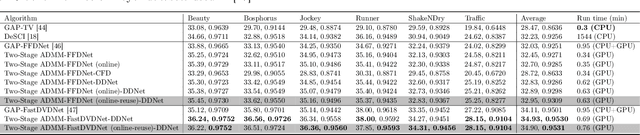


Abstract:Video Snapshot compressive imaging (SCI) is a promising technique to capture high-speed videos, which transforms the imaging speed from the detector to mask modulating and only needs a single measurement to capture multiple frames. The algorithm to reconstruct high-speed frames from the measurement plays a vital role in SCI. In this paper, we consider the promising reconstruction algorithm framework, namely plug-and-play (PnP), which is flexible to the encoding process comparing with other deep learning networks. One drawback of existing PnP algorithms is that they use a pre-trained denoising network as a plugged prior while the training data of the network might be different from the task in real applications. Towards this end, in this work, we propose the online PnP algorithm which can adaptively update the network's parameters within the PnP iteration; this makes the denoising network more applicable to the desired data in the SCI reconstruction. Furthermore, for color video imaging, RGB frames need to be recovered from Bayer pattern or named demosaicing in the camera pipeline. To address this challenge, we design a two-stage reconstruction framework to optimize these two coupled ill-posed problems and introduce a deep demosaicing prior specifically for video demosaicing which does not have much past works instead of using single image demosaicing networks. Extensive results on both simulation and real datasets verify the superiority of our adaptive deep PnP algorithm.
Utilizing High-level Visual Feature for Indoor Shopping Mall Navigation
Feb 18, 2017



Abstract:Towards robust and convenient indoor shopping mall navigation, we propose a novel learning-based scheme to utilize the high-level visual information from the storefront images captured by personal devices of users. Specifically, we decompose the visual navigation problem into localization and map generation respectively. Given a storefront input image, a novel feature fusion scheme (denoted as FusionNet) is proposed by fusing the distinguishing DNN-based appearance feature and text feature for robust recognition of store brands, which serves for accurate localization. Regarding the map generation, we convert the user-captured indicator map of the shopping mall into a topological map by parsing the stores and their connectivity. Experimental results conducted on the real shopping malls demonstrate that the proposed system achieves robust localization and precise map generation, enabling accurate navigation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge