Qiaozhi He
APR: Penalizing Structural Redundancy in Large Reasoning Models via Anchor-based Process Rewards
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:Test-Time Scaling (TTS) has significantly enhanced the capabilities of Large Reasoning Models (LRMs) but introduces a critical side-effect known as Overthinking. We conduct a preliminary study to rethink this phenomenon from a fine-grained perspective. We observe that LRMs frequently conduct repetitive self-verification without revision even after obtaining the final answer during the reasoning process. We formally define this specific position where the answer first stabilizes as the Reasoning Anchor. By analyzing pre- and post-anchor reasoning behaviors, we uncover the structural redundancy fixed in LRMs: the meaningless repetitive verification after deriving the first complete answer, which we term the Answer-Stable Tail (AST). Motivated by this observation, we propose Anchor-based Process Reward (APR), a structure-aware reward shaping method that localizes the reasoning anchor and penalizes exclusively the post-anchor AST. Leveraging the policy optimization algorithm suitable for length penalties, our APR models achieved the performance-efficiency Pareto frontier at 1.5B and 7B scales averaged across five mathematical reasoning datasets while requiring significantly fewer computational resources for RL training.
SERM: Self-Evolving Relevance Model with Agent-Driven Learning from Massive Query Streams
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:Due to the dynamically evolving nature of real-world query streams, relevance models struggle to generalize to practical search scenarios. A sophisticated solution is self-evolution techniques. However, in large-scale industrial settings with massive query streams, this technique faces two challenges: (1) informative samples are often sparse and difficult to identify, and (2) pseudo-labels generated by the current model could be unreliable. To address these challenges, in this work, we propose a Self-Evolving Relevance Model approach (SERM), which comprises two complementary multi-agent modules: a multi-agent sample miner, designed to detect distributional shifts and identify informative training samples, and a multi-agent relevance annotator, which provides reliable labels through a two-level agreement framework. We evaluate SERM in a large-scale industrial setting, which serves billions of user requests daily. Experimental results demonstrate that SERM can achieve significant performance gains through iterative self-evolution, as validated by extensive offline multilingual evaluations and online testing.
Probing Preference Representations: A Multi-Dimensional Evaluation and Analysis Method for Reward Models
Nov 16, 2025Abstract:Previous methods evaluate reward models by testing them on a fixed pairwise ranking test set, but they typically do not provide performance information on each preference dimension. In this work, we address the evaluation challenge of reward models by probing preference representations. To confirm the effectiveness of this evaluation method, we construct a Multi-dimensional Reward Model Benchmark (MRMBench), a collection of six probing tasks for different preference dimensions. We design it to favor and encourage reward models that better capture preferences across different dimensions. Furthermore, we introduce an analysis method, inference-time probing, which identifies the dimensions used during the reward prediction and enhances its interpretability. Through extensive experiments, we find that MRMBench strongly correlates with the alignment performance of large language models (LLMs), making it a reliable reference for developing advanced reward models. Our analysis of MRMBench evaluation results reveals that reward models often struggle to capture preferences across multiple dimensions, highlighting the potential of multi-objective optimization in reward modeling. Additionally, our findings show that the proposed inference-time probing method offers a reliable metric for assessing the confidence of reward predictions, which ultimately improves the alignment of LLMs.
GRAM: A Generative Foundation Reward Model for Reward Generalization
Jun 18, 2025Abstract:In aligning large language models (LLMs), reward models have played an important role, but are standardly trained as discriminative models and rely only on labeled human preference data. In this paper, we explore methods that train reward models using both unlabeled and labeled data. Building on the generative models in LLMs, we develop a generative reward model that is first trained via large-scale unsupervised learning and then fine-tuned via supervised learning. We also show that by using label smoothing, we are in fact optimizing a regularized pairwise ranking loss. This result, in turn, provides a new view of training reward models, which links generative models and discriminative models under the same class of training objectives. The outcome of these techniques is a foundation reward model, which can be applied to a wide range of tasks with little or no further fine-tuning effort. Extensive experiments show that this model generalizes well across several tasks, including response ranking, reinforcement learning from human feedback, and task adaptation with fine-tuning, achieving significant performance improvements over several strong baseline models.
StickMotion: Generating 3D Human Motions by Drawing a Stickman
Mar 05, 2025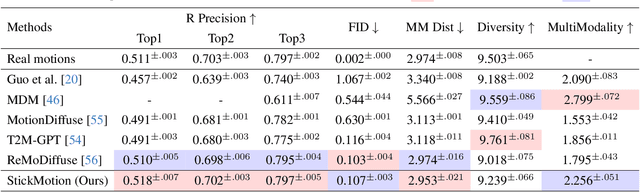
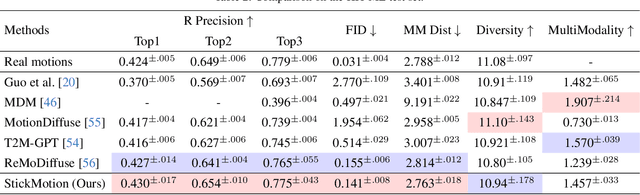
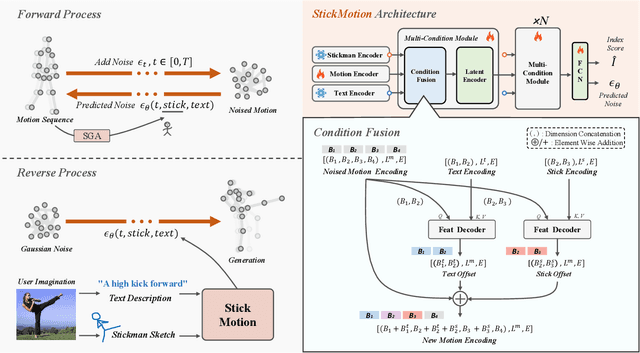
Abstract:Text-to-motion generation, which translates textual descriptions into human motions, has been challenging in accurately capturing detailed user-imagined motions from simple text inputs. This paper introduces StickMotion, an efficient diffusion-based network designed for multi-condition scenarios, which generates desired motions based on traditional text and our proposed stickman conditions for global and local control of these motions, respectively. We address the challenges introduced by the user-friendly stickman from three perspectives: 1) Data generation. We develop an algorithm to generate hand-drawn stickmen automatically across different dataset formats. 2) Multi-condition fusion. We propose a multi-condition module that integrates into the diffusion process and obtains outputs of all possible condition combinations, reducing computational complexity and enhancing StickMotion's performance compared to conventional approaches with the self-attention module. 3) Dynamic supervision. We empower StickMotion to make minor adjustments to the stickman's position within the output sequences, generating more natural movements through our proposed dynamic supervision strategy. Through quantitative experiments and user studies, sketching stickmen saves users about 51.5% of their time generating motions consistent with their imagination. Our codes, demos, and relevant data will be released to facilitate further research and validation within the scientific community.
Boosting Text-To-Image Generation via Multilingual Prompting in Large Multimodal Models
Jan 13, 2025Abstract:Previous work on augmenting large multimodal models (LMMs) for text-to-image (T2I) generation has focused on enriching the input space of in-context learning (ICL). This includes providing a few demonstrations and optimizing image descriptions to be more detailed and logical. However, as demand for more complex and flexible image descriptions grows, enhancing comprehension of input text within the ICL paradigm remains a critical yet underexplored area. In this work, we extend this line of research by constructing parallel multilingual prompts aimed at harnessing the multilingual capabilities of LMMs. More specifically, we translate the input text into several languages and provide the models with both the original text and the translations. Experiments on two LMMs across 3 benchmarks show that our method, PMT2I, achieves superior performance in general, compositional, and fine-grained assessments, especially in human preference alignment. Additionally, with its advantage of generating more diverse images, PMT2I significantly outperforms baseline prompts when incorporated with reranking methods. Our code and parallel multilingual data can be found at https://github.com/takagi97/PMT2I.
LRHP: Learning Representations for Human Preferences via Preference Pairs
Oct 06, 2024



Abstract:To improve human-preference alignment training, current research has developed numerous preference datasets consisting of preference pairs labeled as "preferred" or "dispreferred". These preference pairs are typically used to encode human preferences into a single numerical value through reward modeling, which acts as a reward signal during reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF). However, representing these human preferences as a numerical value complicates the analysis of these preferences and restricts their broader applications other than RLHF. In contrast, in this work, we introduce a preference representation learning task that aims to construct a richer and more structured representation of human preferences. We further develop a more generalizable framework, Learning Representations for Human Preferences via preference pairs (namely LRHP), which extends beyond traditional reward modeling to tackle this task. We verify the utility of preference representations in two downstream tasks: preference data selection and preference margin prediction. Building upon the human preferences in representations, we achieve strong performance in both tasks, significantly outperforming baselines.
RoVRM: A Robust Visual Reward Model Optimized via Auxiliary Textual Preference Data
Aug 22, 2024



Abstract:Large vision-language models (LVLMs) often fail to align with human preferences, leading to issues like generating misleading content without proper visual context (also known as hallucination). A promising solution to this problem is using human-preference alignment techniques, such as best-of-n sampling and reinforcement learning. However, these techniques face the difficulty arising from the scarcity of visual preference data, which is required to train a visual reward model (VRM). In this work, we continue the line of research. We present a Robust Visual Reward Model (RoVRM) which improves human-preference alignment for LVLMs. RoVRM leverages auxiliary textual preference data through a three-phase progressive training and optimal transport-based preference data selection to effectively mitigate the scarcity of visual preference data. We experiment with RoVRM on the commonly used vision-language tasks based on the LLaVA-1.5-7B and -13B models. Experimental results demonstrate that RoVRM consistently outperforms traditional VRMs. Furthermore, our three-phase progressive training and preference data selection approaches can yield consistent performance gains over ranking-based alignment techniques, such as direct preference optimization.
Cross-layer Attention Sharing for Large Language Models
Aug 04, 2024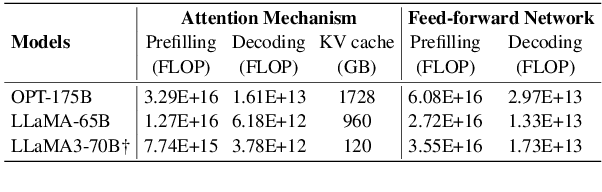
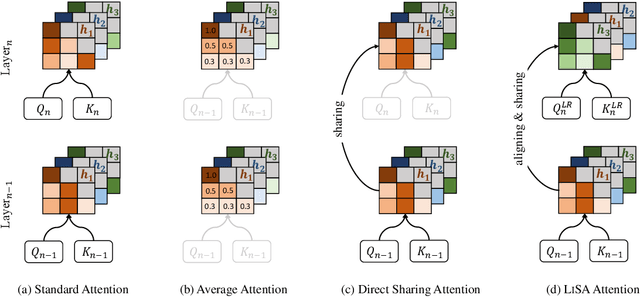
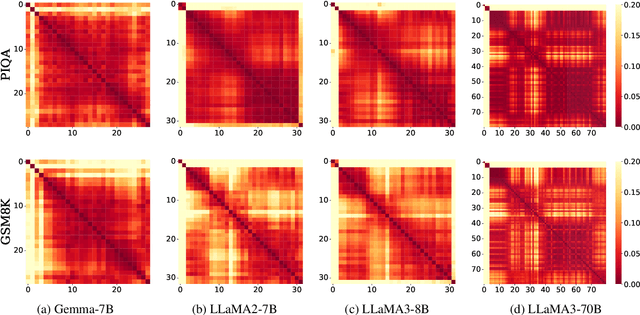
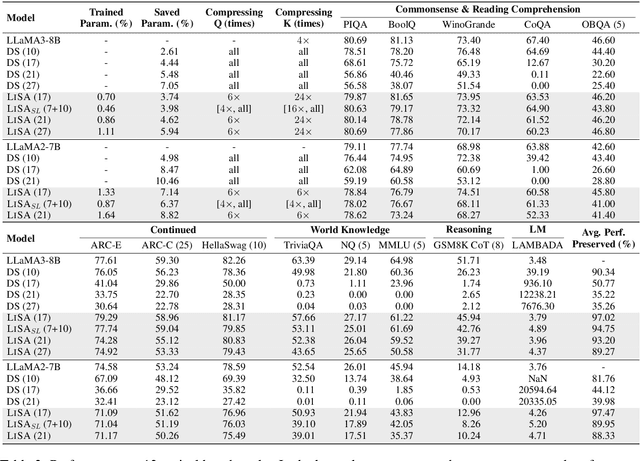
Abstract:As large language models (LLMs) evolve, the increase in model depth and parameter number leads to substantial redundancy. To enhance the efficiency of the attention mechanism, previous works primarily compress the KV cache or group attention heads, while largely overlooking redundancy between layers. Our comprehensive analyses across various LLMs show that highly similar attention patterns persist within most layers. It's intuitive to save the computation by sharing attention weights across layers. However, further analysis reveals two challenges: (1) Directly sharing the weight matrix without carefully rearranging the attention heads proves to be ineffective; (2) Shallow layers are vulnerable to small deviations in attention weights. Driven by these insights, we introduce LiSA, a lightweight substitute for self-attention in well-trained LLMs. LiSA employs tiny feed-forward networks to align attention heads between adjacent layers and low-rank matrices to approximate differences in layer-wise attention weights. Evaluations encompassing 13 typical benchmarks demonstrate that LiSA maintains high response quality in terms of accuracy and perplexity while reducing redundant attention calculations within 53-84% of the total layers. Our implementations of LiSA achieve a 6X compression of Q and K, with maximum throughput improvements of 19.5% for LLaMA3-8B and 32.3% for LLaMA2-7B.
ChuXin: 1.6B Technical Report
May 08, 2024



Abstract:In this report, we present ChuXin, an entirely open-source language model with a size of 1.6 billion parameters. Unlike the majority of works that only open-sourced the model weights and architecture, we have made everything needed to train a model available, including the training data, the training process, and the evaluation code. Our goal is to empower and strengthen the open research community, fostering transparency and enabling a new wave of innovation in the field of language modeling. Furthermore, we extend the context length to 1M tokens through lightweight continual pretraining and demonstrate strong needle-in-a-haystack retrieval performance. The weights for both models are available at Hugging Face to download and use.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge