Karin de Langis
Mary, the Cheeseburger-Eating Vegetarian: Do LLMs Recognize Incoherence in Narratives?
Dec 08, 2025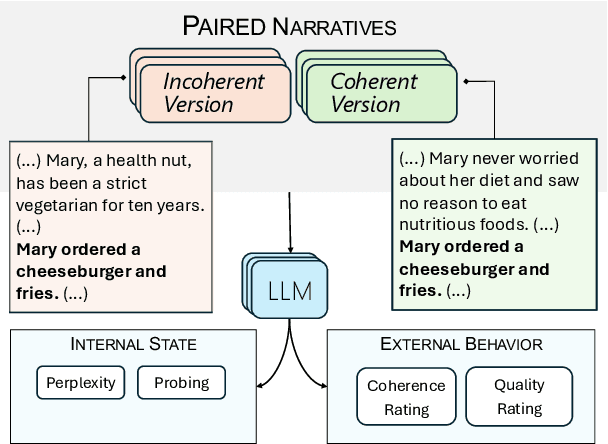
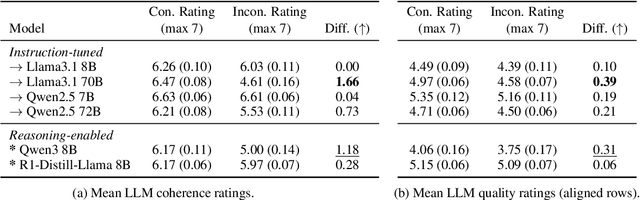
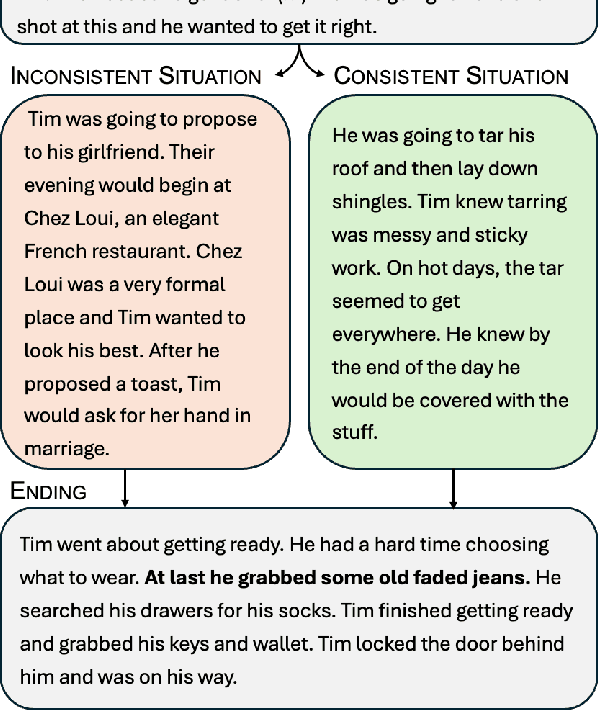
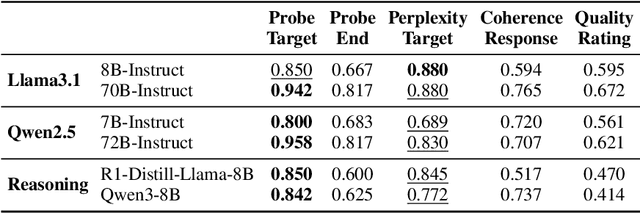
Abstract:Leveraging a dataset of paired narratives, we investigate the extent to which large language models (LLMs) can reliably separate incoherent and coherent stories. A probing study finds that LLMs' internal representations can reliably identify incoherent narratives. However, LLMs generate responses to rating questions that fail to satisfactorily separate the coherent and incoherent narratives across several prompt variations, hinting at a gap in LLM's understanding of storytelling. The reasoning LLMs tested do not eliminate these deficits, indicating that thought strings may not be able to fully address the discrepancy between model internal state and behavior. Additionally, we find that LLMs appear to be more sensitive to incoherence resulting from an event that violates the setting (e.g., a rainy day in the desert) than to incoherence arising from a character violating an established trait (e.g., Mary, a vegetarian, later orders a cheeseburger), suggesting that LLMs may rely more on prototypical world knowledge than building meaning-based narrative coherence. The consistent asymmetry found in our results suggests that LLMs do not have a complete grasp on narrative coherence.
A Framework for Robust Cognitive Evaluation of LLMs
Apr 03, 2025Abstract:Emergent cognitive abilities in large language models (LLMs) have been widely observed, but their nature and underlying mechanisms remain poorly understood. A growing body of research draws on cognitive science to investigate LLM cognition, but standard methodologies and experimen-tal pipelines have not yet been established. To address this gap we develop CognitivEval, a framework for systematically evaluating the artificial cognitive capabilities of LLMs, with a particular emphasis on robustness in response collection. The key features of CognitivEval include: (i) automatic prompt permutations, and (ii) testing that gathers both generations and model probability estimates. Our experiments demonstrate that these features lead to more robust experimental outcomes. Using CognitivEval, we replicate five classic experiments in cognitive science, illustrating the framework's generalizability across various experimental tasks and obtaining a cognitive profile of several state of the art LLMs. CognitivEval will be released publicly to foster broader collaboration within the cognitive science community.
Reinforcement Learning with Dynamic Multi-Reward Weighting for Multi-Style Controllable Generation
Feb 21, 2024Abstract:Style is an integral component of text that expresses a diverse set of information, including interpersonal dynamics (e.g. formality) and the author's emotions or attitudes (e.g. disgust). Humans often employ multiple styles simultaneously. An open question is how large language models can be explicitly controlled so that they weave together target styles when generating text: for example, to produce text that is both negative and non-toxic. Previous work investigates the controlled generation of a single style, or else controlled generation of a style and other attributes. In this paper, we expand this into controlling multiple styles simultaneously. Specifically, we investigate various formulations of multiple style rewards for a reinforcement learning (RL) approach to controlled multi-style generation. These reward formulations include calibrated outputs from discriminators and dynamic weighting by discriminator gradient magnitudes. We find that dynamic weighting generally outperforms static weighting approaches, and we explore its effectiveness in 2- and 3-style control, even compared to strong baselines like plug-and-play model. All code and data for RL pipelines with multiple style attributes will be publicly available.
infoVerse: A Universal Framework for Dataset Characterization with Multidimensional Meta-information
Jun 12, 2023



Abstract:The success of NLP systems often relies on the availability of large, high-quality datasets. However, not all samples in these datasets are equally valuable for learning, as some may be redundant or noisy. Several methods for characterizing datasets based on model-driven meta-information (e.g., model's confidence) have been developed, but the relationship and complementary effects of these methods have received less attention. In this paper, we introduce infoVerse, a universal framework for dataset characterization, which provides a new feature space that effectively captures multidimensional characteristics of datasets by incorporating various model-driven meta-information. infoVerse reveals distinctive regions of the dataset that are not apparent in the original semantic space, hence guiding users (or models) in identifying which samples to focus on for exploration, assessment, or annotation. Additionally, we propose a novel sampling method on infoVerse to select a set of data points that maximizes informativeness. In three real-world applications (data pruning, active learning, and data annotation), the samples chosen on infoVerse space consistently outperform strong baselines in all applications. Our code and demo are publicly available.
An Analysis of Reader Engagement in Literary Fiction through Eye Tracking and Linguistic Features
Jun 06, 2023Abstract:Capturing readers' engagement in fiction is a challenging but important aspect of narrative understanding. In this study, we collected 23 readers' reactions to 2 short stories through eye tracking, sentence-level annotations, and an overall engagement scale survey. We analyzed the significance of various qualities of the text in predicting how engaging a reader is likely to find it. As enjoyment of fiction is highly contextual, we also investigated individual differences in our data. Furthering our understanding of what captivates readers in fiction will help better inform models used in creative narrative generation and collaborative writing tools.
A Comparative Study on Textual Saliency of Styles from Eye Tracking, Annotations, and Language Models
Dec 19, 2022Abstract:There is growing interest in incorporating eye-tracking data and other implicit measures of human language processing into natural language processing (NLP) pipelines. The data from human language processing contain unique insight into human linguistic understanding that could be exploited by language models. However, many unanswered questions remain about the nature of this data and how it can best be utilized in downstream NLP tasks. In this paper, we present eyeStyliency, an eye-tracking dataset for human processing of stylistic text (e.g., politeness). We develop a variety of methods to derive style saliency scores over text using the collected eye dataset. We further investigate how this saliency data compares to both human annotation methods and model-based interpretability metrics. We find that while eye-tracking data is unique, it also intersects with both human annotations and model-based importance scores, providing a possible bridge between human- and machine-based perspectives. In downstream few-shot learning tasks, adding salient words to prompts generally improved style classification, with eye-tracking-based and annotation-based salient words achieving the highest accuracy.
Semantically-Aware Strategies for Stereo-Visual Robotic Obstacle Avoidance
Jul 13, 2021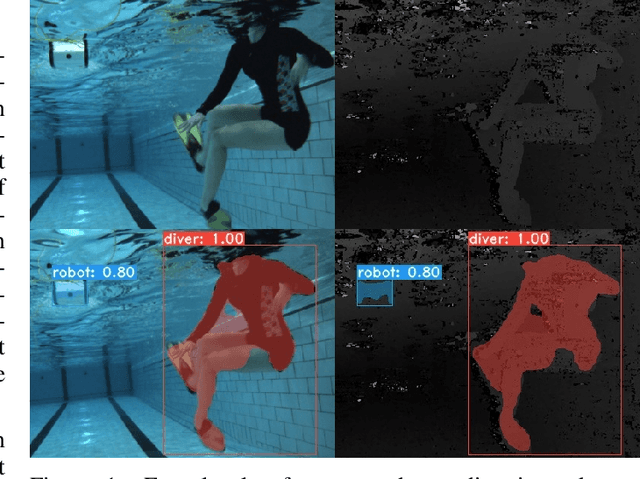
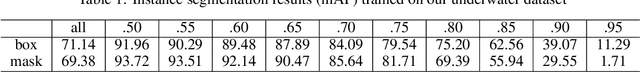
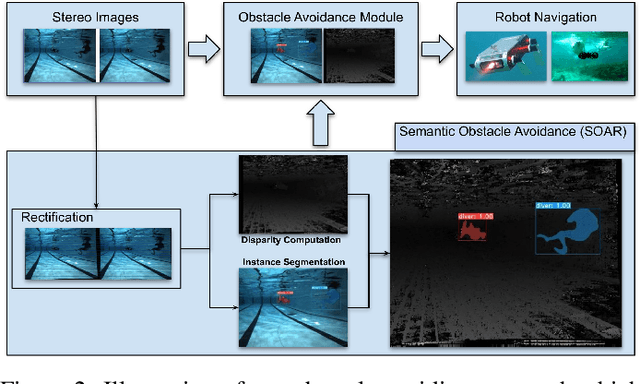
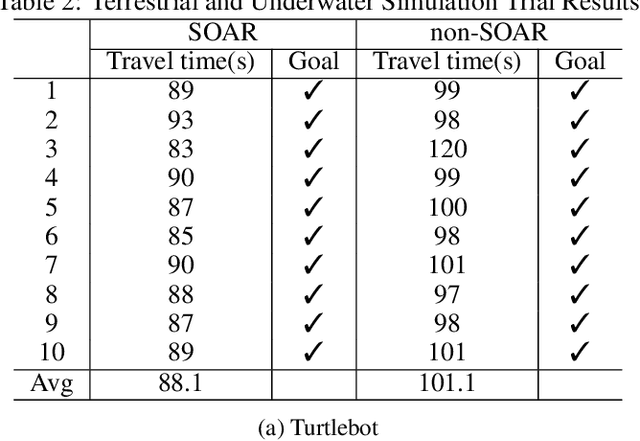
Abstract:Mobile robots in unstructured, mapless environments must rely on an obstacle avoidance module to navigate safely. The standard avoidance techniques estimate the locations of obstacles with respect to the robot but are unaware of the obstacles' identities. Consequently, the robot cannot take advantage of semantic information about obstacles when making decisions about how to navigate. We propose an obstacle avoidance module that combines visual instance segmentation with a depth map to classify and localize objects in the scene. The system avoids obstacles differentially, based on the identity of the objects: for example, the system is more cautious in response to unpredictable objects such as humans. The system can also navigate closer to harmless obstacles and ignore obstacles that pose no collision danger, enabling it to navigate more efficiently. We validate our approach in two simulated environments: one terrestrial and one underwater. Results indicate that our approach is feasible and can enable more efficient navigation strategies.
An Analysis of Deep Object Detectors For Diver Detection
Nov 25, 2020
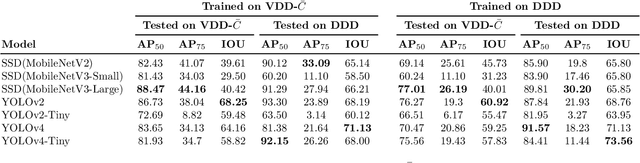

Abstract:With the end goal of selecting and using diver detection models to support human-robot collaboration capabilities such as diver following, we thoroughly analyze a large set of deep neural networks for diver detection. We begin by producing a dataset of approximately 105,000 annotated images of divers sourced from videos -- one of the largest and most varied diver detection datasets ever created. Using this dataset, we train a variety of state-of-the-art deep neural networks for object detection, including SSD with Mobilenet, Faster R-CNN, and YOLO. Along with these single-frame detectors, we also train networks designed for detection of objects in a video stream, using temporal information as well as single-frame image information. We evaluate these networks on typical accuracy and efficiency metrics, as well as on the temporal stability of their detections. Finally, we analyze the failures of these detectors, pointing out the most common scenarios of failure. Based on our results, we recommend SSDs or Tiny-YOLOv4 for real-time applications on robots and recommend further investigation of video object detection methods.
SVAM: Saliency-guided Visual Attention Modeling by Autonomous Underwater Robots
Nov 12, 2020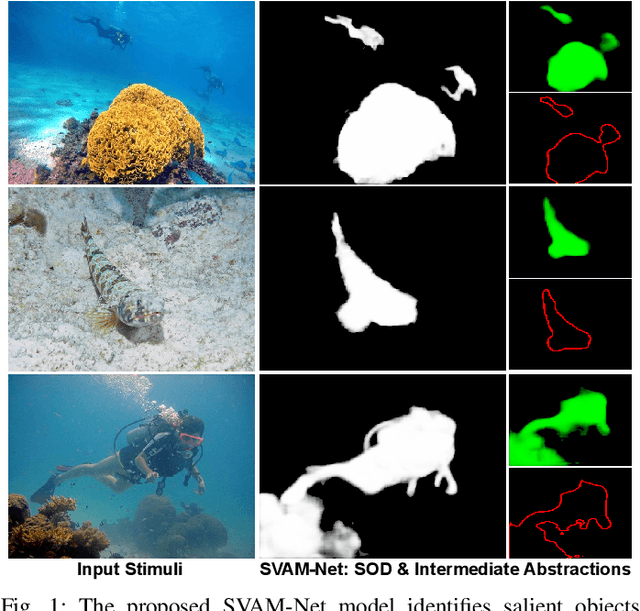

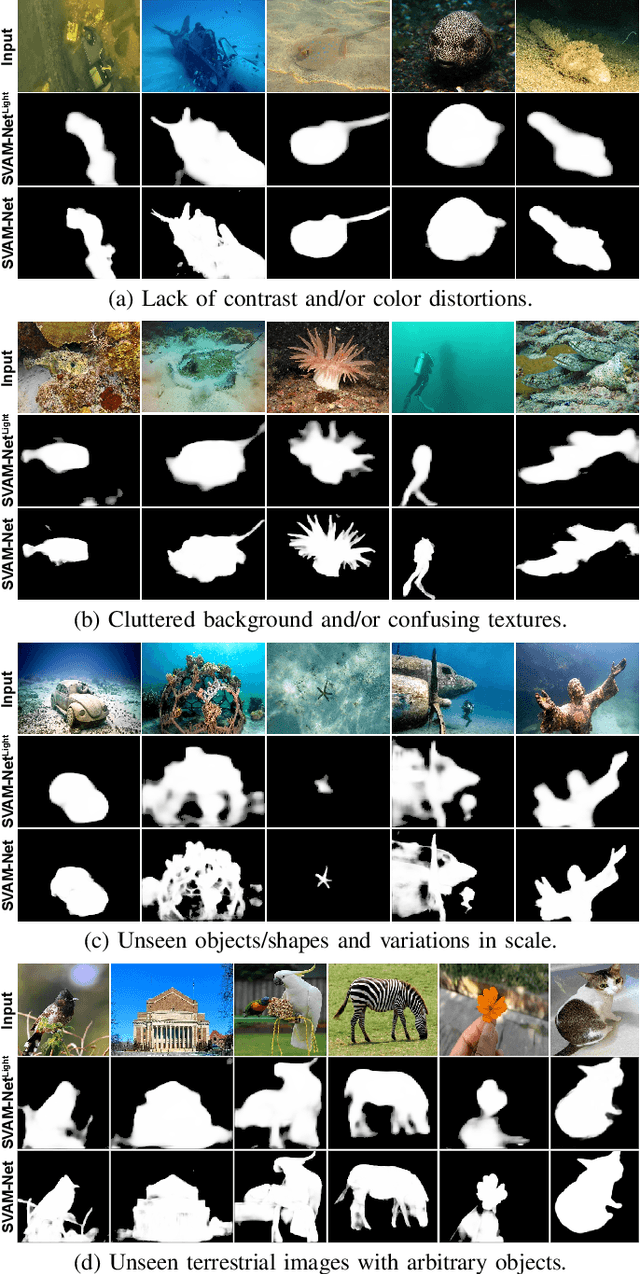
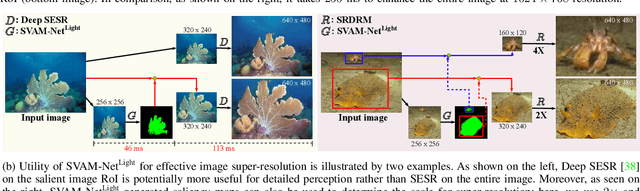
Abstract:This paper presents a holistic approach to saliency-guided visual attention modeling (SVAM) for use by autonomous underwater robots. Our proposed model, named SVAM-Net, integrates deep visual features at various scales and semantics for effective salient object detection (SOD) in natural underwater images. The SVAM-Net architecture is configured in a unique way to jointly accommodate bottom-up and top-down learning within two separate branches of the network while sharing the same encoding layers. We design dedicated spatial attention modules (SAMs) along these learning pathways to exploit the coarse-level and fine-level semantic features for SOD at four stages of abstractions. The bottom-up branch performs a rough yet reasonably accurate saliency estimation at a fast rate, whereas the deeper top-down branch incorporates a residual refinement module (RRM) that provides fine-grained localization of the salient objects. Extensive performance evaluation of SVAM-Net on benchmark datasets clearly demonstrates its effectiveness for underwater SOD. We also validate its generalization performance by several ocean trials' data that include test images of diverse underwater scenes and waterbodies, and also images with unseen natural objects. Moreover, we analyze its computational feasibility for robotic deployments and demonstrate its utility in several important use cases of visual attention modeling.
Real-Time Multi-Diver Tracking and Re-identification for Underwater Human-Robot Collaboration
Oct 21, 2019



Abstract:Autonomous underwater robots working with teams of human divers may need to distinguish between different divers, e.g. to recognize a lead diver or to follow a specific team member. This paper describes a technique that enables autonomous underwater robots to track divers in real time as well as to reidentify them. The approach is an extension of Simple Online Realtime Tracking (SORT) with an appearance metric (deep SORT). Initial diver detection is performed with a custom CNN designed for realtime diver detection, and appearance features are subsequently extracted for each detected diver. Next, realtime tracking-by-detection is performed with an extension of the deep SORT algorithm. We evaluate this technique on a series of videos of divers performing human-robot collaborative tasks and show that our methods result in more divers being accurately identified during tracking. We also discuss the practical considerations of applying multi-person tracking to on-board autonomous robot operations, and we consider how failure cases can be addressed during on-board tracking.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge