Jiangxia Cao
From Agnostic to Specific: Latent Preference Diffusion for Multi-Behavior Sequential Recommendation
Feb 26, 2026Abstract:Multi-behavior sequential recommendation (MBSR) aims to learn the dynamic and heterogeneous interactions of users' multi-behavior sequences, so as to capture user preferences under target behavior for the next interacted item prediction. Unlike previous methods that adopt unidirectional modeling by mapping auxiliary behaviors to target behavior, recent concerns are shifting from behavior-fixed to behavior-specific recommendation. However, these methods still ignore the user's latent preference that underlying decision-making, leading to suboptimal solutions. Meanwhile, due to the asymmetric deterministic between items and behaviors, discriminative paradigm based on preference scoring is unsuitable to capture the uncertainty from low-entropy behaviors to high-entropy items, failing to provide efficient and diverse recommendation. To address these challenges, we propose \textbf{FatsMB}, a framework based diffusion model that guides preference generation \textit{\textbf{F}rom Behavior-\textbf{A}gnostic \textbf{T}o Behavior-\textbf{S}pecific} in latent spaces, enabling diverse and accurate \textit{\textbf{M}ulti-\textbf{B}ehavior Sequential Recommendation}. Specifically, we design a Multi-Behavior AutoEncoder (MBAE) to construct a unified user latent preference space, facilitating interaction and collaboration across Behaviors, within Behavior-aware RoPE (BaRoPE) employed for multiple information fusion. Subsequently, we conduct target behavior-specific preference transfer in the latent space, enriching with informative priors. A Multi-Condition Guided Layer Normalization (MCGLN) is introduced for the denoising. Extensive experiments on real-world datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our model.
MaRI: Accelerating Ranking Model Inference via Structural Re-parameterization in Large Scale Recommendation System
Feb 26, 2026Abstract:Ranking models, i.e., coarse-ranking and fine-ranking models, serve as core components in large-scale recommendation systems, responsible for scoring massive item candidates based on user preferences. To meet the stringent latency requirements of online serving, structural lightweighting or knowledge distillation techniques are commonly employed for ranking model acceleration. However, these approaches typically lead to a non-negligible drop in accuracy. Notably, the angle of lossless acceleration by optimizing feature fusion matrix multiplication, particularly through structural reparameterization, remains underexplored. In this paper, we propose MaRI, a novel Matrix Re-parameterized Inference framework, which serves as a complementary approach to existing techniques while accelerating ranking model inference without any accuracy loss. MaRI is motivated by the observation that user-side computation is redundant in feature fusion matrix multiplication, and we therefore adopt the philosophy of structural reparameterization to alleviate such redundancy.
CREM: Compression-Driven Representation Enhancement for Multimodal Retrieval and Comprehension
Feb 22, 2026Abstract:Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have shown remarkable success in comprehension tasks such as visual description and visual question answering. However, their direct application to embedding-based tasks like retrieval remains challenging due to the discrepancy between output formats and optimization objectives. Previous approaches often employ contrastive fine-tuning to adapt MLLMs for retrieval, but at the cost of losing their generative capabilities. We argue that both generative and embedding tasks fundamentally rely on shared cognitive mechanisms, specifically cross-modal representation alignment and contextual comprehension. To this end, we propose CREM (Compression-driven Representation Enhanced Model), with a unified framework that enhances multimodal representations for retrieval while preserving generative ability. Specifically, we introduce a compression-based prompt design with learnable chorus tokens to aggregate multimodal semantics and a compression-driven training strategy that integrates contrastive and generative objectives through compression-aware attention. Extensive experiments demonstrate that CREM achieves state-of-the-art retrieval performance on MMEB while maintaining strong generative performance on multiple comprehension benchmarks. Our findings highlight that generative supervision can further improve the representational quality of MLLMs under the proposed compression-driven paradigm.
Kelix Technical Report
Feb 12, 2026Abstract:Autoregressive large language models (LLMs) scale well by expressing diverse tasks as sequences of discrete natural-language tokens and training with next-token prediction, which unifies comprehension and generation under self-supervision. Extending this paradigm to multimodal data requires a shared, discrete representation across modalities. However, most vision-language models (VLMs) still rely on a hybrid interface: discrete text tokens paired with continuous Vision Transformer (ViT) features. Because supervision is largely text-driven, these models are often biased toward understanding and cannot fully leverage large-scale self-supervised learning on non-text data. Recent work has explored discrete visual tokenization to enable fully autoregressive multimodal modeling, showing promising progress toward unified understanding and generation. Yet existing discrete vision tokens frequently lose information due to limited code capacity, resulting in noticeably weaker understanding than continuous-feature VLMs. We present Kelix, a fully discrete autoregressive unified model that closes the understanding gap between discrete and continuous visual representations.
SARM: LLM-Augmented Semantic Anchor for End-to-End Live-Streaming Ranking
Feb 10, 2026Abstract:Large-scale live-streaming recommendation requires precise modeling of non-stationary content semantics under strict real-time serving constraints. In industrial deployment, two common approaches exhibit fundamental limitations: discrete semantic abstractions sacrifice descriptive precision through clustering, while dense multimodal embeddings are extracted independently and remain weakly aligned with ranking optimization, limiting fine-grained content-aware ranking. To address these limitations, we propose \textbf{SARM}, an end-to-end ranking architecture that integrates natural-language semantic anchors directly into ranking optimization, enabling fine-grained author representations conditioned on multimodal content. Each semantic anchor is represented as learnable text tokens jointly optimized with ranking features, allowing the model to adapt content descriptions to ranking objectives. A lightweight dual-token gated design captures domain-specific live-streaming semantics, while an asymmetric deployment strategy preserves low-latency online training and serving. Extensive offline evaluation and large-scale A/B tests show consistent improvements over production baselines. SARM is fully deployed and serves over 400 million users daily.
OneLive: Dynamically Unified Generative Framework for Live-Streaming Recommendation
Feb 09, 2026Abstract:Live-streaming recommender system serves as critical infrastructure that bridges the patterns of real-time interactions between users and authors. Similar to traditional industrial recommender systems, live-streaming recommendation also relies on cascade architectures to support large-scale concurrency. Recent advances in generative recommendation unify the multi-stage recommendation process with Transformer-based architectures, offering improved scalability and higher computational efficiency. However, the inherent complexity of live-streaming prevents the direct transfer of these methods to live-streaming scenario, where continuously evolving content, limited lifecycles, strict real-time constraints, and heterogeneous multi-objectives introduce unique challenges that invalidate static tokenization and conventional model framework. To address these issues, we propose OneLive, a dynamically unified generative recommendation framework tailored for live-streaming scenario. OneLive integrates four key components: (i) A Dynamic Tokenizer that continuously encodes evolving real-time live content fused with behavior signal through residual quantization; (ii) A Time-Aware Gated Attention mechanism that explicitly models temporal dynamics for timely decision making; (iii) An efficient decoder-only generative architecture enhanced with Sequential MTP and QK Norm for stable training and accelerated inference; (iv) A Unified Multi-Objective Alignment Framework reinforces policy optimization for personalized preferences.
QARM V2: Quantitative Alignment Multi-Modal Recommendation for Reasoning User Sequence Modeling
Feb 09, 2026Abstract:With the evolution of large language models (LLMs), there is growing interest in leveraging their rich semantic understanding to enhance industrial recommendation systems (RecSys). Traditional RecSys relies on ID-based embeddings for user sequence modeling in the General Search Unit (GSU) and Exact Search Unit (ESU) paradigm, which suffers from low information density, knowledge isolation, and weak generalization ability. While LLMs offer complementary strengths with dense semantic representations and strong generalization, directly applying LLM embeddings to RecSys faces critical challenges: representation unmatch with business objectives and representation unlearning end-to-end with downstream tasks. In this paper, we present QARM V2, a unified framework that bridges LLM semantic understanding with RecSys business requirements for user sequence modeling.
OneMall: One Architecture, More Scenarios -- End-to-End Generative Recommender Family at Kuaishou E-Commerce
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:In the wave of generative recommendation, we present OneMall, an end-to-end generative recommendation framework tailored for e-commerce services at Kuaishou. Our OneMall systematically unifies the e-commerce's multiple item distribution scenarios, such as Product-card, short-video and live-streaming. Specifically, it comprises three key components, aligning the entire model training pipeline to the LLM's pre-training/post-training: (1) E-commerce Semantic Tokenizer: we provide a tokenizer solution that captures both real-world semantics and business-specific item relations across different scenarios; (2) Transformer-based Architecture: we largely utilize Transformer as our model backbone, e.g., employing Query-Former for long sequence compression, Cross-Attention for multi-behavior sequence fusion, and Sparse MoE for scalable auto-regressive generation; (3) Reinforcement Learning Pipeline: we further connect retrieval and ranking models via RL, enabling the ranking model to serve as a reward signal for end-to-end policy retrieval model optimization. Extensive experiments demonstrate that OneMall achieves consistent improvements across all e-commerce scenarios: +13.01\% GMV in product-card, +15.32\% Orders in Short-Video, and +2.78\% Orders in Live-Streaming. OneMall has been deployed, serving over 400 million daily active users at Kuaishou.
OneMall: One Model, More Scenarios -- End-to-End Generative Recommender Family at Kuaishou E-Commerce
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:In the wave of generative recommendation, we present OneMall, an end-to-end generative recommendation framework tailored for e-commerce services at Kuaishou. Our OneMall systematically unifies the e-commerce's multiple item distribution scenarios, such as Product-card, short-video and live-streaming. Specifically, it comprises three key components, aligning the entire model training pipeline to the LLM's pre-training/post-training: (1) E-commerce Semantic Tokenizer: we provide a tokenizer solution that captures both real-world semantics and business-specific item relations across different scenarios; (2) Transformer-based Architecture: we largely utilize Transformer as our model backbone, e.g., employing Query-Former for long sequence compression, Cross-Attention for multi-behavior sequence fusion, and Sparse MoE for scalable auto-regressive generation; (3) Reinforcement Learning Pipeline: we further connect retrieval and ranking models via RL, enabling the ranking model to serve as a reward signal for end-to-end policy retrieval model optimization. Extensive experiments demonstrate that OneMall achieves consistent improvements across all e-commerce scenarios: +13.01\% GMV in product-card, +15.32\% Orders in Short-Video, and +2.78\% Orders in Live-Streaming. OneMall has been deployed, serving over 400 million daily active users at Kuaishou.
PushGen: Push Notifications Generation with LLM
Dec 16, 2025
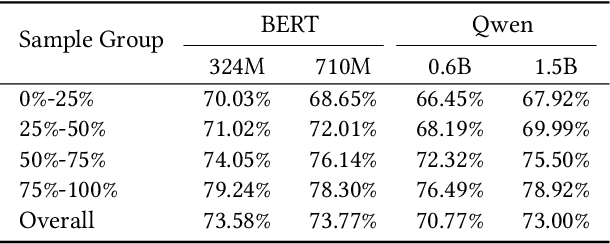
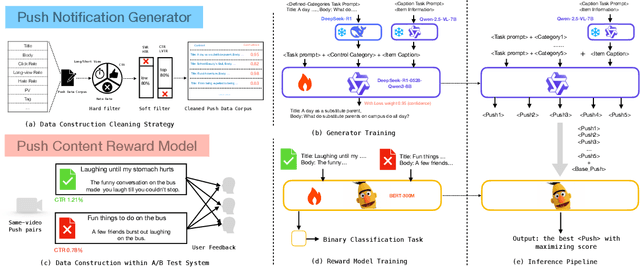

Abstract:We present PushGen, an automated framework for generating high-quality push notifications comparable to human-crafted content. With the rise of generative models, there is growing interest in leveraging LLMs for push content generation. Although LLMs make content generation straightforward and cost-effective, maintaining stylistic control and reliable quality assessment remains challenging, as both directly impact user engagement. To address these issues, PushGen combines two key components: (1) a controllable category prompt technique to guide LLM outputs toward desired styles, and (2) a reward model that ranks and selects generated candidates. Extensive offline and online experiments demonstrate its effectiveness, which has been deployed in large-scale industrial applications, serving hundreds of millions of users daily.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge