Ranjan Sapkota
YOLOE-26: Integrating YOLO26 with YOLOE for Real-Time Open-Vocabulary Instance Segmentation
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:This paper presents YOLOE-26, a unified framework that integrates the deployment-optimized YOLO26(or YOLOv26) architecture with the open-vocabulary learning paradigm of YOLOE for real-time open-vocabulary instance segmentation. Building on the NMS-free, end-to-end design of YOLOv26, the proposed approach preserves the hallmark efficiency and determinism of the YOLO family while extending its capabilities beyond closed-set recognition. YOLOE-26 employs a convolutional backbone with PAN/FPN-style multi-scale feature aggregation, followed by end-to-end regression and instance segmentation heads. A key architectural contribution is the replacement of fixed class logits with an object embedding head, which formulates classification as similarity matching against prompt embeddings derived from text descriptions, visual examples, or a built-in vocabulary. To enable efficient open-vocabulary reasoning, the framework incorporates Re-Parameterizable Region-Text Alignment (RepRTA) for zero-overhead text prompting, a Semantic-Activated Visual Prompt Encoder (SAVPE) for example-guided segmentation, and Lazy Region Prompt Contrast for prompt-free inference. All prompting modalities operate within a unified object embedding space, allowing seamless switching between text-prompted, visual-prompted, and fully autonomous segmentation. Extensive experiments demonstrate consistent scaling behavior and favorable accuracy-efficiency trade-offs across model sizes in both prompted and prompt-free settings. The training strategy leverages large-scale detection and grounding datasets with multi-task optimization and remains fully compatible with the Ultralytics ecosystem for training, validation, and deployment. Overall, YOLOE-26 provides a practical and scalable solution for real-time open-vocabulary instance segmentation in dynamic, real-world environments.
Generalization vs. Specialization: Evaluating Segment Anything Model (SAM3) Zero-Shot Segmentation Against Fine-Tuned YOLO Detectors
Dec 09, 2025Abstract:Deep learning has advanced two fundamentally different paradigms for instance segmentation: specialized models optimized through task-specific fine-tuning and generalist foundation models capable of zero-shot segmentation. This work presents a comprehensive comparison between SAM3 (Segment Anything Model, also called SAMv3) operating in zero-shot mode and three variants of Ultralytics YOLO11 (nano, medium, and large) fine-tuned for instance segmentation. The evaluation is conducted on the MinneApple dataset, a dense benchmark comprising 670 orchard images with 28,179 annotated apple instances, enabling rigorous validation of model behavior under high object density and occlusion. Our analysis shows IoU choices can inflate performance gaps by up to 30%. At the appropriate IoU = 0.15 threshold, YOLO models achieve 68.9%, 72.2%, and 71.9% F1, while SAM3 reaches 59.8% in pure zero-shot mode. However, YOLO exhibits steep degradation 48-50 points across IoU ranges whereas SAM3 drops only 4 points, revealing 12 times superior boundary stability of SAM3. This highlights the strength of SAMv3 in mask precision versus specialization in detection completeness of YOLO11. We provide open-source code, evaluation pipelines, and methodological recommendations, contributing to a deeper understanding of when specialized fine-tuned models or generalist foundation models are preferable for dense instance segmentation tasks. This project repository is available on GitHub as https://github.com/Applied-AI-Research-Lab/Segment-Anything-Model-SAM3-Zero-Shot-Segmentation-Against-Fine-Tuned-YOLO-Detectors
PoultryTalk: A Multi-modal Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) System for Intelligent Poultry Management and Decision Support
Dec 08, 2025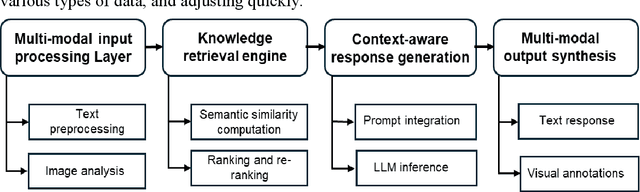

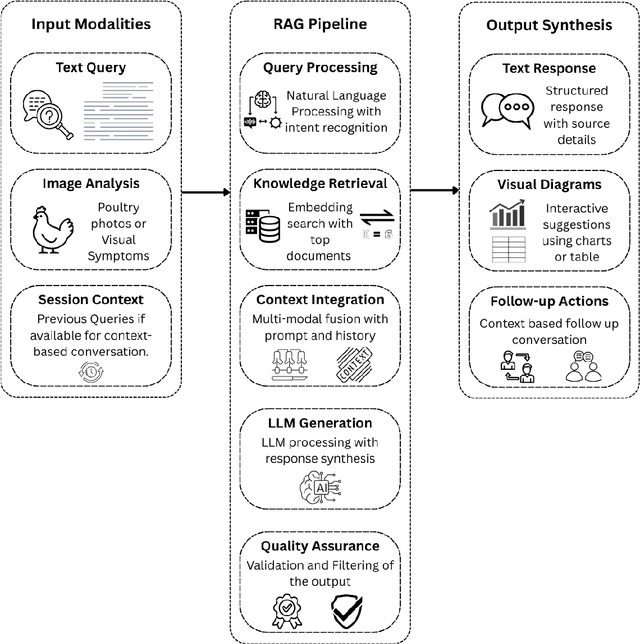
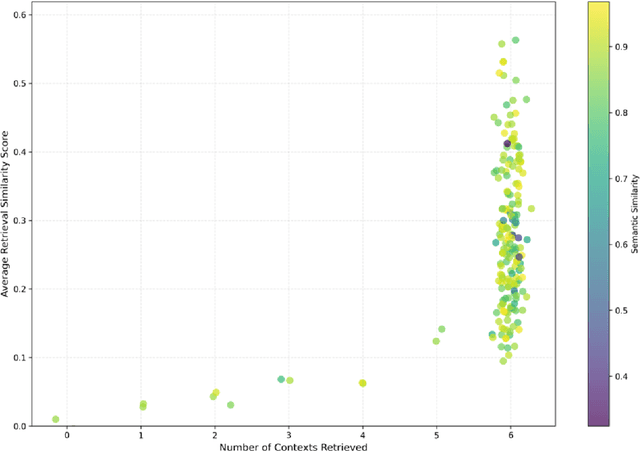
Abstract:The Poultry industry plays a vital role in global food security, yet small- and medium-scale farmers frequently lack timely access to expert-level support for disease diagnosis, nutrition planning, and management decisions. With rising climate stress, unpredictable feed prices, and persistent disease threats, poultry producers often struggle to make quick, informed decisions. Therefore, there is a critical need for intelligent, data-driven systems that can deliver reliable, on-demand consultation. This paper presents PoultryTalk, a novel multi-modal Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) system designed to provide real-time expert guidance through text and image-based interaction. PoultryTalk uses OpenAI's text-embedding-3-small and GPT-4o to provide smart, context-aware poultry management advice from text, images, or questions. System usability and performance were evaluated using 200 expert-verified queries and feedback from 34 participants who submitted 267 queries to the PoultryTalk prototype. The expert-verified benchmark queries confirmed strong technical performance, achieving a semantic similarity of 84.0% and an average response latency of 3.6 seconds. Compared with OpenAI's GPT-4o, PoultryTalk delivered more accurate and reliable information related to poultry. Based on participants' evaluations, PoultryTalk achieved a response accuracy of 89.9%, with about 9.1% of responses rated as incorrect. A post-use survey indicated high user satisfaction: 95.6% of participants reported that the chatbot provided "always correct" and "mostly correct" answers. 82.6% indicated they would recommend the tool, and 17.4% responded "maybe." These results collectively demonstrate that PoultryTalk not only delivers accurate, contextually relevant information but also demonstrates strong user acceptance and scalability potential.
3D Reconstruction and Information Fusion between Dormant and Canopy Seasons in Commercial Orchards Using Deep Learning and Fast GICP
Jul 02, 2025
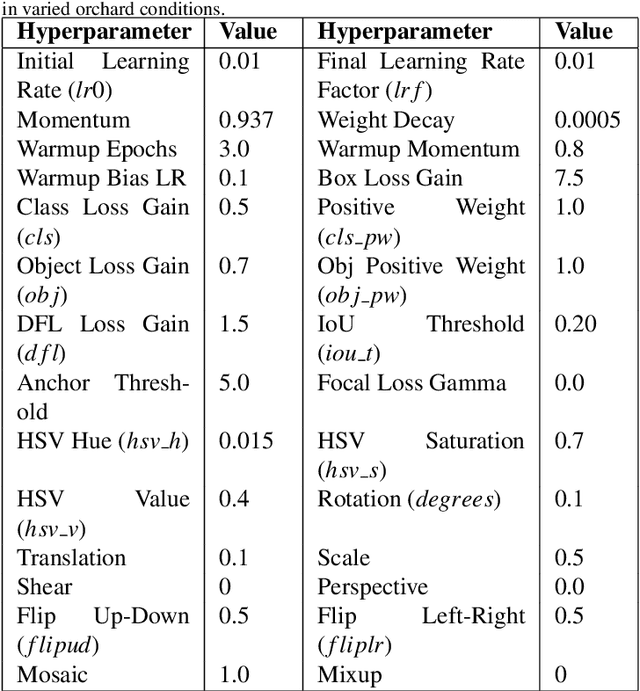
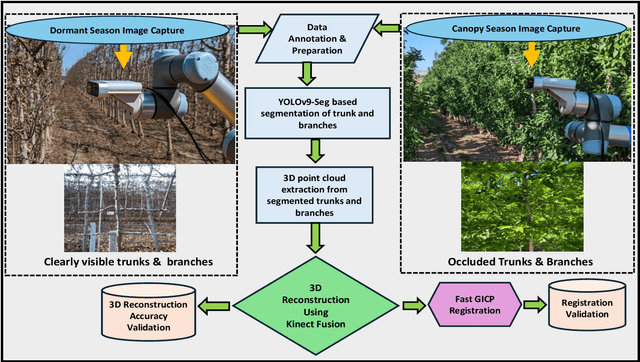
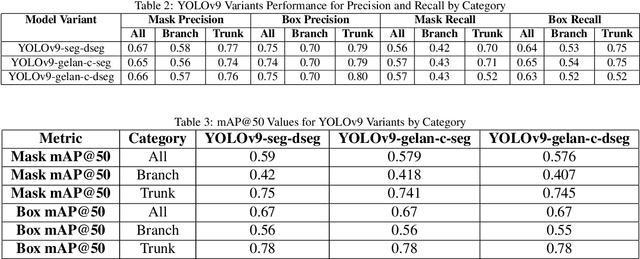
Abstract:In orchard automation, dense foliage during the canopy season severely occludes tree structures, minimizing visibility to various canopy parts such as trunks and branches, which limits the ability of a machine vision system. However, canopy structure is more open and visible during the dormant season when trees are defoliated. In this work, we present an information fusion framework that integrates multi-seasonal structural data to support robotic and automated crop load management during the entire growing season. The framework combines high-resolution RGB-D imagery from both dormant and canopy periods using YOLOv9-Seg for instance segmentation, Kinect Fusion for 3D reconstruction, and Fast Generalized Iterative Closest Point (Fast GICP) for model alignment. Segmentation outputs from YOLOv9-Seg were used to extract depth-informed masks, which enabled accurate 3D point cloud reconstruction via Kinect Fusion; these reconstructed models from each season were subsequently aligned using Fast GICP to achieve spatially coherent multi-season fusion. The YOLOv9-Seg model, trained on manually annotated images, achieved a mean squared error (MSE) of 0.0047 and segmentation mAP@50 scores up to 0.78 for trunks in dormant season dataset. Kinect Fusion enabled accurate reconstruction of tree geometry, validated with field measurements resulting in root mean square errors (RMSE) of 5.23 mm for trunk diameter, 4.50 mm for branch diameter, and 13.72 mm for branch spacing. Fast GICP achieved precise cross-seasonal registration with a minimum fitness score of 0.00197, allowing integrated, comprehensive tree structure modeling despite heavy occlusions during the growing season. This fused structural representation enables robotic systems to access otherwise obscured architectural information, improving the precision of pruning, thinning, and other automated orchard operations.
Thinking Beyond Tokens: From Brain-Inspired Intelligence to Cognitive Foundations for Artificial General Intelligence and its Societal Impact
Jul 01, 2025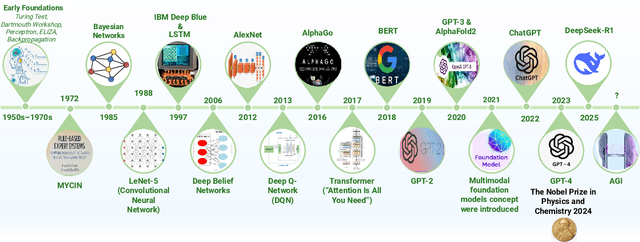
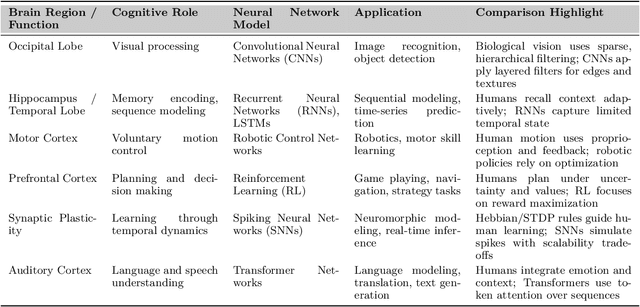
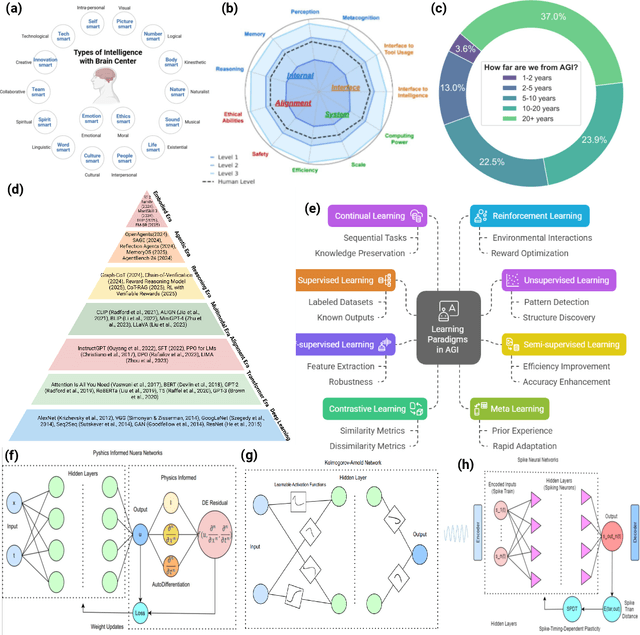
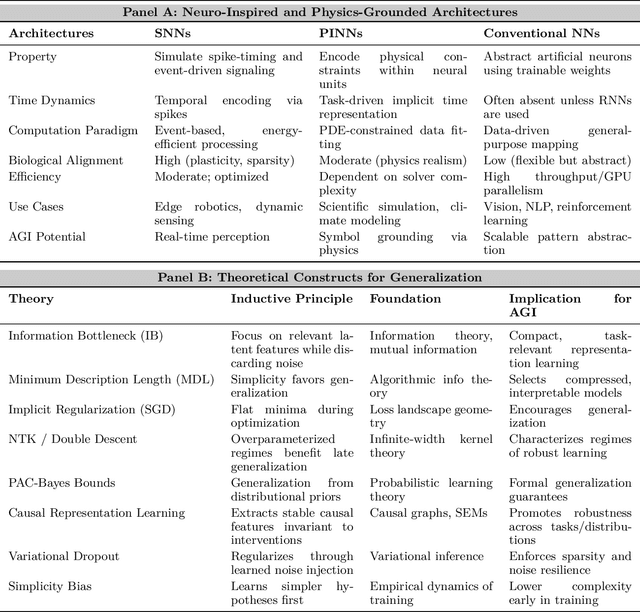
Abstract:Can machines truly think, reason and act in domains like humans? This enduring question continues to shape the pursuit of Artificial General Intelligence (AGI). Despite the growing capabilities of models such as GPT-4.5, DeepSeek, Claude 3.5 Sonnet, Phi-4, and Grok 3, which exhibit multimodal fluency and partial reasoning, these systems remain fundamentally limited by their reliance on token-level prediction and lack of grounded agency. This paper offers a cross-disciplinary synthesis of AGI development, spanning artificial intelligence, cognitive neuroscience, psychology, generative models, and agent-based systems. We analyze the architectural and cognitive foundations of general intelligence, highlighting the role of modular reasoning, persistent memory, and multi-agent coordination. In particular, we emphasize the rise of Agentic RAG frameworks that combine retrieval, planning, and dynamic tool use to enable more adaptive behavior. We discuss generalization strategies, including information compression, test-time adaptation, and training-free methods, as critical pathways toward flexible, domain-agnostic intelligence. Vision-Language Models (VLMs) are reexamined not just as perception modules but as evolving interfaces for embodied understanding and collaborative task completion. We also argue that true intelligence arises not from scale alone but from the integration of memory and reasoning: an orchestration of modular, interactive, and self-improving components where compression enables adaptive behavior. Drawing on advances in neurosymbolic systems, reinforcement learning, and cognitive scaffolding, we explore how recent architectures begin to bridge the gap between statistical learning and goal-directed cognition. Finally, we identify key scientific, technical, and ethical challenges on the path to AGI.
UAVs Meet Agentic AI: A Multidomain Survey of Autonomous Aerial Intelligence and Agentic UAVs
Jun 08, 2025Abstract:Agentic UAVs represent a new frontier in autonomous aerial intelligence, integrating perception, decision-making, memory, and collaborative planning to operate adaptively in complex, real-world environments. Driven by recent advances in Agentic AI, these systems surpass traditional UAVs by exhibiting goal-driven behavior, contextual reasoning, and interactive autonomy. We provide a comprehensive foundation for understanding the architectural components and enabling technologies that distinguish Agentic UAVs from traditional autonomous UAVs. Furthermore, a detailed comparative analysis highlights advancements in autonomy with AI agents, learning, and mission flexibility. This study explores seven high-impact application domains precision agriculture, construction & mining, disaster response, environmental monitoring, infrastructure inspection, logistics, security, and wildlife conservation, illustrating the broad societal value of agentic aerial intelligence. Furthermore, we identify key challenges in technical constraints, regulatory limitations, and data-model reliability, and we present emerging solutions across hardware innovation, learning architectures, and human-AI interaction. Finally, a future roadmap is proposed, outlining pathways toward self-evolving aerial ecosystems, system-level collaboration, and sustainable, equitable deployments. This survey establishes a foundational framework for the future development, deployment, and governance of agentic aerial systems (Agentic UAVs) across diverse societal and industrial domains.
TRiSM for Agentic AI: A Review of Trust, Risk, and Security Management in LLM-based Agentic Multi-Agent Systems
Jun 04, 2025Abstract:Agentic AI systems, built on large language models (LLMs) and deployed in multi-agent configurations, are redefining intelligent autonomy, collaboration and decision-making across enterprise and societal domains. This review presents a structured analysis of Trust, Risk, and Security Management (TRiSM) in the context of LLM-based agentic multi-agent systems (AMAS). We begin by examining the conceptual foundations of agentic AI, its architectural differences from traditional AI agents, and the emerging system designs that enable scalable, tool-using autonomy. The TRiSM in the agentic AI framework is then detailed through four pillars governance, explainability, ModelOps, and privacy/security each contextualized for agentic LLMs. We identify unique threat vectors and introduce a comprehensive risk taxonomy for the agentic AI applications, supported by case studies illustrating real-world vulnerabilities. Furthermore, the paper also surveys trust-building mechanisms, transparency and oversight techniques, and state-of-the-art explainability strategies in distributed LLM agent systems. Additionally, metrics for evaluating trust, interpretability, and human-centered performance are reviewed alongside open benchmarking challenges. Security and privacy are addressed through encryption, adversarial defense, and compliance with evolving AI regulations. The paper concludes with a roadmap for responsible agentic AI, proposing research directions to align emerging multi-agent systems with robust TRiSM principles for safe, accountable, and transparent deployment.
Vibe Coding vs. Agentic Coding: Fundamentals and Practical Implications of Agentic AI
May 26, 2025Abstract:This review presents a comprehensive analysis of two emerging paradigms in AI-assisted software development: vibe coding and agentic coding. While both leverage large language models (LLMs), they differ fundamentally in autonomy, architectural design, and the role of the developer. Vibe coding emphasizes intuitive, human-in-the-loop interaction through prompt-based, conversational workflows that support ideation, experimentation, and creative exploration. In contrast, agentic coding enables autonomous software development through goal-driven agents capable of planning, executing, testing, and iterating tasks with minimal human intervention. We propose a detailed taxonomy spanning conceptual foundations, execution models, feedback loops, safety mechanisms, debugging strategies, and real-world tool ecosystems. Through comparative workflow analysis and 20 detailed use cases, we illustrate how vibe systems thrive in early-stage prototyping and education, while agentic systems excel in enterprise-grade automation, codebase refactoring, and CI/CD integration. We further examine emerging trends in hybrid architectures, where natural language interfaces are coupled with autonomous execution pipelines. Finally, we articulate a future roadmap for agentic AI, outlining the infrastructure needed for trustworthy, explainable, and collaborative systems. Our findings suggest that successful AI software engineering will rely not on choosing one paradigm, but on harmonizing their strengths within a unified, human-centered development lifecycle.
AI Agents vs. Agentic AI: A Conceptual Taxonomy, Applications and Challenge
May 15, 2025Abstract:This study critically distinguishes between AI Agents and Agentic AI, offering a structured conceptual taxonomy, application mapping, and challenge analysis to clarify their divergent design philosophies and capabilities. We begin by outlining the search strategy and foundational definitions, characterizing AI Agents as modular systems driven by Large Language Models (LLMs) and Large Image Models (LIMs) for narrow, task-specific automation. Generative AI is positioned as a precursor, with AI Agents advancing through tool integration, prompt engineering, and reasoning enhancements. In contrast, Agentic AI systems represent a paradigmatic shift marked by multi-agent collaboration, dynamic task decomposition, persistent memory, and orchestrated autonomy. Through a sequential evaluation of architectural evolution, operational mechanisms, interaction styles, and autonomy levels, we present a comparative analysis across both paradigms. Application domains such as customer support, scheduling, and data summarization are contrasted with Agentic AI deployments in research automation, robotic coordination, and medical decision support. We further examine unique challenges in each paradigm including hallucination, brittleness, emergent behavior, and coordination failure and propose targeted solutions such as ReAct loops, RAG, orchestration layers, and causal modeling. This work aims to provide a definitive roadmap for developing robust, scalable, and explainable AI agent and Agentic AI-driven systems. >AI Agents, Agent-driven, Vision-Language-Models, Agentic AI Decision Support System, Agentic-AI Applications
Vision-Language-Action Models: Concepts, Progress, Applications and Challenges
May 07, 2025Abstract:Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models mark a transformative advancement in artificial intelligence, aiming to unify perception, natural language understanding, and embodied action within a single computational framework. This foundational review presents a comprehensive synthesis of recent advancements in Vision-Language-Action models, systematically organized across five thematic pillars that structure the landscape of this rapidly evolving field. We begin by establishing the conceptual foundations of VLA systems, tracing their evolution from cross-modal learning architectures to generalist agents that tightly integrate vision-language models (VLMs), action planners, and hierarchical controllers. Our methodology adopts a rigorous literature review framework, covering over 80 VLA models published in the past three years. Key progress areas include architectural innovations, parameter-efficient training strategies, and real-time inference accelerations. We explore diverse application domains such as humanoid robotics, autonomous vehicles, medical and industrial robotics, precision agriculture, and augmented reality navigation. The review further addresses major challenges across real-time control, multimodal action representation, system scalability, generalization to unseen tasks, and ethical deployment risks. Drawing from the state-of-the-art, we propose targeted solutions including agentic AI adaptation, cross-embodiment generalization, and unified neuro-symbolic planning. In our forward-looking discussion, we outline a future roadmap where VLA models, VLMs, and agentic AI converge to power socially aligned, adaptive, and general-purpose embodied agents. This work serves as a foundational reference for advancing intelligent, real-world robotics and artificial general intelligence. >Vision-language-action, Agentic AI, AI Agents, Vision-language Models
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge