Jaehyung Kim
INDIBATOR: Diverse and Fact-Grounded Individuality for Multi-Agent Debate in Molecular Discovery
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Multi-agent systems have emerged as a powerful paradigm for automating scientific discovery. To differentiate agent behavior in the multi-agent system, current frameworks typically assign generic role-based personas such as ''reviewer'' or ''writer'' or rely on coarse grained keyword-based personas. While functional, this approach oversimplifies how human scientists operate, whose contributions are shaped by their unique research trajectories. In response, we propose INDIBATOR, a framework for molecular discovery that grounds agents in individualized scientist profiles constructed from two modalities: publication history for literature-derived knowledge and molecular history for structural priors. These agents engage in multi-turn debate through proposal, critique, and voting phases. Our evaluation demonstrates that these fine-grained individuality-grounded agents consistently outperform systems relying on coarse-grained personas, achieving competitive or state-of-the-art performance. These results validate that capturing the ``scientific DNA'' of individual agents is essential for high-quality discovery.
Reasoning or Fluency? Dissecting Probabilistic Confidence in Best-of-N Selection
Jan 20, 2026Abstract:Probabilistic confidence metrics are increasingly adopted as proxies for reasoning quality in Best-of-N selection, under the assumption that higher confidence reflects higher reasoning fidelity. In this work, we challenge this assumption by investigating whether these metrics truly capture inter-step causal dependencies necessary for valid reasoning. We introduce three classes of inter-step causality perturbations that systematically disrupt dependencies between reasoning steps while preserving local fluency. Surprisingly, across diverse model families and reasoning benchmarks, we find that selection accuracy degrades only marginally under these disruptions. Even severe interventions, such as applying hard attention masks that directly prevent the model from attending to prior reasoning steps, do not substantially reduce selection performance. These findings provide strong evidence that current probabilistic metrics are largely insensitive to logical structure, and primarily capture surface-level fluency or in-distribution priors instead. Motivated by this gap, we propose a contrastive causality metric that explicitly isolates inter-step causal dependencies, and demonstrate that it yields more faithful output selection than existing probability-based approaches.
Gap-K%: Measuring Top-1 Prediction Gap for Detecting Pretraining Data
Jan 16, 2026Abstract:The opacity of massive pretraining corpora in Large Language Models (LLMs) raises significant privacy and copyright concerns, making pretraining data detection a critical challenge. Existing state-of-the-art methods typically rely on token likelihoods, yet they often overlook the divergence from the model's top-1 prediction and local correlation between adjacent tokens. In this work, we propose Gap-K%, a novel pretraining data detection method grounded in the optimization dynamics of LLM pretraining. By analyzing the next-token prediction objective, we observe that discrepancies between the model's top-1 prediction and the target token induce strong gradient signals, which are explicitly penalized during training. Motivated by this, Gap-K% leverages the log probability gap between the top-1 predicted token and the target token, incorporating a sliding window strategy to capture local correlations and mitigate token-level fluctuations. Extensive experiments on the WikiMIA and MIMIR benchmarks demonstrate that Gap-K% achieves state-of-the-art performance, consistently outperforming prior baselines across various model sizes and input lengths.
SPRInG: Continual LLM Personalization via Selective Parametric Adaptation and Retrieval-Interpolated Generation
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:Personalizing Large Language Models typically relies on static retrieval or one-time adaptation, assuming user preferences remain invariant over time. However, real-world interactions are dynamic, where user interests continuously evolve, posing a challenge for models to adapt to preference drift without catastrophic forgetting. Standard continual learning approaches often struggle in this context, as they indiscriminately update on noisy interaction streams, failing to distinguish genuine preference shifts from transient contexts. To address this, we introduce SPRInG, a novel semi-parametric framework designed for effective continual personalization. During training, SPRInG employs drift-driven selective adaptation, which utilizes a likelihood-based scoring function to identify high-novelty interactions. This allows the model to selectively update the user-specific adapter on drift signals while preserving hard-to-learn residuals in a replay buffer. During inference, we apply strict relevance gating and fuse parametric knowledge with retrieved history via logit interpolation. Experiments on the long-form personalized generation benchmark demonstrate that SPRInG outperforms existing baselines, validating its robustness for real-world continual personalization.
Learning from the Undesirable: Robust Adaptation of Language Models without Forgetting
Nov 17, 2025
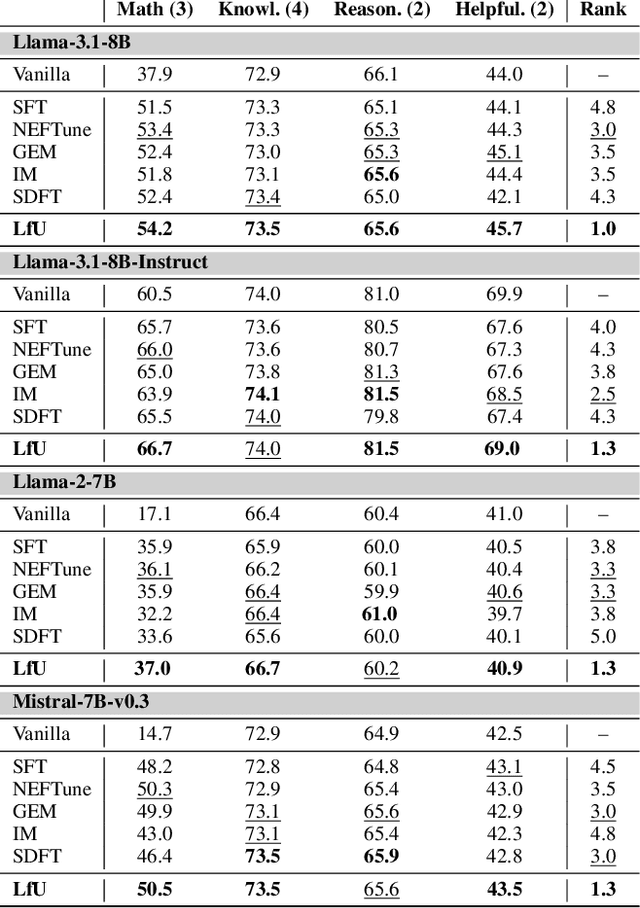
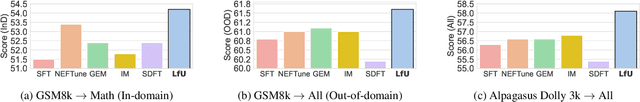
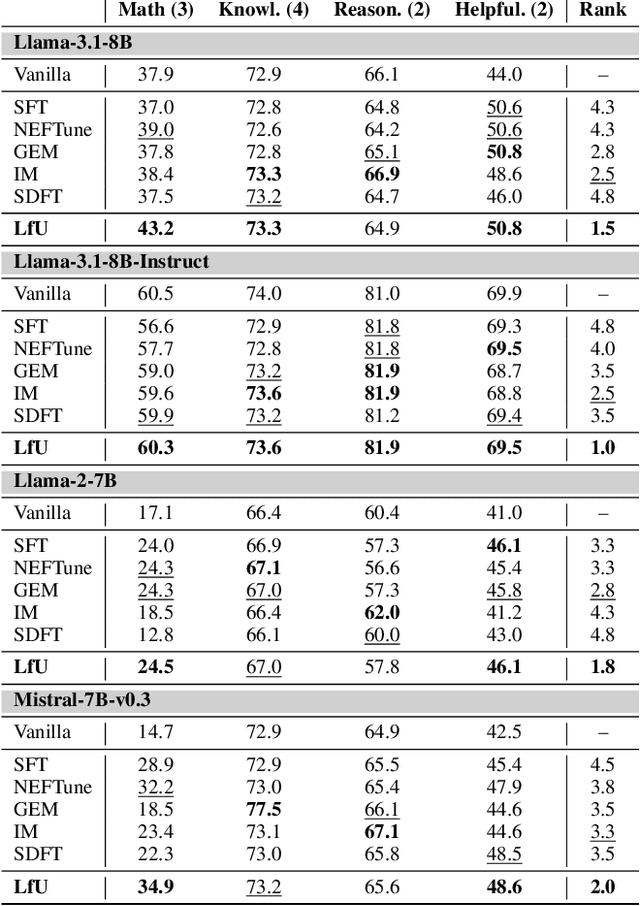
Abstract:Language models (LMs) are often adapted through supervised fine-tuning (SFT) to specialize their capabilities for downstream tasks. However, in typical scenarios where the fine-tuning data is limited, e.g., compared to pre-training, SFT can lead LMs to overfit, causing them to rely on spurious patterns within the target task or to compromise other broadly useful capabilities as a side effect of narrow specialization. In this paper, we propose Learning-from-the-Undesirable (LfU), a simple yet effective regularization scheme for SFT to mitigate overfitting issues when fine-tuning LMs with limited data. Specifically, we aim to regularize the fine-tuning process to favor solutions that are resilient to "undesirable" model updates, e.g., gradient ascent steps that steer the model toward undesirable behaviors. To this end, we propose a novel form of consistency regularization that directly aligns internal representations of the model with those after an undesirable update. By leveraging representation-level data augmentation through undesirable updates, LfU effectively promotes generalization under limited data. Our experiments on diverse LM downstream tasks show that LfU serves as an effective prior that enhances adaptability while preserving pretrained knowledge. For example, our LM from LfU achieves a 16.8% average improvement on math tasks compared to vanilla SFT on the same dataset, where the latter even leads to degraded performance on those tasks. Furthermore, LfU exhibits improved robustness to prompt variations, e.g., yielding a 92.1% lower standard deviation in output performances compared to SFT, highlighting its versatile effects.
TiTok: Transfer Token-level Knowledge via Contrastive Excess to Transplant LoRA
Oct 06, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) are widely applied in real world scenarios, but fine-tuning them comes with significant computational and storage costs. Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning (PEFT) methods such as LoRA mitigate these costs, but the adapted parameters are dependent on the base model and cannot be transferred across different backbones. One way to address this issue is through knowledge distillation, but its effectiveness inherently depends on training data. Recent work such as TransLoRA avoids this by generating synthetic data, but this adds complexity because it requires training an additional discriminator model. In this paper, we propose TiTok, a new framework that enables effective LoRA Transplantation through Token-level knowledge transfer. Specifically, TiTok captures task-relevant information through a contrastive excess between a source model with and without LoRA. This excess highlights informative tokens and enables selective filtering of synthetic data, all without additional models or overhead. Through experiments on three benchmarks across multiple transfer settings, our experiments show that the proposed method is consistently effective, achieving average performance gains of +4~8% compared to baselines overall.
Fast and Fluent Diffusion Language Models via Convolutional Decoding and Rejective Fine-tuning
Sep 18, 2025Abstract:Autoregressive (AR) language models generate text one token at a time, which limits their inference speed. Diffusion-based language models offer a promising alternative, as they can decode multiple tokens in parallel. However, we identify a key bottleneck in current diffusion LMs: the long decoding-window problem, where tokens generated far from the input context often become irrelevant or repetitive. Previous solutions like semi-autoregressive address this issue by splitting windows into blocks, but this sacrifices speed and bidirectionality, eliminating the main advantage of diffusion models. To overcome this, we propose Convolutional decoding (Conv), a normalization-based method that narrows the decoding window without hard segmentation, leading to better fluency and flexibility. Additionally, we introduce Rejecting Rule-based Fine-Tuning (R2FT), a post-hoc training scheme that better aligns tokens at positions far from context. Our methods achieve state-of-the-art results on open-ended generation benchmarks (e.g., AlpacaEval) among diffusion LM baselines, with significantly lower step size than previous works, demonstrating both speed and quality improvements.
Towards an Introspective Dynamic Model of Globally Distributed Computing Infrastructures
Jun 24, 2025Abstract:Large-scale scientific collaborations like ATLAS, Belle II, CMS, DUNE, and others involve hundreds of research institutes and thousands of researchers spread across the globe. These experiments generate petabytes of data, with volumes soon expected to reach exabytes. Consequently, there is a growing need for computation, including structured data processing from raw data to consumer-ready derived data, extensive Monte Carlo simulation campaigns, and a wide range of end-user analysis. To manage these computational and storage demands, centralized workflow and data management systems are implemented. However, decisions regarding data placement and payload allocation are often made disjointly and via heuristic means. A significant obstacle in adopting more effective heuristic or AI-driven solutions is the absence of a quick and reliable introspective dynamic model to evaluate and refine alternative approaches. In this study, we aim to develop such an interactive system using real-world data. By examining job execution records from the PanDA workflow management system, we have pinpointed key performance indicators such as queuing time, error rate, and the extent of remote data access. The dataset includes five months of activity. Additionally, we are creating a generative AI model to simulate time series of payloads, which incorporate visible features like category, event count, and submitting group, as well as hidden features like the total computational load-derived from existing PanDA records and computing site capabilities. These hidden features, which are not visible to job allocators, whether heuristic or AI-driven, influence factors such as queuing times and data movement.
Collaborative LLM Inference via Planning for Efficient Reasoning
Jun 13, 2025



Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) excel at complex reasoning tasks, but those with strong capabilities (e.g., whose numbers of parameters are larger than 100B) are often accessible only through paid APIs, making them too costly for applications of frequent use. In contrast, smaller open-sourced LLMs (e.g., whose numbers of parameters are less than 3B) are freely available and easy to deploy locally (e.g., under a single GPU having 8G VRAM), but lack suff icient reasoning ability. This trade-off raises a natural question: can small (free) and large (costly) models collaborate at test time to combine their strengths? We propose a test-time collaboration framework in which a planner model first generates a plan, defined as a distilled and high-level abstraction of the problem. This plan serves as a lightweight intermediate that guides a reasoner model, which generates a complete solution. Small and large models take turns acting as planner and reasoner, exchanging plans in a multi-round cascade to collaboratively solve complex tasks. Our method achieves accuracy comparable to strong proprietary models alone, while significantly reducing reliance on paid inference. These results highlight planning as an effective prior for orchestrating cost-aware, cross-model inference under real-world deployment constraints.
Personalized LLM Decoding via Contrasting Personal Preference
Jun 13, 2025Abstract:As large language models (LLMs) are progressively deployed in various real-world applications, personalization of LLMs has become increasingly important. While various approaches to LLM personalization such as prompt-based and training-based methods have been actively explored, the development of effective decoding-time algorithms remains largely overlooked, despite their demonstrated potential. In this paper, we propose CoPe (Contrasting Personal Preference), a novel decoding-time approach applied after performing parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) on user-specific data. Our core idea is to leverage reward-guided decoding specifically for personalization by maximizing each user's implicit reward signal. We evaluate CoPe across five open-ended personalized text generation tasks. Our empirical results demonstrate that CoPe achieves strong performance, improving personalization by an average of 10.57% in ROUGE-L, without relying on external reward models or additional training procedures.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge