Ben Wang
Tony
MMSF: Multitask and Multimodal Supervised Framework for WSI Classification and Survival Analysis
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Multimodal evidence is critical in computational pathology: gigapixel whole slide images capture tumor morphology, while patient-level clinical descriptors preserve complementary context for prognosis. Integrating such heterogeneous signals remains challenging because feature spaces exhibit distinct statistics and scales. We introduce MMSF, a multitask and multimodal supervised framework built on a linear-complexity MIL backbone that explicitly decomposes and fuses cross-modal information. MMSF comprises a graph feature extraction module embedding tissue topology at the patch level, a clinical data embedding module standardizing patient attributes, a feature fusion module aligning modality-shared and modality-specific representations, and a Mamba-based MIL encoder with multitask prediction heads. Experiments on CAMELYON16 and TCGA-NSCLC demonstrate 2.1--6.6\% accuracy and 2.2--6.9\% AUC improvements over competitive baselines, while evaluations on five TCGA survival cohorts yield 7.1--9.8\% C-index improvements compared with unimodal methods and 5.6--7.1\% over multimodal alternatives.
The Geometric Reasoner: Manifold-Informed Latent Foresight Search for Long-Context Reasoning
Jan 25, 2026Abstract:Scaling test-time compute enhances long chain-of-thought (CoT) reasoning, yet existing approaches face a fundamental trade-off between computational cost and coverage quality: either incurring high training expense or yielding redundant trajectories. We introduce The Geometric Reasoner (TGR), a training-free framework that performs manifold-informed latent foresight search under strict memory bounds. At each chunk boundary, TGR scores candidate latent anchors via a lightweight look-ahead estimate combined with soft geometric regularizers that encourage smooth trajectories and diverse exploration. Chunk-wise KV cache resets keep memory linear in chunk length. On challenging math and code benchmarks, TGR improves robust trajectory coverage, measured by the area under the Pass@$k$ curve (AUC), by up to 13 points on Qwen3-8B, with negligible overhead of about 1.1--1.3 times.
Solar PV Installation Potential Assessment on Building Facades Based on Vision and Language Foundation Models
Oct 01, 2025
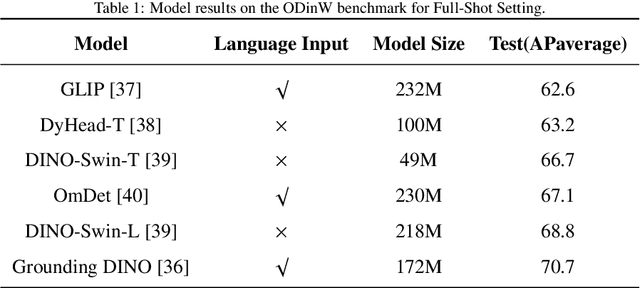
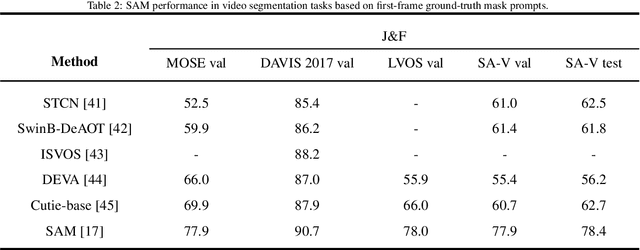

Abstract:Building facades represent a significant untapped resource for solar energy generation in dense urban environments, yet assessing their photovoltaic (PV) potential remains challenging due to complex geometries and semantic com ponents. This study introduces SF-SPA (Semantic Facade Solar-PV Assessment), an automated framework that transforms street-view photographs into quantitative PV deployment assessments. The approach combines com puter vision and artificial intelligence techniques to address three key challenges: perspective distortion correction, semantic understanding of facade elements, and spatial reasoning for PV layout optimization. Our four-stage pipeline processes images through geometric rectification, zero-shot semantic segmentation, Large Language Model (LLM) guided spatial reasoning, and energy simulation. Validation across 80 buildings in four countries demonstrates ro bust performance with mean area estimation errors of 6.2% ± 2.8% compared to expert annotations. The auto mated assessment requires approximately 100 seconds per building, a substantial gain in efficiency over manual methods. Simulated energy yield predictions confirm the method's reliability and applicability for regional poten tial studies, urban energy planning, and building-integrated photovoltaic (BIPV) deployment. Code is available at: https:github.com/CodeAXu/Solar-PV-Installation
Accelerating Chain-of-Thought Reasoning: When Goal-Gradient Importance Meets Dynamic Skipping
May 13, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models leverage Chain-of-Thought (CoT) prompting for complex tasks, but their reasoning traces are often excessively verbose and inefficient, leading to significant computational costs and latency. Current CoT compression techniques typically rely on generic importance metrics and static compression rates, which may inadvertently remove functionally critical tokens or fail to adapt to varying reasoning complexity. To overcome these limitations, we propose Adaptive GoGI-Skip, a novel framework learning dynamic CoT compression via supervised fine-tuning. This approach introduces two synergistic innovations: (1) Goal-Gradient Importance (GoGI), a novel metric accurately identifying functionally relevant tokens by measuring the gradient influence of their intermediate representations on the final answer loss, and (2) Adaptive Dynamic Skipping (ADS), a mechanism dynamically regulating the compression rate based on runtime model uncertainty while ensuring local coherence through an adaptive N-token constraint. To our knowledge, this is the first work unifying a goal-oriented, gradient-based importance metric with dynamic, uncertainty-aware skipping for CoT compression. Trained on compressed MATH data, Adaptive GoGI-Skip demonstrates strong cross-domain generalization across diverse reasoning benchmarks including AIME, GPQA, and GSM8K. It achieves substantial efficiency gains - reducing CoT token counts by over 45% on average and delivering 1.6-2.0 times inference speedups - while maintaining high reasoning accuracy. Notably, it significantly outperforms existing baselines by preserving accuracy even at high effective compression rates, advancing the state of the art in the CoT reasoning efficiency-accuracy trade-off.
xMTF: A Formula-Free Model for Reinforcement-Learning-Based Multi-Task Fusion in Recommender Systems
Apr 08, 2025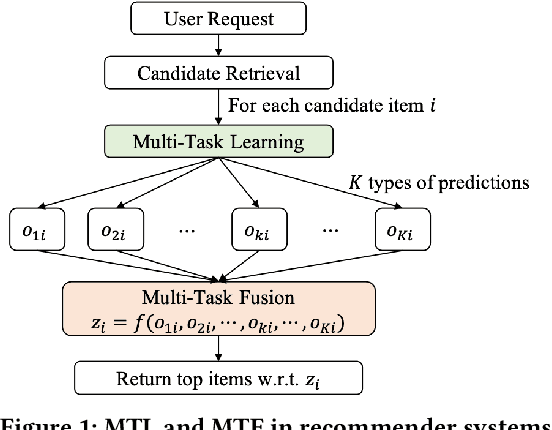
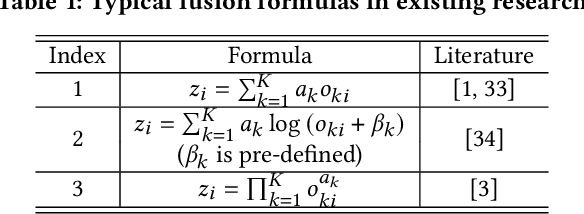
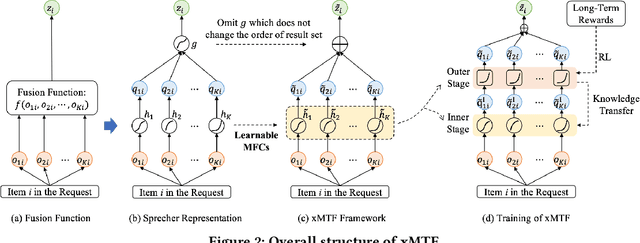
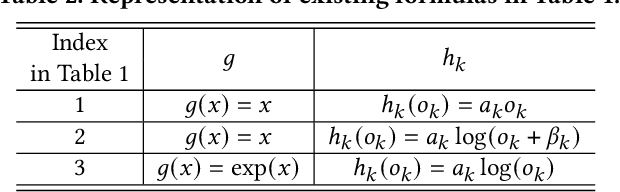
Abstract:Recommender systems need to optimize various types of user feedback, e.g., clicks, likes, and shares. A typical recommender system handling multiple types of feedback has two components: a multi-task learning (MTL) module, predicting feedback such as click-through rate and like rate; and a multi-task fusion (MTF) module, integrating these predictions into a single score for item ranking. MTF is essential for ensuring user satisfaction, as it directly influences recommendation outcomes. Recently, reinforcement learning (RL) has been applied to MTF tasks to improve long-term user satisfaction. However, existing RL-based MTF methods are formula-based methods, which only adjust limited coefficients within pre-defined formulas. The pre-defined formulas restrict the RL search space and become a bottleneck for MTF. To overcome this, we propose a formula-free MTF framework. We demonstrate that any suitable fusion function can be expressed as a composition of single-variable monotonic functions, as per the Sprecher Representation Theorem. Leveraging this, we introduce a novel learnable monotonic fusion cell (MFC) to replace pre-defined formulas. We call this new MFC-based model eXtreme MTF (xMTF). Furthermore, we employ a two-stage hybrid (TSH) learning strategy to train xMTF effectively. By expanding the MTF search space, xMTF outperforms existing methods in extensive offline and online experiments.
Unleashing the Potential of Two-Tower Models: Diffusion-Based Cross-Interaction for Large-Scale Matching
Feb 28, 2025Abstract:Two-tower models are widely adopted in the industrial-scale matching stage across a broad range of application domains, such as content recommendations, advertisement systems, and search engines. This model efficiently handles large-scale candidate item screening by separating user and item representations. However, the decoupling network also leads to a neglect of potential information interaction between the user and item representations. Current state-of-the-art (SOTA) approaches include adding a shallow fully connected layer(i.e., COLD), which is limited by performance and can only be used in the ranking stage. For performance considerations, another approach attempts to capture historical positive interaction information from the other tower by regarding them as the input features(i.e., DAT). Later research showed that the gains achieved by this method are still limited because of lacking the guidance on the next user intent. To address the aforementioned challenges, we propose a "cross-interaction decoupling architecture" within our matching paradigm. This user-tower architecture leverages a diffusion module to reconstruct the next positive intention representation and employs a mixed-attention module to facilitate comprehensive cross-interaction. During the next positive intention generation, we further enhance the accuracy of its reconstruction by explicitly extracting the temporal drift within user behavior sequences. Experiments on two real-world datasets and one industrial dataset demonstrate that our method outperforms the SOTA two-tower models significantly, and our diffusion approach outperforms other generative models in reconstructing item representations.
Creator-Side Recommender System: Challenges, Designs, and Applications
Feb 25, 2025Abstract:Users and creators are two crucial components of recommender systems. Typical recommender systems focus on the user side, providing the most suitable items based on each user's request. In such scenarios, a few items receive a majority of exposures, while many items receive very few. This imbalance leads to poorer experiences and decreased activity among the creators receiving less feedback, harming the recommender system in the long term. To this end, we develop a creator-side recommender system, called DualRec, to answer the following question: how to find the most suitable users for each item to enhance the creators' experience? We show that typical user-side recommendation algorithms, such as retrieval and ranking algorithms, can be adapted into the creator-side versions with just a few modifications. This greatly simplifies algorithm design in DualRec. Moreover, we discuss a unique challenge in DualRec: the user availability issue, which is not present in user-side recommender systems. To tackle this issue, we incorporate a user availability calculation (UAC) module to effectively enhance DualRec's performance. DualRec has already been implemented in Kwai, a short video recommendation system with over 100 millions user and over 10 million creators, significantly improving the experience for creators.
MARM: Unlocking the Future of Recommendation Systems through Memory Augmentation and Scalable Complexity
Nov 14, 2024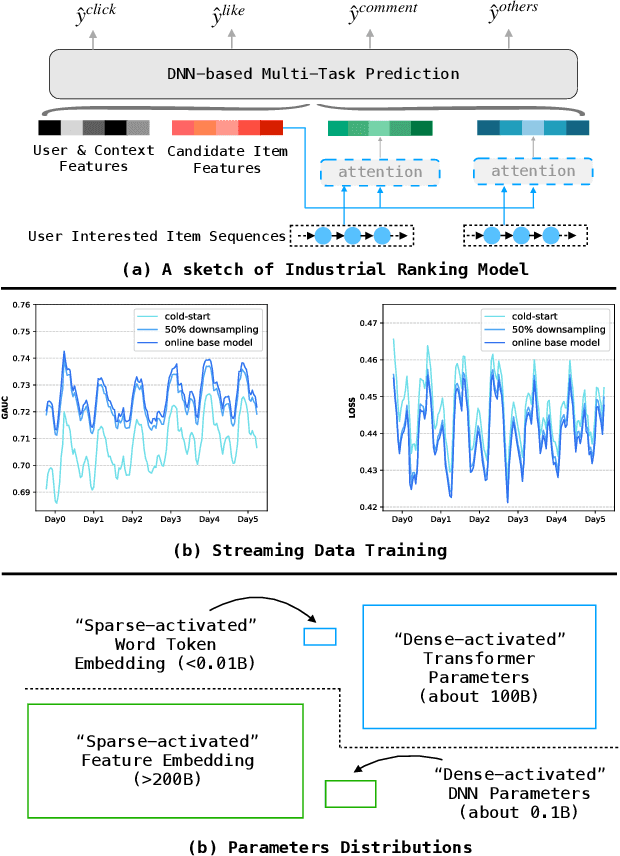
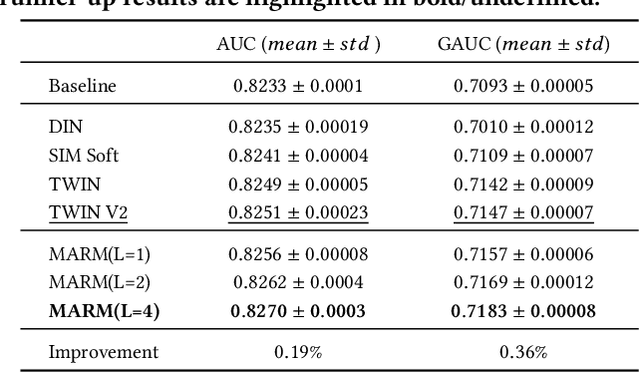
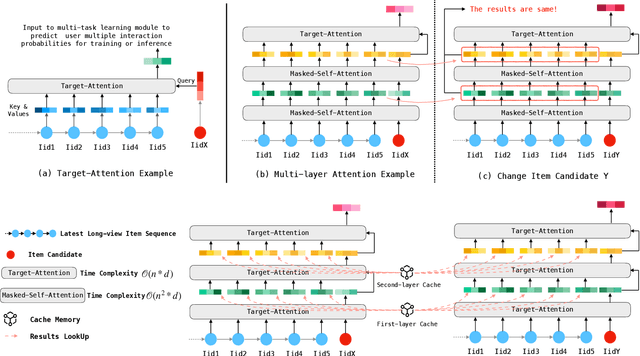
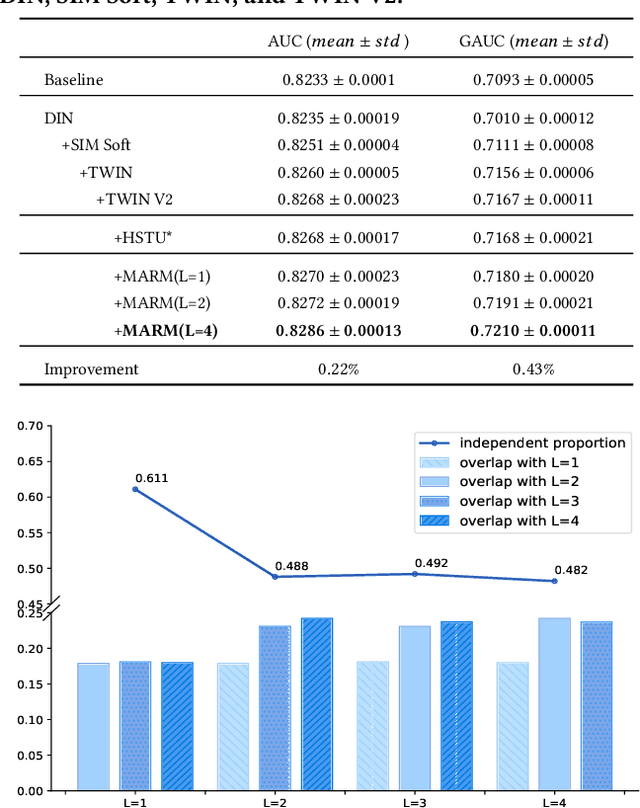
Abstract:Scaling-law has guided the language model designing for past years, however, it is worth noting that the scaling laws of NLP cannot be directly applied to RecSys due to the following reasons: (1) The amount of training samples and model parameters is typically not the bottleneck for the model. Our recommendation system can generate over 50 billion user samples daily, and such a massive amount of training data can easily allow our model parameters to exceed 200 billion, surpassing many LLMs (about 100B). (2) To ensure the stability and robustness of the recommendation system, it is essential to control computational complexity FLOPs carefully. Considering the above differences with LLM, we can draw a conclusion that: for a RecSys model, compared to model parameters, the computational complexity FLOPs is a more expensive factor that requires careful control. In this paper, we propose our milestone work, MARM (Memory Augmented Recommendation Model), which explores a new cache scaling-laws successfully.
GPT-4o System Card
Oct 25, 2024Abstract:GPT-4o is an autoregressive omni model that accepts as input any combination of text, audio, image, and video, and generates any combination of text, audio, and image outputs. It's trained end-to-end across text, vision, and audio, meaning all inputs and outputs are processed by the same neural network. GPT-4o can respond to audio inputs in as little as 232 milliseconds, with an average of 320 milliseconds, which is similar to human response time in conversation. It matches GPT-4 Turbo performance on text in English and code, with significant improvement on text in non-English languages, while also being much faster and 50\% cheaper in the API. GPT-4o is especially better at vision and audio understanding compared to existing models. In line with our commitment to building AI safely and consistent with our voluntary commitments to the White House, we are sharing the GPT-4o System Card, which includes our Preparedness Framework evaluations. In this System Card, we provide a detailed look at GPT-4o's capabilities, limitations, and safety evaluations across multiple categories, focusing on speech-to-speech while also evaluating text and image capabilities, and measures we've implemented to ensure the model is safe and aligned. We also include third-party assessments on dangerous capabilities, as well as discussion of potential societal impacts of GPT-4o's text and vision capabilities.
Enhancing Playback Performance in Video Recommender Systems with an On-Device Gating and Ranking Framework
Oct 08, 2024Abstract:Video recommender systems (RSs) have gained increasing attention in recent years. Existing mainstream RSs focus on optimizing the matching function between users and items. However, we noticed that users frequently encounter playback issues such as slow loading or stuttering while browsing the videos, especially in weak network conditions, which will lead to a subpar browsing experience, and may cause users to leave, even when the video content and recommendations are superior. It is quite a serious issue, yet easily overlooked. To tackle this issue, we propose an on-device Gating and Ranking Framework (GRF) that cooperates with server-side RS. Specifically, we utilize a gate model to identify videos that may have playback issues in real-time, and then we employ a ranking model to select the optimal result from a locally-cached pool to replace the stuttering videos. Our solution has been fully deployed on Kwai, a large-scale short video platform with hundreds of millions of users globally. Moreover, it significantly enhances video playback performance and improves overall user experience and retention rates.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge