Yufan Jiang
Robust Skin Color Driven Privacy Preserving Face Recognition via Function Secret Sharing
Jul 06, 2024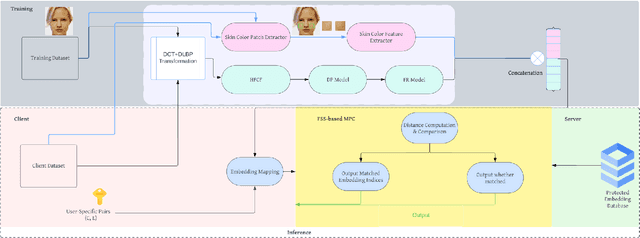

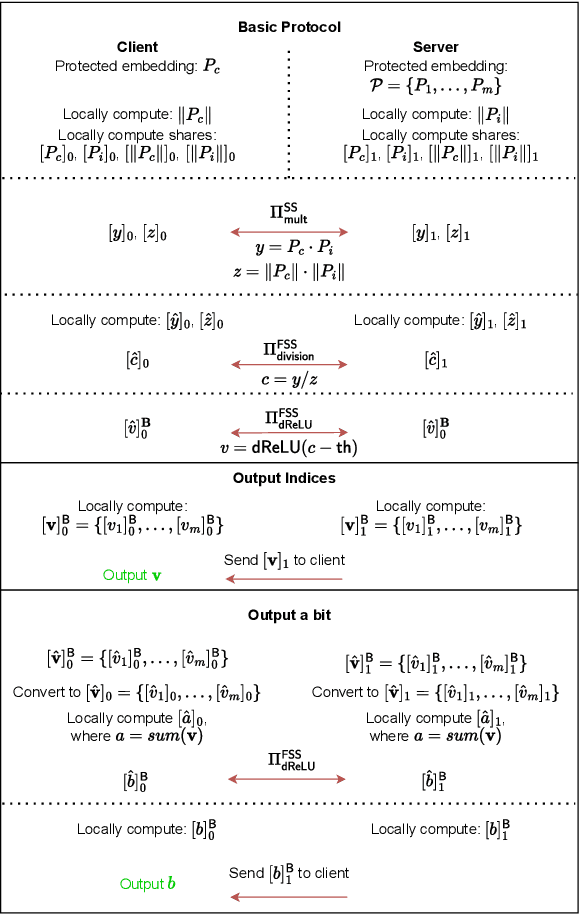

Abstract:In this work, we leverage the pure skin color patch from the face image as the additional information to train an auxiliary skin color feature extractor and face recognition model in parallel to improve performance of state-of-the-art (SOTA) privacy-preserving face recognition (PPFR) systems. Our solution is robust against black-box attacking and well-established generative adversarial network (GAN) based image restoration. We analyze the potential risk in previous work, where the proposed cosine similarity computation might directly leak the protected precomputed embedding stored on the server side. We propose a Function Secret Sharing (FSS) based face embedding comparison protocol without any intermediate result leakage. In addition, we show in experiments that the proposed protocol is more efficient compared to the Secret Sharing (SS) based protocol.
ChuXin: 1.6B Technical Report
May 08, 2024



Abstract:In this report, we present ChuXin, an entirely open-source language model with a size of 1.6 billion parameters. Unlike the majority of works that only open-sourced the model weights and architecture, we have made everything needed to train a model available, including the training data, the training process, and the evaluation code. Our goal is to empower and strengthen the open research community, fostering transparency and enabling a new wave of innovation in the field of language modeling. Furthermore, we extend the context length to 1M tokens through lightweight continual pretraining and demonstrate strong needle-in-a-haystack retrieval performance. The weights for both models are available at Hugging Face to download and use.
Transfer Learning Enhanced Single-choice Decision for Multi-choice Question Answering
Apr 27, 2024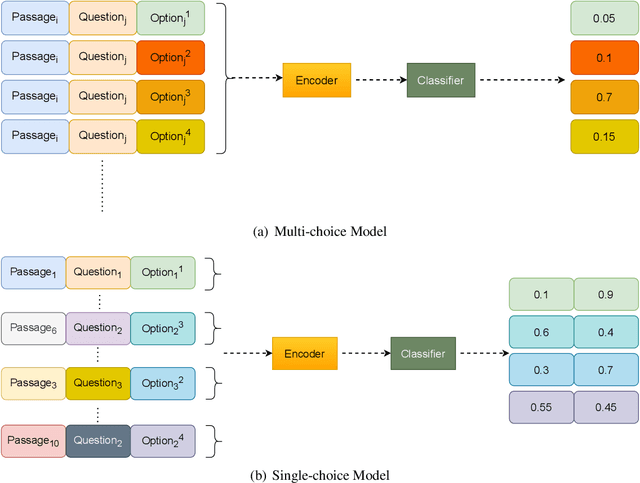



Abstract:Multi-choice Machine Reading Comprehension (MMRC) aims to select the correct answer from a set of options based on a given passage and question. The existing methods employ the pre-trained language model as the encoder, share and transfer knowledge through fine-tuning.These methods mainly focus on the design of exquisite mechanisms to effectively capture the relationships among the triplet of passage, question and answers. It is non-trivial but ignored to transfer knowledge from other MRC tasks such as SQuAD due to task specific of MMRC.In this paper, we reconstruct multi-choice to single-choice by training a binary classification to distinguish whether a certain answer is correct. Then select the option with the highest confidence score as the final answer. Our proposed method gets rid of the multi-choice framework and can leverage resources of other tasks. We construct our model based on the ALBERT-xxlarge model and evaluate it on the RACE and DREAM datasets. Experimental results show that our model performs better than multi-choice methods. In addition, by transferring knowledge from other kinds of MRC tasks, our model achieves state-of-the-art results in both single and ensemble settings.
Code Comparison Tuning for Code Large Language Models
Mar 28, 2024



Abstract:We present Code Comparison Tuning (CCT), a simple and effective tuning method for code large language models (Code LLMs) to better handle subtle code errors. Specifically, we integrate the concept of comparison into instruction tuning, both at the token and sequence levels, enabling the model to discern even the slightest deviations in code. To compare the original code with an erroneous version containing manually added code errors, we use token-level preference loss for detailed token-level comparisons. Additionally, we combine code segments to create a new instruction tuning sample for sequence-level comparisons, enhancing the model's bug-fixing capability. Experimental results on the HumanEvalFix benchmark show that CCT surpasses instruction tuning in pass@1 scores by up to 4 points across diverse code LLMs, and extensive analysis demonstrates the effectiveness of our method.
RecycleGPT: An Autoregressive Language Model with Recyclable Module
Aug 08, 2023Abstract:Existing large language models have to run K times to generate a sequence of K tokens. In this paper, we present RecycleGPT, a generative language model with fast decoding speed by recycling pre-generated model states without running the whole model in multiple steps. Our approach relies on the observation that adjacent tokens in a sequence usually have strong correlations and the next token in a sequence can be reasonably guessed or inferred based on the preceding ones. Experiments and analysis demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach in lowering inference latency, achieving up to 1.4x speedup while preserving high performance.
Soft Language Clustering for Multilingual Model Pre-training
Jun 13, 2023
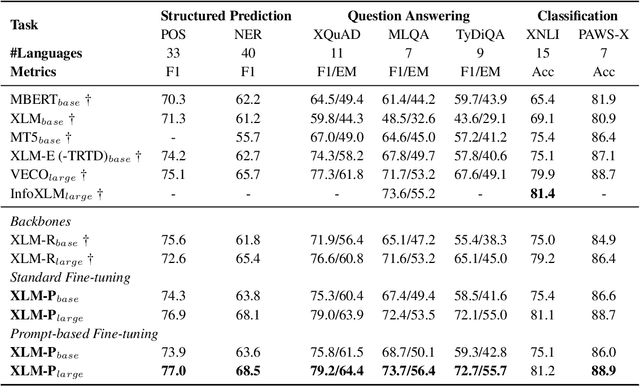
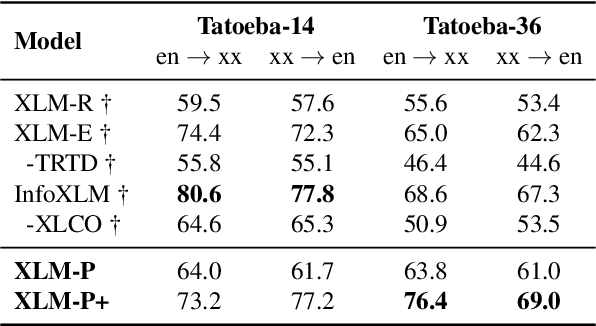
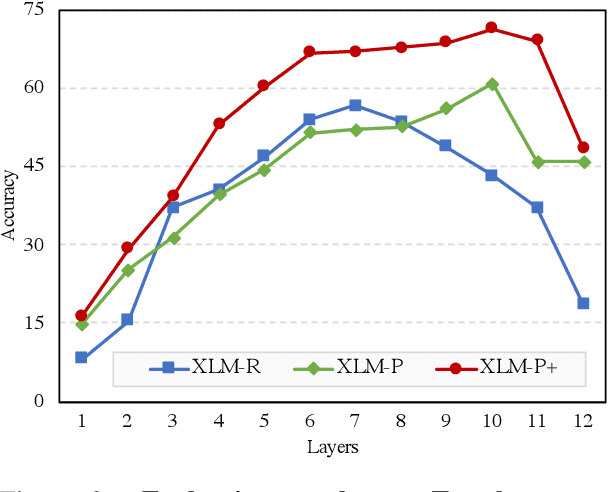
Abstract:Multilingual pre-trained language models have demonstrated impressive (zero-shot) cross-lingual transfer abilities, however, their performance is hindered when the target language has distant typology from source languages or when pre-training data is limited in size. In this paper, we propose XLM-P, which contextually retrieves prompts as flexible guidance for encoding instances conditionally. Our XLM-P enables (1) lightweight modeling of language-invariant and language-specific knowledge across languages, and (2) easy integration with other multilingual pre-training methods. On the tasks of XTREME including text classification, sequence labeling, question answering, and sentence retrieval, both base- and large-size language models pre-trained with our proposed method exhibit consistent performance improvement. Furthermore, it provides substantial advantages for low-resource languages in unsupervised sentence retrieval and for target languages that differ greatly from the source language in cross-lingual transfer.
DialogQAE: N-to-N Question Answer Pair Extraction from Customer Service Chatlog
Dec 14, 2022



Abstract:Harvesting question-answer (QA) pairs from customer service chatlog in the wild is an efficient way to enrich the knowledge base for customer service chatbots in the cold start or continuous integration scenarios. Prior work attempts to obtain 1-to-1 QA pairs from growing customer service chatlog, which fails to integrate the incomplete utterances from the dialog context for composite QA retrieval. In this paper, we propose N-to-N QA extraction task in which the derived questions and corresponding answers might be separated across different utterances. We introduce a suite of generative/discriminative tagging based methods with end-to-end and two-stage variants that perform well on 5 customer service datasets and for the first time setup a benchmark for N-to-N DialogQAE with utterance and session level evaluation metrics. With a deep dive into extracted QA pairs, we find that the relations between and inside the QA pairs can be indicators to analyze the dialogue structure, e.g. information seeking, clarification, barge-in and elaboration. We also show that the proposed models can adapt to different domains and languages, and reduce the labor cost of knowledge accumulation in the real-world product dialogue platform.
DualNER: A Dual-Teaching framework for Zero-shot Cross-lingual Named Entity Recognition
Nov 15, 2022



Abstract:We present DualNER, a simple and effective framework to make full use of both annotated source language corpus and unlabeled target language text for zero-shot cross-lingual named entity recognition (NER). In particular, we combine two complementary learning paradigms of NER, i.e., sequence labeling and span prediction, into a unified multi-task framework. After obtaining a sufficient NER model trained on the source data, we further train it on the target data in a {\it dual-teaching} manner, in which the pseudo-labels for one task are constructed from the prediction of the other task. Moreover, based on the span prediction, an entity-aware regularization is proposed to enhance the intrinsic cross-lingual alignment between the same entities in different languages. Experiments and analysis demonstrate the effectiveness of our DualNER. Code is available at https://github.com/lemon0830/dualNER.
Contrastive Learning with Prompt-derived Virtual Semantic Prototypes for Unsupervised Sentence Embedding
Nov 07, 2022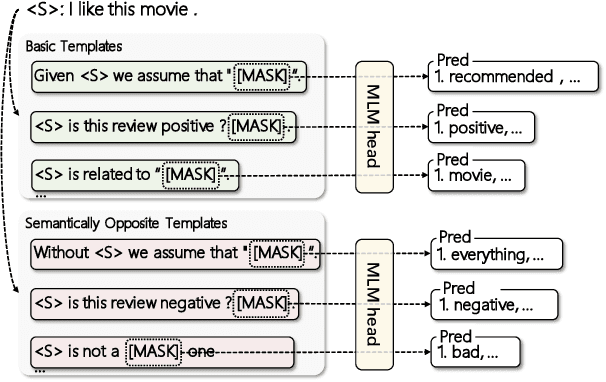

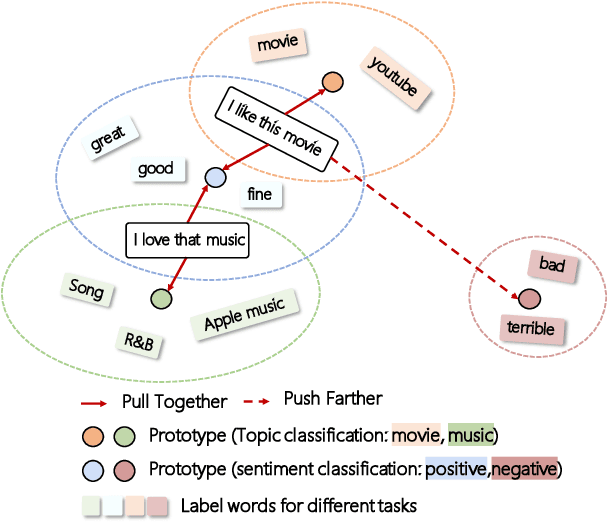
Abstract:Contrastive learning has become a new paradigm for unsupervised sentence embeddings. Previous studies focus on instance-wise contrastive learning, attempting to construct positive pairs with textual data augmentation. In this paper, we propose a novel Contrastive learning method with Prompt-derived Virtual semantic Prototypes (ConPVP). Specifically, with the help of prompts, we construct virtual semantic prototypes to each instance, and derive negative prototypes by using the negative form of the prompts. Using a prototypical contrastive loss, we enforce the anchor sentence embedding to be close to its corresponding semantic prototypes, and far apart from the negative prototypes as well as the prototypes of other sentences. Extensive experimental results on semantic textual similarity, transfer, and clustering tasks demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed model compared to strong baselines. Code is available at https://github.com/lemon0830/promptCSE.
Modeling Paragraph-Level Vision-Language Semantic Alignment for Multi-Modal Summarization
Aug 24, 2022
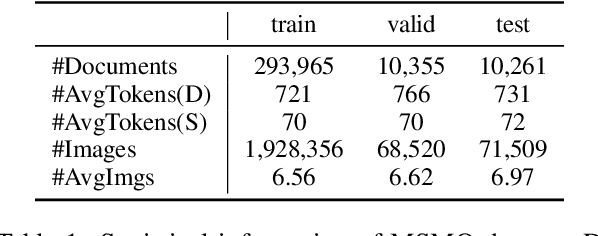
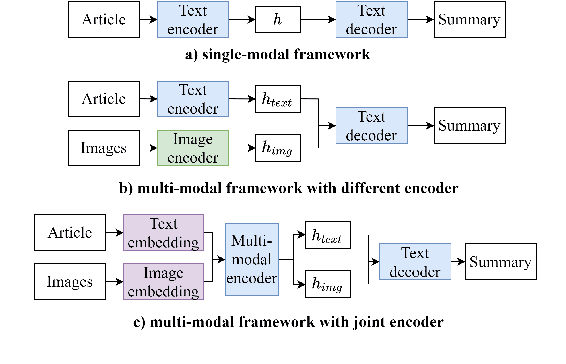
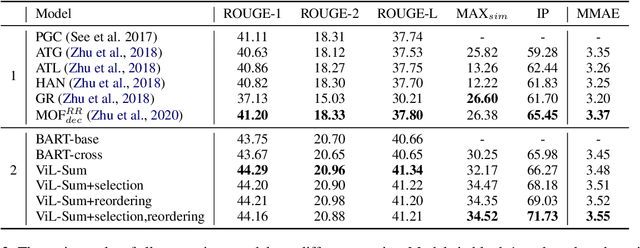
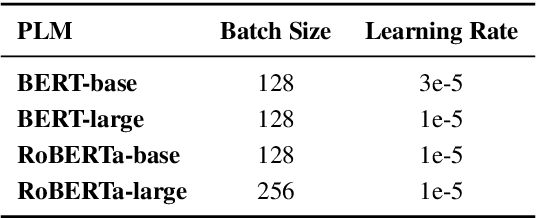
Abstract:Most current multi-modal summarization methods follow a cascaded manner, where an off-the-shelf object detector is first used to extract visual features, then these features are fused with language representations to generate the summary with an encoder-decoder model. The cascaded way cannot capture the semantic alignments between images and paragraphs, which are crucial to a precise summary. In this paper, we propose ViL-Sum to jointly model paragraph-level \textbf{Vi}sion-\textbf{L}anguage Semantic Alignment and Multi-Modal \textbf{Sum}marization. The core of ViL-Sum is a joint multi-modal encoder with two well-designed tasks, image reordering and image selection. The joint multi-modal encoder captures the interactions between modalities, where the reordering task guides the model to learn paragraph-level semantic alignment and the selection task guides the model to selected summary-related images in the final summary. Experimental results show that our proposed ViL-Sum significantly outperforms current state-of-the-art methods. In further analysis, we find that two well-designed tasks and joint multi-modal encoder can effectively guide the model to learn reasonable paragraphs-images and summary-images relations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge