Kaiqiao Zhan
Towards End-to-End Alignment of User Satisfaction via Questionnaire in Video Recommendation
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Short-video recommender systems typically optimize ranking models using dense user behavioral signals, such as clicks and watch time. However, these signals are only indirect proxies of user satisfaction and often suffer from noise and bias. Recently, explicit satisfaction feedback collected through questionnaires has emerged as a high-quality direct alignment supervision, but is extremely sparse and easily overwhelmed by abundant behavioral data, making it difficult to incorporate into online recommendation models. To address these challenges, we propose a novel framework which is towards End-to-End Alignment of user Satisfaction via Questionaire, named EASQ, to enable real-time alignment of ranking models with true user satisfaction. Specifically, we first construct an independent parameter pathway for sparse questionnaire signals by combining a multi-task architecture and a lightweight LoRA module. The multi-task design separates sparse satisfaction supervision from dense behavioral signals, preventing the former from being overwhelmed. The LoRA module pre-inject these preferences in a parameter-isolated manner, ensuring stability in the backbone while optimizing user satisfaction. Furthermore, we employ a DPO-based optimization objective tailored for online learning, which aligns the main model outputs with sparse satisfaction signals in real time. This design enables end-to-end online learning, allowing the model to continuously adapt to new questionnaire feedback while maintaining the stability and effectiveness of the backbone. Extensive offline experiments and large-scale online A/B tests demonstrate that EASQ consistently improves user satisfaction metrics across multiple scenarios. EASQ has been successfully deployed in a production short-video recommendation system, delivering significant and stable business gains.
S$^2$GR: Stepwise Semantic-Guided Reasoning in Latent Space for Generative Recommendation
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:Generative Recommendation (GR) has emerged as a transformative paradigm with its end-to-end generation advantages. However, existing GR methods primarily focus on direct Semantic ID (SID) generation from interaction sequences, failing to activate deeper reasoning capabilities analogous to those in large language models and thus limiting performance potential. We identify two critical limitations in current reasoning-enhanced GR approaches: (1) Strict sequential separation between reasoning and generation steps creates imbalanced computational focus across hierarchical SID codes, degrading quality for SID codes; (2) Generated reasoning vectors lack interpretable semantics, while reasoning paths suffer from unverifiable supervision. In this paper, we propose stepwise semantic-guided reasoning in latent space (S$^2$GR), a novel reasoning enhanced GR framework. First, we establish a robust semantic foundation via codebook optimization, integrating item co-occurrence relationship to capture behavioral patterns, and load balancing and uniformity objectives that maximize codebook utilization while reinforcing coarse-to-fine semantic hierarchies. Our core innovation introduces the stepwise reasoning mechanism inserting thinking tokens before each SID generation step, where each token explicitly represents coarse-grained semantics supervised via contrastive learning against ground-truth codebook cluster distributions ensuring physically grounded reasoning paths and balanced computational focus across all SID codes. Extensive experiments demonstrate the superiority of S$^2$GR, and online A/B test confirms efficacy on large-scale industrial short video platform.
PushGen: Push Notifications Generation with LLM
Dec 16, 2025
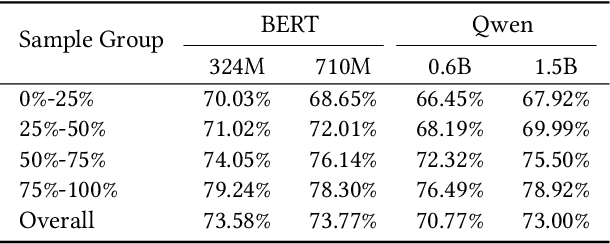
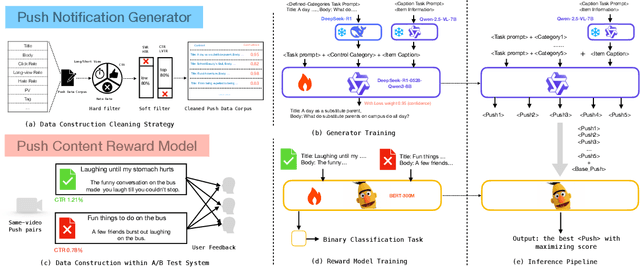

Abstract:We present PushGen, an automated framework for generating high-quality push notifications comparable to human-crafted content. With the rise of generative models, there is growing interest in leveraging LLMs for push content generation. Although LLMs make content generation straightforward and cost-effective, maintaining stylistic control and reliable quality assessment remains challenging, as both directly impact user engagement. To address these issues, PushGen combines two key components: (1) a controllable category prompt technique to guide LLM outputs toward desired styles, and (2) a reward model that ranks and selects generated candidates. Extensive offline and online experiments demonstrate its effectiveness, which has been deployed in large-scale industrial applications, serving hundreds of millions of users daily.
xMTF: A Formula-Free Model for Reinforcement-Learning-Based Multi-Task Fusion in Recommender Systems
Apr 08, 2025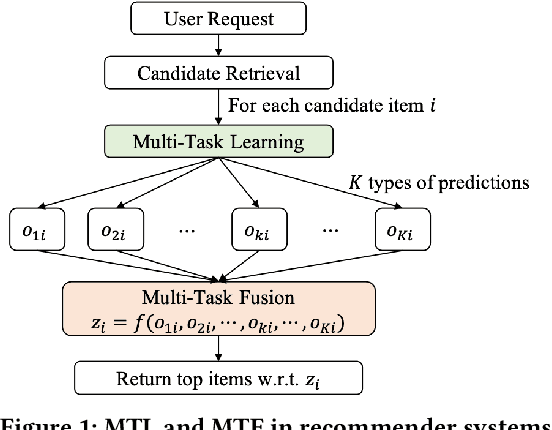
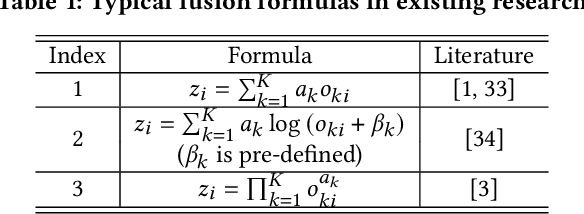
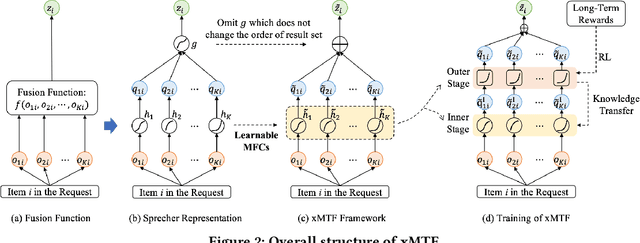
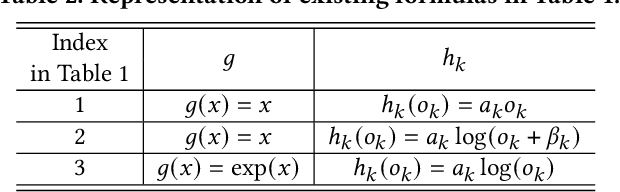
Abstract:Recommender systems need to optimize various types of user feedback, e.g., clicks, likes, and shares. A typical recommender system handling multiple types of feedback has two components: a multi-task learning (MTL) module, predicting feedback such as click-through rate and like rate; and a multi-task fusion (MTF) module, integrating these predictions into a single score for item ranking. MTF is essential for ensuring user satisfaction, as it directly influences recommendation outcomes. Recently, reinforcement learning (RL) has been applied to MTF tasks to improve long-term user satisfaction. However, existing RL-based MTF methods are formula-based methods, which only adjust limited coefficients within pre-defined formulas. The pre-defined formulas restrict the RL search space and become a bottleneck for MTF. To overcome this, we propose a formula-free MTF framework. We demonstrate that any suitable fusion function can be expressed as a composition of single-variable monotonic functions, as per the Sprecher Representation Theorem. Leveraging this, we introduce a novel learnable monotonic fusion cell (MFC) to replace pre-defined formulas. We call this new MFC-based model eXtreme MTF (xMTF). Furthermore, we employ a two-stage hybrid (TSH) learning strategy to train xMTF effectively. By expanding the MTF search space, xMTF outperforms existing methods in extensive offline and online experiments.
Unleashing the Potential of Two-Tower Models: Diffusion-Based Cross-Interaction for Large-Scale Matching
Feb 28, 2025Abstract:Two-tower models are widely adopted in the industrial-scale matching stage across a broad range of application domains, such as content recommendations, advertisement systems, and search engines. This model efficiently handles large-scale candidate item screening by separating user and item representations. However, the decoupling network also leads to a neglect of potential information interaction between the user and item representations. Current state-of-the-art (SOTA) approaches include adding a shallow fully connected layer(i.e., COLD), which is limited by performance and can only be used in the ranking stage. For performance considerations, another approach attempts to capture historical positive interaction information from the other tower by regarding them as the input features(i.e., DAT). Later research showed that the gains achieved by this method are still limited because of lacking the guidance on the next user intent. To address the aforementioned challenges, we propose a "cross-interaction decoupling architecture" within our matching paradigm. This user-tower architecture leverages a diffusion module to reconstruct the next positive intention representation and employs a mixed-attention module to facilitate comprehensive cross-interaction. During the next positive intention generation, we further enhance the accuracy of its reconstruction by explicitly extracting the temporal drift within user behavior sequences. Experiments on two real-world datasets and one industrial dataset demonstrate that our method outperforms the SOTA two-tower models significantly, and our diffusion approach outperforms other generative models in reconstructing item representations.
Creator-Side Recommender System: Challenges, Designs, and Applications
Feb 25, 2025Abstract:Users and creators are two crucial components of recommender systems. Typical recommender systems focus on the user side, providing the most suitable items based on each user's request. In such scenarios, a few items receive a majority of exposures, while many items receive very few. This imbalance leads to poorer experiences and decreased activity among the creators receiving less feedback, harming the recommender system in the long term. To this end, we develop a creator-side recommender system, called DualRec, to answer the following question: how to find the most suitable users for each item to enhance the creators' experience? We show that typical user-side recommendation algorithms, such as retrieval and ranking algorithms, can be adapted into the creator-side versions with just a few modifications. This greatly simplifies algorithm design in DualRec. Moreover, we discuss a unique challenge in DualRec: the user availability issue, which is not present in user-side recommender systems. To tackle this issue, we incorporate a user availability calculation (UAC) module to effectively enhance DualRec's performance. DualRec has already been implemented in Kwai, a short video recommendation system with over 100 millions user and over 10 million creators, significantly improving the experience for creators.
Enhancing Playback Performance in Video Recommender Systems with an On-Device Gating and Ranking Framework
Oct 08, 2024Abstract:Video recommender systems (RSs) have gained increasing attention in recent years. Existing mainstream RSs focus on optimizing the matching function between users and items. However, we noticed that users frequently encounter playback issues such as slow loading or stuttering while browsing the videos, especially in weak network conditions, which will lead to a subpar browsing experience, and may cause users to leave, even when the video content and recommendations are superior. It is quite a serious issue, yet easily overlooked. To tackle this issue, we propose an on-device Gating and Ranking Framework (GRF) that cooperates with server-side RS. Specifically, we utilize a gate model to identify videos that may have playback issues in real-time, and then we employ a ranking model to select the optimal result from a locally-cached pool to replace the stuttering videos. Our solution has been fully deployed on Kwai, a large-scale short video platform with hundreds of millions of users globally. Moreover, it significantly enhances video playback performance and improves overall user experience and retention rates.
Cache-Aware Reinforcement Learning in Large-Scale Recommender Systems
Apr 23, 2024Abstract:Modern large-scale recommender systems are built upon computation-intensive infrastructure and usually suffer from a huge difference in traffic between peak and off-peak periods. In peak periods, it is challenging to perform real-time computation for each request due to the limited budget of computational resources. The recommendation with a cache is a solution to this problem, where a user-wise result cache is used to provide recommendations when the recommender system cannot afford a real-time computation. However, the cached recommendations are usually suboptimal compared to real-time computation, and it is challenging to determine the items in the cache for each user. In this paper, we provide a cache-aware reinforcement learning (CARL) method to jointly optimize the recommendation by real-time computation and by the cache. We formulate the problem as a Markov decision process with user states and a cache state, where the cache state represents whether the recommender system performs recommendations by real-time computation or by the cache. The computational load of the recommender system determines the cache state. We perform reinforcement learning based on such a model to improve user engagement over multiple requests. Moreover, we show that the cache will introduce a challenge called critic dependency, which deteriorates the performance of reinforcement learning. To tackle this challenge, we propose an eigenfunction learning (EL) method to learn independent critics for CARL. Experiments show that CARL can significantly improve the users' engagement when considering the result cache. CARL has been fully launched in Kwai app, serving over 100 million users.
CREAD: A Classification-Restoration Framework with Error Adaptive Discretization for Watch Time Prediction in Video Recommender Systems
Jan 15, 2024Abstract:The watch time is a significant indicator of user satisfaction in video recommender systems. However, the prediction of watch time as a target variable is often hindered by its highly imbalanced distribution with a scarcity of observations for larger target values and over-populated samples for small values. State-of-the-art watch time prediction models discretize the continuous watch time into a set of buckets in order to consider the distribution of watch time. However, it is highly uninvestigated how these discrete buckets should be created from the continuous watch time distribution, and existing discretization approaches suffer from either a large learning error or a large restoration error. To address this challenge, we propose a Classification-Restoration framework with Error-Adaptive-Discretization (CREAD) to accurately predict the watch time. The proposed framework contains a discretization module, a classification module, and a restoration module. It predicts the watch time through multiple classification problems. The discretization process is a key contribution of the CREAD framework. We theoretically analyze the impacts of the discretization on the learning error and the restoration error, and then propose the error-adaptive discretization (EAD) technique to better balance the two errors, which achieves better performance over traditional discretization approaches. We conduct detailed offline evaluations on a public dataset and an industrial dataset, both showing performance gains through the proposed approach. Moreover, We have fully launched our framework to Kwai App, an online video platform, which resulted in a significant increase in users' video watch time by 0.29% through A/B testing. These results highlight the effectiveness of the CREAD framework in watch time prediction in video recommender systems.
UNEX-RL: Reinforcing Long-Term Rewards in Multi-Stage Recommender Systems with UNidirectional EXecution
Jan 12, 2024Abstract:In recent years, there has been a growing interest in utilizing reinforcement learning (RL) to optimize long-term rewards in recommender systems. Since industrial recommender systems are typically designed as multi-stage systems, RL methods with a single agent face challenges when optimizing multiple stages simultaneously. The reason is that different stages have different observation spaces, and thus cannot be modeled by a single agent. To address this issue, we propose a novel UNidirectional-EXecution-based multi-agent Reinforcement Learning (UNEX-RL) framework to reinforce the long-term rewards in multi-stage recommender systems. We show that the unidirectional execution is a key feature of multi-stage recommender systems, bringing new challenges to the applications of multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL), namely the observation dependency and the cascading effect. To tackle these challenges, we provide a cascading information chain (CIC) method to separate the independent observations from action-dependent observations and use CIC to train UNEX-RL effectively. We also discuss practical variance reduction techniques for UNEX-RL. Finally, we show the effectiveness of UNEX-RL on both public datasets and an online recommender system with over 100 million users. Specifically, UNEX-RL reveals a 0.558% increase in users' usage time compared with single-agent RL algorithms in online A/B experiments, highlighting the effectiveness of UNEX-RL in industrial recommender systems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge