Shijie Guan
MARM: Unlocking the Future of Recommendation Systems through Memory Augmentation and Scalable Complexity
Nov 14, 2024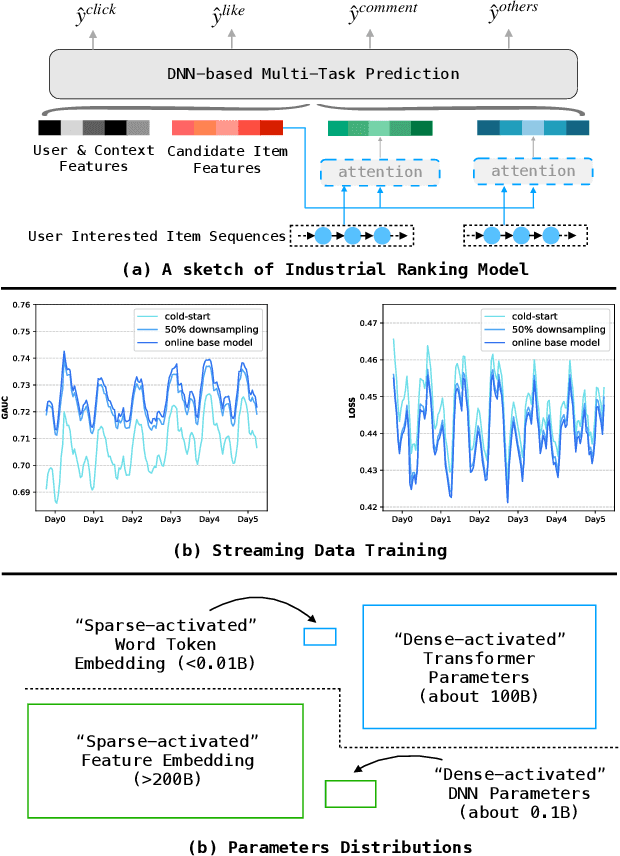
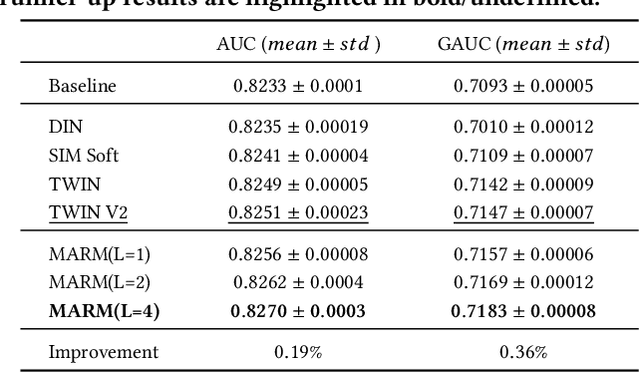
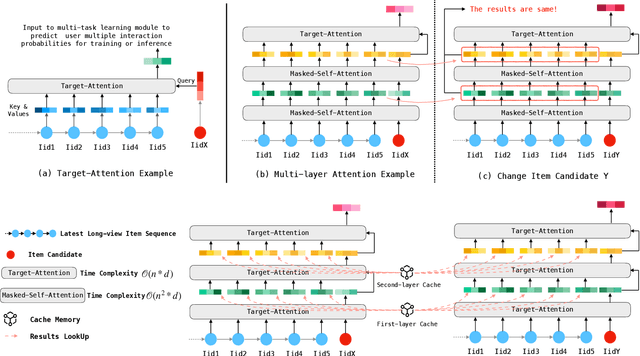
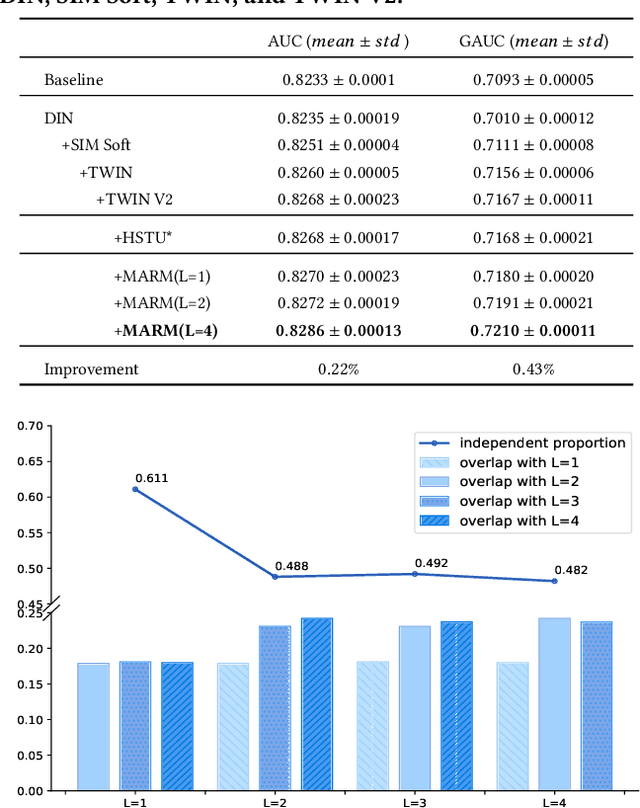
Abstract:Scaling-law has guided the language model designing for past years, however, it is worth noting that the scaling laws of NLP cannot be directly applied to RecSys due to the following reasons: (1) The amount of training samples and model parameters is typically not the bottleneck for the model. Our recommendation system can generate over 50 billion user samples daily, and such a massive amount of training data can easily allow our model parameters to exceed 200 billion, surpassing many LLMs (about 100B). (2) To ensure the stability and robustness of the recommendation system, it is essential to control computational complexity FLOPs carefully. Considering the above differences with LLM, we can draw a conclusion that: for a RecSys model, compared to model parameters, the computational complexity FLOPs is a more expensive factor that requires careful control. In this paper, we propose our milestone work, MARM (Memory Augmented Recommendation Model), which explores a new cache scaling-laws successfully.
FCDNet: Frequency-Guided Complementary Dependency Modeling for Multivariate Time-Series Forecasting
Dec 27, 2023



Abstract:Multivariate time-series (MTS) forecasting is a challenging task in many real-world non-stationary dynamic scenarios. In addition to intra-series temporal signals, the inter-series dependency also plays a crucial role in shaping future trends. How to enable the model's awareness of dependency information has raised substantial research attention. Previous approaches have either presupposed dependency constraints based on domain knowledge or imposed them using real-time feature similarity. However, MTS data often exhibit both enduring long-term static relationships and transient short-term interactions, which mutually influence their evolving states. It is necessary to recognize and incorporate the complementary dependencies for more accurate MTS prediction. The frequency information in time series reflects the evolutionary rules behind complex temporal dynamics, and different frequency components can be used to well construct long-term and short-term interactive dependency structures between variables. To this end, we propose FCDNet, a concise yet effective framework for multivariate time-series forecasting. Specifically, FCDNet overcomes the above limitations by applying two light-weight dependency constructors to help extract long- and short-term dependency information adaptively from multi-level frequency patterns. With the growth of input variables, the number of trainable parameters in FCDNet only increases linearly, which is conducive to the model's scalability and avoids over-fitting. Additionally, adopting a frequency-based perspective can effectively mitigate the influence of noise within MTS data, which helps capture more genuine dependencies. The experimental results on six real-world datasets from multiple fields show that FCDNet significantly exceeds strong baselines, with an average improvement of 6.82% on MAE, 4.98% on RMSE, and 4.91% on MAPE.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge