Chenhao Cui
Transfer Learning Enhanced Single-choice Decision for Multi-choice Question Answering
Apr 27, 2024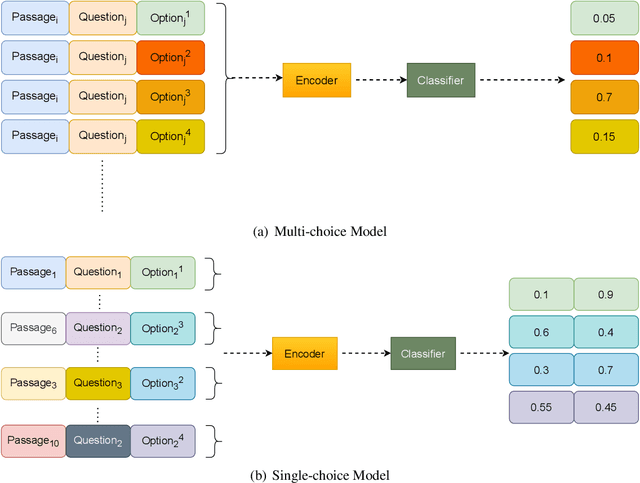



Abstract:Multi-choice Machine Reading Comprehension (MMRC) aims to select the correct answer from a set of options based on a given passage and question. The existing methods employ the pre-trained language model as the encoder, share and transfer knowledge through fine-tuning.These methods mainly focus on the design of exquisite mechanisms to effectively capture the relationships among the triplet of passage, question and answers. It is non-trivial but ignored to transfer knowledge from other MRC tasks such as SQuAD due to task specific of MMRC.In this paper, we reconstruct multi-choice to single-choice by training a binary classification to distinguish whether a certain answer is correct. Then select the option with the highest confidence score as the final answer. Our proposed method gets rid of the multi-choice framework and can leverage resources of other tasks. We construct our model based on the ALBERT-xxlarge model and evaluate it on the RACE and DREAM datasets. Experimental results show that our model performs better than multi-choice methods. In addition, by transferring knowledge from other kinds of MRC tasks, our model achieves state-of-the-art results in both single and ensemble settings.
Enhancing Dialogue Summarization with Topic-Aware Global- and Local- Level Centrality
Jan 29, 2023



Abstract:Dialogue summarization aims to condense a given dialogue into a simple and focused summary text. Typically, both the roles' viewpoints and conversational topics change in the dialogue stream. Thus how to effectively handle the shifting topics and select the most salient utterance becomes one of the major challenges of this task. In this paper, we propose a novel topic-aware Global-Local Centrality (GLC) model to help select the salient context from all sub-topics. The centralities are constructed at both the global and local levels. The global one aims to identify vital sub-topics in the dialogue and the local one aims to select the most important context in each sub-topic. Specifically, the GLC collects sub-topic based on the utterance representations. And each utterance is aligned with one sub-topic. Based on the sub-topics, the GLC calculates global- and local-level centralities. Finally, we combine the two to guide the model to capture both salient context and sub-topics when generating summaries. Experimental results show that our model outperforms strong baselines on three public dialogue summarization datasets: CSDS, MC, and SAMSUM. Further analysis demonstrates that our GLC can exactly identify vital contents from sub-topics.~\footnote{\url{https://github.com/xnliang98/bart-glc}}
Modeling Paragraph-Level Vision-Language Semantic Alignment for Multi-Modal Summarization
Aug 24, 2022
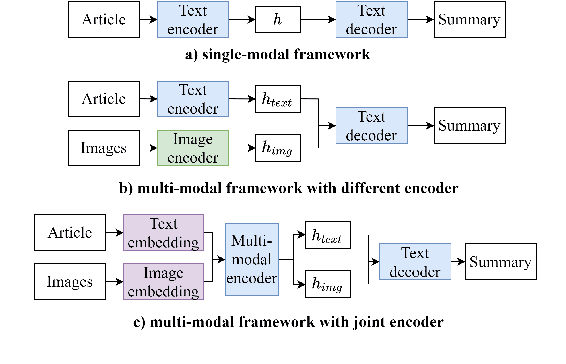
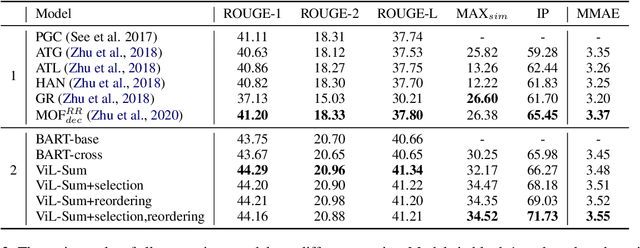
Abstract:Most current multi-modal summarization methods follow a cascaded manner, where an off-the-shelf object detector is first used to extract visual features, then these features are fused with language representations to generate the summary with an encoder-decoder model. The cascaded way cannot capture the semantic alignments between images and paragraphs, which are crucial to a precise summary. In this paper, we propose ViL-Sum to jointly model paragraph-level \textbf{Vi}sion-\textbf{L}anguage Semantic Alignment and Multi-Modal \textbf{Sum}marization. The core of ViL-Sum is a joint multi-modal encoder with two well-designed tasks, image reordering and image selection. The joint multi-modal encoder captures the interactions between modalities, where the reordering task guides the model to learn paragraph-level semantic alignment and the selection task guides the model to selected summary-related images in the final summary. Experimental results show that our proposed ViL-Sum significantly outperforms current state-of-the-art methods. In further analysis, we find that two well-designed tasks and joint multi-modal encoder can effectively guide the model to learn reasonable paragraphs-images and summary-images relations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge