Qintong Li
DynaAct: Large Language Model Reasoning with Dynamic Action Spaces
Nov 11, 2025Abstract:In modern sequential decision-making systems, the construction of an optimal candidate action space is critical to efficient inference. However, existing approaches either rely on manually defined action spaces that lack scalability or utilize unstructured spaces that render exhaustive search computationally prohibitive. In this paper, we propose a novel framework named \textsc{DynaAct} for automatically constructing a compact action space to enhance sequential reasoning in complex problem-solving scenarios. Our method first estimates a proxy for the complete action space by extracting general sketches observed in a corpus covering diverse complex reasoning problems using large language models. We then formulate a submodular function that jointly evaluates candidate actions based on their utility to the current state and their diversity, and employ a greedy algorithm to select an optimal candidate set. Extensive experiments on six diverse standard benchmarks demonstrate that our approach significantly improves overall performance, while maintaining efficient inference without introducing substantial latency. The implementation is available at https://github.com/zhaoxlpku/DynaAct.
ScienceBoard: Evaluating Multimodal Autonomous Agents in Realistic Scientific Workflows
May 26, 2025



Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have extended their impact beyond Natural Language Processing, substantially fostering the development of interdisciplinary research. Recently, various LLM-based agents have been developed to assist scientific discovery progress across multiple aspects and domains. Among these, computer-using agents, capable of interacting with operating systems as humans do, are paving the way to automated scientific problem-solving and addressing routines in researchers' workflows. Recognizing the transformative potential of these agents, we introduce ScienceBoard, which encompasses two complementary contributions: (i) a realistic, multi-domain environment featuring dynamic and visually rich scientific workflows with integrated professional software, where agents can autonomously interact via different interfaces to accelerate complex research tasks and experiments; and (ii) a challenging benchmark of 169 high-quality, rigorously validated real-world tasks curated by humans, spanning scientific-discovery workflows in domains such as biochemistry, astronomy, and geoinformatics. Extensive evaluations of agents with state-of-the-art backbones (e.g., GPT-4o, Claude 3.7, UI-TARS) show that, despite some promising results, they still fall short of reliably assisting scientists in complex workflows, achieving only a 15% overall success rate. In-depth analysis further provides valuable insights for addressing current agent limitations and more effective design principles, paving the way to build more capable agents for scientific discovery. Our code, environment, and benchmark are at https://qiushisun.github.io/ScienceBoard-Home/.
Activation-Guided Consensus Merging for Large Language Models
May 20, 2025Abstract:Recent research has increasingly focused on reconciling the reasoning capabilities of System 2 with the efficiency of System 1. While existing training-based and prompt-based approaches face significant challenges in terms of efficiency and stability, model merging emerges as a promising strategy to integrate the diverse capabilities of different Large Language Models (LLMs) into a unified model. However, conventional model merging methods often assume uniform importance across layers, overlooking the functional heterogeneity inherent in neural components. To address this limitation, we propose \textbf{A}ctivation-Guided \textbf{C}onsensus \textbf{M}erging (\textbf{ACM}), a plug-and-play merging framework that determines layer-specific merging coefficients based on mutual information between activations of pre-trained and fine-tuned models. ACM effectively preserves task-specific capabilities without requiring gradient computations or additional training. Extensive experiments on Long-to-Short (L2S) and general merging tasks demonstrate that ACM consistently outperforms all baseline methods. For instance, in the case of Qwen-7B models, TIES-Merging equipped with ACM achieves a \textbf{55.3\%} reduction in response length while simultaneously improving reasoning accuracy by \textbf{1.3} points. We submit the code with the paper for reproducibility, and it will be publicly available.
TreeSynth: Synthesizing Diverse Data from Scratch via Tree-Guided Subspace Partitioning
Mar 21, 2025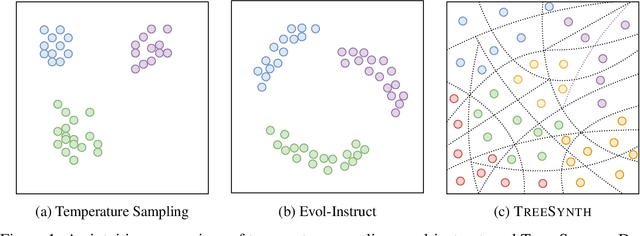
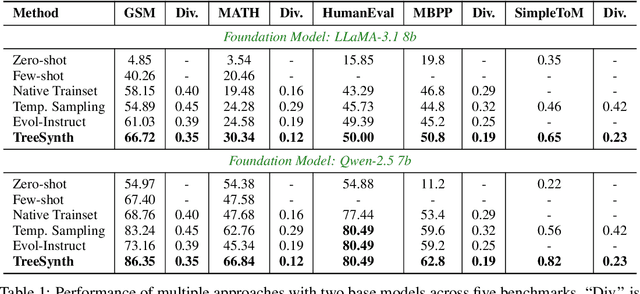
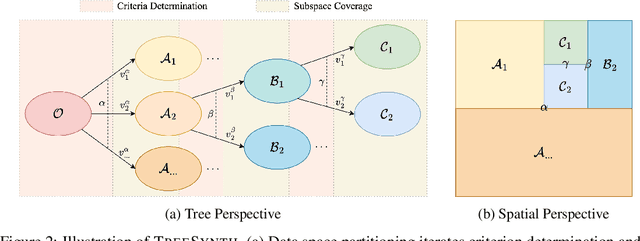
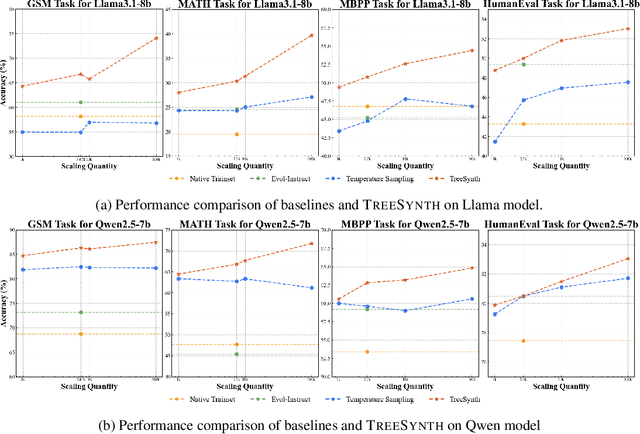
Abstract:Model customization requires high-quality and diverse datasets, but acquiring such data remains challenging and costly. Although large language models (LLMs) can synthesize training data, current approaches are constrained by limited seed data, model bias and insufficient control over the generation process, resulting in limited diversity and biased distribution with the increase of data scales. To tackle this challenge, we present TreeSynth, a tree-guided subspace-based data synthesis framework that recursively partitions the entire data space into hierar-chical subspaces, enabling comprehensive and diverse scaling of data synthesis. Briefly, given a task-specific description, we construct a data space partitioning tree by iteratively executing criteria determination and subspace coverage steps. This hierarchically divides the whole space (i.e., root node) into mutually exclusive and complementary atomic subspaces (i.e., leaf nodes). By collecting synthesized data according to the attributes of each leaf node, we obtain a diverse dataset that fully covers the data space. Empirically, our extensive experiments demonstrate that TreeSynth surpasses both human-designed datasets and the state-of-the-art data synthesis baselines, achieving maximum improvements of 45.2% in data diversity and 17.6% in downstream task performance across various models and tasks. Hopefully, TreeSynth provides a scalable solution to synthesize diverse and comprehensive datasets from scratch without human intervention.
Forewarned is Forearmed: Leveraging LLMs for Data Synthesis through Failure-Inducing Exploration
Oct 22, 2024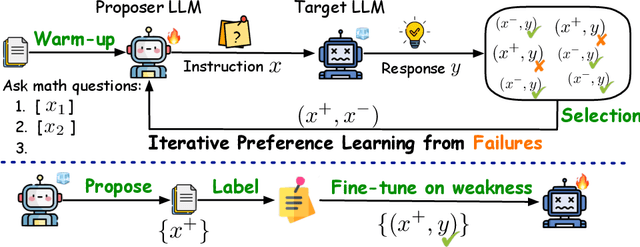
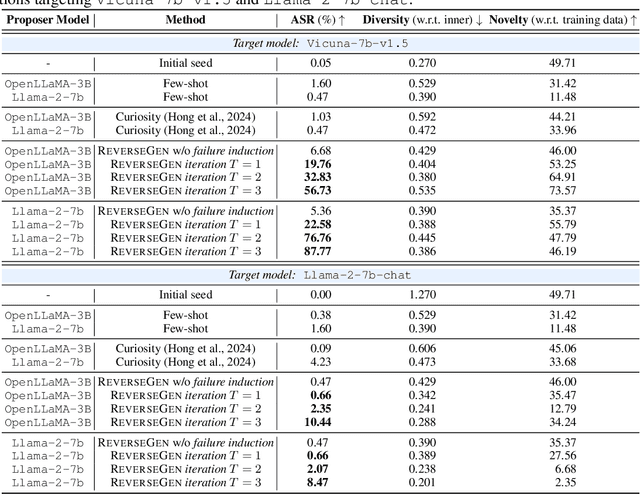
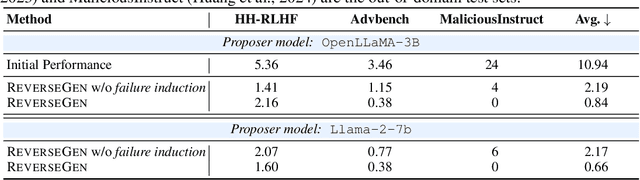
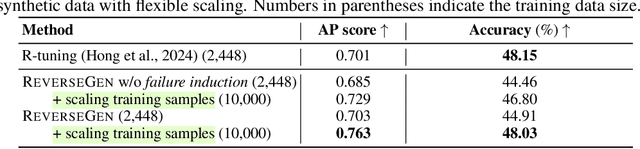
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have significantly benefited from training on diverse, high-quality task-specific data, leading to impressive performance across a range of downstream applications. Current methods often rely on human-annotated data or predefined task templates to direct powerful LLMs in synthesizing task-relevant data for effective model training. However, this dependence on manually designed components may constrain the scope of generated data, potentially overlooking critical edge cases or novel scenarios that could challenge the model. In this paper, we present a novel approach, ReverseGen, designed to automatically generate effective training samples that expose the weaknesses of LLMs. Specifically, we introduce a dedicated proposer trained to produce queries that lead target models to generate unsatisfactory responses. These failure-inducing queries are then used to construct training data, helping to address the models' shortcomings and improve overall performance. Our approach is flexible and can be applied to models of various scales (3B, 7B, and 8B). We evaluate ReverseGen on three key applications (safety, honesty, and math), demonstrating that our generated data is both highly effective and diverse. Models fine-tuned with ReverseGen-generated data consistently outperform those trained on human-annotated or general model-generated data, offering a new perspective on data synthesis for task-specific LLM enhancement.
Privacy in LLM-based Recommendation: Recent Advances and Future Directions
Jun 03, 2024Abstract:Nowadays, large language models (LLMs) have been integrated with conventional recommendation models to improve recommendation performance. However, while most of the existing works have focused on improving the model performance, the privacy issue has only received comparatively less attention. In this paper, we review recent advancements in privacy within LLM-based recommendation, categorizing them into privacy attacks and protection mechanisms. Additionally, we highlight several challenges and propose future directions for the community to address these critical problems.
GSM-Plus: A Comprehensive Benchmark for Evaluating the Robustness of LLMs as Mathematical Problem Solvers
Feb 29, 2024



Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have achieved impressive performance across various mathematical reasoning benchmarks. However, there are increasing debates regarding whether these models truly understand and apply mathematical knowledge or merely rely on shortcuts for mathematical reasoning. One essential and frequently occurring evidence is that when the math questions are slightly changed, LLMs can behave incorrectly. This motivates us to evaluate the robustness of LLMs' math reasoning capability by testing a wide range of question variations. We introduce the adversarial grade school math (\datasetname) dataset, an extension of GSM8K augmented with various mathematical perturbations. Our experiments on 25 LLMs and 4 prompting techniques show that while LLMs exhibit different levels of math reasoning abilities, their performances are far from robust. In particular, even for problems that have been solved in GSM8K, LLMs can make mistakes when new statements are added or the question targets are altered. We also explore whether more robust performance can be achieved by composing existing prompting methods, in which we try an iterative method that generates and verifies each intermediate thought based on its reasoning goal and calculation result. Code and data are available at \url{https://github.com/qtli/GSM-Plus}.
BBA: Bi-Modal Behavioral Alignment for Reasoning with Large Vision-Language Models
Feb 21, 2024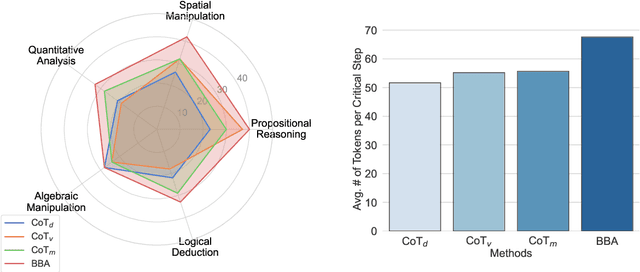
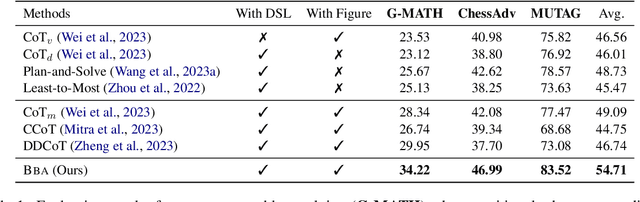
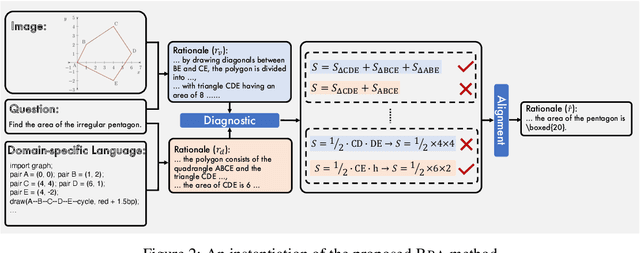
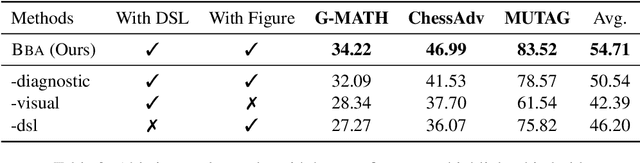
Abstract:Multimodal reasoning stands as a pivotal capability for large vision-language models (LVLMs). The integration with Domain-Specific Languages (DSL), offering precise visual representations, equips these models with the opportunity to execute more accurate reasoning in complex and professional domains. However, the vanilla Chain-of-Thought (CoT) prompting method faces challenges in effectively leveraging the unique strengths of visual and DSL representations, primarily due to their differing reasoning mechanisms. Additionally, it often falls short in addressing critical steps in multi-step reasoning tasks. To mitigate these challenges, we introduce the \underline{B}i-Modal \underline{B}ehavioral \underline{A}lignment (BBA) prompting method, designed to maximize the potential of DSL in augmenting complex multi-modal reasoning tasks. This method initiates by guiding LVLMs to create separate reasoning chains for visual and DSL representations. Subsequently, it aligns these chains by addressing any inconsistencies, thus achieving a cohesive integration of behaviors from different modalities. Our experiments demonstrate that BBA substantially improves the performance of GPT-4V(ision) on geometry problem solving ($28.34\% \to 34.22\%$), chess positional advantage prediction ($42.08\% \to 46.99\%$) and molecular property prediction ($77.47\% \to 83.52\%$).
Collaborative Evaluation: Exploring the Synergy of Large Language Models and Humans for Open-ended Generation Evaluation
Oct 30, 2023
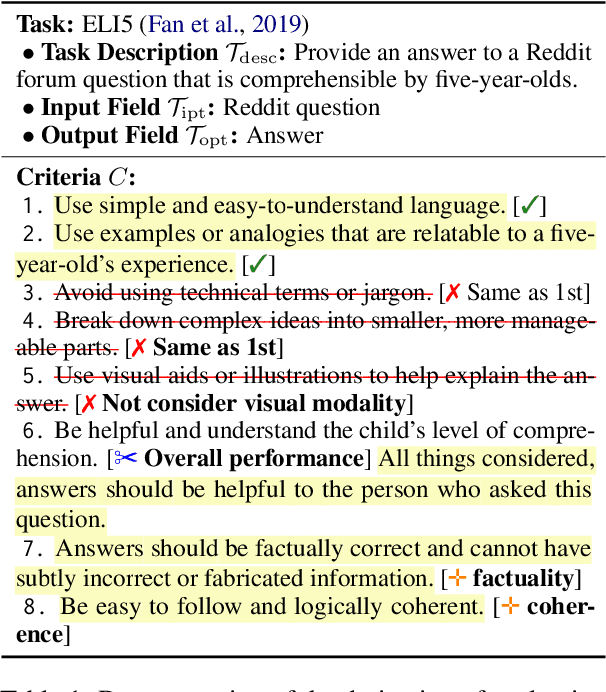
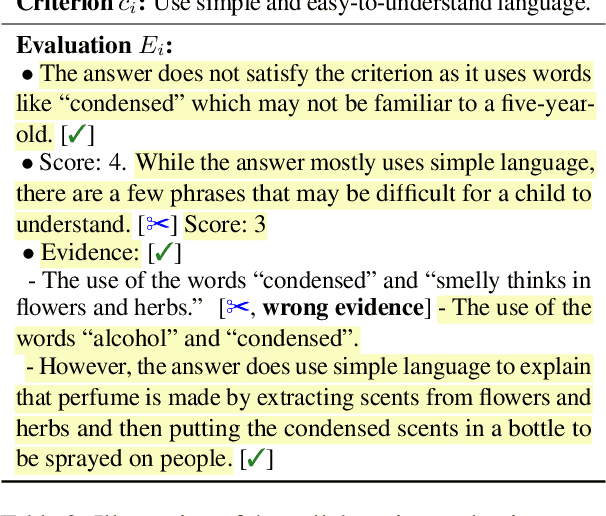
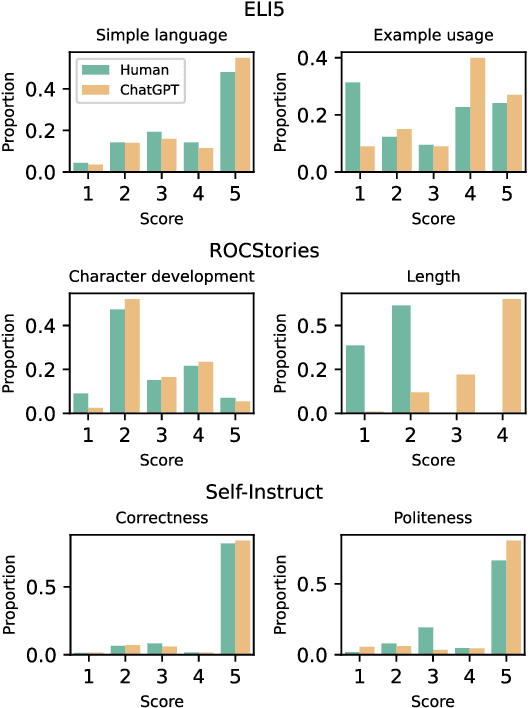
Abstract:Humans are widely involved in the evaluation of open-ended natural language generation tasks (NLG) that demand creativity, as automatic metrics often exhibit weak correlations with human judgments. Large language models (LLMs) recently have emerged as a scalable and cost-effective alternative to human evaluations. However, both humans and LLMs have limitations, i.e., inherent subjectivity and unreliable judgments, particularly for open-ended tasks that require adaptable metrics tailored to diverse task requirements. To explore the synergy between humans and LLM-based evaluators and address the challenges of existing inconsistent evaluation criteria in open-ended NLG tasks, we propose a Collaborative Evaluation pipeline CoEval, involving the design of a checklist of task-specific criteria and the detailed evaluation of texts, in which LLM generates initial ideation, and then humans engage in scrutiny. We conducted a series of experiments to investigate the mutual effects between LLMs and humans in CoEval. Results show that, by utilizing LLMs, CoEval effectively evaluates lengthy texts, saving significant time and reducing human evaluation outliers. Human scrutiny still plays a role, revising around 20% of LLM evaluation scores for ultimate reliability.
Deepfake Text Detection in the Wild
May 22, 2023



Abstract:Recent advances in large language models have enabled them to reach a level of text generation comparable to that of humans. These models show powerful capabilities across a wide range of content, including news article writing, story generation, and scientific writing. Such capability further narrows the gap between human-authored and machine-generated texts, highlighting the importance of deepfake text detection to avoid potential risks such as fake news propagation and plagiarism. However, previous work has been limited in that they testify methods on testbed of specific domains or certain language models. In practical scenarios, the detector faces texts from various domains or LLMs without knowing their sources. To this end, we build a wild testbed by gathering texts from various human writings and deepfake texts generated by different LLMs. Human annotators are only slightly better than random guessing at identifying machine-generated texts. Empirical results on automatic detection methods further showcase the challenges of deepfake text detection in a wild testbed. In addition, out-of-distribution poses a greater challenge for a detector to be employed in realistic application scenarios. We release our resources at https://github.com/yafuly/DeepfakeTextDetect.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge