Md Jahidul Islam
HiRQA: Hierarchical Ranking and Quality Alignment for Opinion-Unaware Image Quality Assessment
Aug 20, 2025Abstract:Despite significant progress in no-reference image quality assessment (NR-IQA), dataset biases and reliance on subjective labels continue to hinder their generalization performance. We propose HiRQA, Hierarchical Ranking and Quality Alignment), a self-supervised, opinion-unaware framework that offers a hierarchical, quality-aware embedding through a combination of ranking and contrastive learning. Unlike prior approaches that depend on pristine references or auxiliary modalities at inference time, HiRQA predicts quality scores using only the input image. We introduce a novel higher-order ranking loss that supervises quality predictions through relational ordering across distortion pairs, along with an embedding distance loss that enforces consistency between feature distances and perceptual differences. A training-time contrastive alignment loss, guided by structured textual prompts, further enhances the learned representation. Trained only on synthetic distortions, HiRQA generalizes effectively to authentic degradations, as demonstrated through evaluation on various distortions such as lens flare, haze, motion blur, and low-light conditions. For real-time deployment, we introduce \textbf{HiRQA-S}, a lightweight variant with an inference time of only 3.5 ms per image. Extensive experiments across synthetic and authentic benchmarks validate HiRQA's state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance, strong generalization ability, and scalability.
NemeSys: An Online Underwater Explorer with Goal-Driven Adaptive Autonomy
Jul 16, 2025Abstract:Adaptive mission control and dynamic parameter reconfiguration are essential for autonomous underwater vehicles (AUVs) operating in GPS-denied, communication-limited marine environments. However, most current AUV platforms execute static, pre-programmed missions or rely on tethered connections and high-latency acoustic channels for mid-mission updates, significantly limiting their adaptability and responsiveness. In this paper, we introduce NemeSys, a novel AUV system designed to support real-time mission reconfiguration through compact optical and magnetoelectric (OME) signaling facilitated by floating buoys. We present the full system design, control architecture, and a semantic mission encoding framework that enables interactive exploration and task adaptation via low-bandwidth communication. The proposed system is validated through analytical modeling, controlled experimental evaluations, and open-water trials. Results confirm the feasibility of online mission adaptation and semantic task updates, highlighting NemeSys as an online AUV platform for goal-driven adaptive autonomy in dynamic and uncertain underwater environments.
Single-Step Latent Diffusion for Underwater Image Restoration
Jul 10, 2025Abstract:Underwater image restoration algorithms seek to restore the color, contrast, and appearance of a scene that is imaged underwater. They are a critical tool in applications ranging from marine ecology and aquaculture to underwater construction and archaeology. While existing pixel-domain diffusion-based image restoration approaches are effective at restoring simple scenes with limited depth variation, they are computationally intensive and often generate unrealistic artifacts when applied to scenes with complex geometry and significant depth variation. In this work we overcome these limitations by combining a novel network architecture (SLURPP) with an accurate synthetic data generation pipeline. SLURPP combines pretrained latent diffusion models -- which encode strong priors on the geometry and depth of scenes -- with an explicit scene decomposition -- which allows one to model and account for the effects of light attenuation and backscattering. To train SLURPP we design a physics-based underwater image synthesis pipeline that applies varied and realistic underwater degradation effects to existing terrestrial image datasets. This approach enables the generation of diverse training data with dense medium/degradation annotations. We evaluate our method extensively on both synthetic and real-world benchmarks and demonstrate state-of-the-art performance. Notably, SLURPP is over 200X faster than existing diffusion-based methods while offering ~ 3 dB improvement in PSNR on synthetic benchmarks. It also offers compelling qualitative improvements on real-world data. Project website https://tianfwang.github.io/slurpp/.
DGIQA: Depth-guided Feature Attention and Refinement for Generalizable Image Quality Assessment
May 29, 2025Abstract:A long-held challenge in no-reference image quality assessment (NR-IQA) learning from human subjective perception is the lack of objective generalization to unseen natural distortions. To address this, we integrate a novel Depth-Guided cross-attention and refinement (Depth-CAR) mechanism, which distills scene depth and spatial features into a structure-aware representation for improved NR-IQA. This brings in the knowledge of object saliency and relative contrast of the scene for more discriminative feature learning. Additionally, we introduce the idea of TCB (Transformer-CNN Bridge) to fuse high-level global contextual dependencies from a transformer backbone with local spatial features captured by a set of hierarchical CNN (convolutional neural network) layers. We implement TCB and Depth-CAR as multimodal attention-based projection functions to select the most informative features, which also improve training time and inference efficiency. Experimental results demonstrate that our proposed DGIQA model achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance on both synthetic and authentic benchmark datasets. More importantly, DGIQA outperforms SOTA models on cross-dataset evaluations as well as in assessing natural image distortions such as low-light effects, hazy conditions, and lens flares.
Adaptive Weight Modified Riesz Mean Filter For High-Density Salt and Pepper Noise Removal
Apr 28, 2025Abstract:This paper introduces a novel filter, the Adaptive Weight Modified Riesz Mean Filter (AWMRmF), designed for the effective removal of high-density salt and pepper noise (SPN). AWMRmF integrates a pixel weight function and adaptivity condition inspired by the Different Adaptive Modified Riesz Mean Filter (DAMRmF). In my simulations, I evaluated the performance of AWMRmF against established filters such as Adaptive Frequency Median Filter (AFMF), Adaptive Weighted Mean Filter (AWMF), Adaptive Cesaro Mean Filter (ACmF), Adaptive Riesz Mean Filter (ARmF), and Improved Adaptive Weighted Mean Filter (IAWMF). The assessment was conducted on 26 typical test images, varying noise levels from 60% to 95%. The findings indicate that, in terms of both Peak Signal to Noise Ratio (PSNR) and Structural Similarity (SSIM) metrics, AWMRmF outperformed other state-of-the-art filters. Furthermore, AWMRmF demonstrated superior performance in mean PSNR and SSIM results as well.
UStyle: Waterbody Style Transfer of Underwater Scenes by Depth-Guided Feature Synthesis
Mar 14, 2025Abstract:The concept of waterbody style transfer remains largely unexplored in the underwater imaging and vision literature. Traditional image style transfer (STx) methods primarily focus on artistic and photorealistic blending, often failing to preserve object and scene geometry in images captured in high-scattering mediums such as underwater. The wavelength-dependent nonlinear attenuation and depth-dependent backscattering artifacts further complicate learning underwater image STx from unpaired data. This paper introduces UStyle, the first data-driven learning framework for transferring waterbody styles across underwater images without requiring prior reference images or scene information. We propose a novel depth-aware whitening and coloring transform (DA-WCT) mechanism that integrates physics-based waterbody synthesis to ensure perceptually consistent stylization while preserving scene structure. To enhance style transfer quality, we incorporate carefully designed loss functions that guide UStyle to maintain colorfulness, lightness, structural integrity, and frequency-domain characteristics, as well as high-level content in VGG and CLIP (contrastive language-image pretraining) feature spaces. By addressing domain-specific challenges, UStyle provides a robust framework for no-reference underwater image STx, surpassing state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods that rely solely on end-to-end reconstruction loss. Furthermore, we introduce the UF7D dataset, a curated collection of high-resolution underwater images spanning seven distinct waterbody styles, establishing a benchmark to support future research in underwater image STx. The UStyle inference pipeline and UF7D dataset are released at: https://github.com/uf-robopi/UStyle.
ClipRover: Zero-shot Vision-Language Exploration and Target Discovery by Mobile Robots
Feb 12, 2025Abstract:Vision-language navigation (VLN) has emerged as a promising paradigm, enabling mobile robots to perform zero-shot inference and execute tasks without specific pre-programming. However, current systems often separate map exploration and path planning, with exploration relying on inefficient algorithms due to limited (partially observed) environmental information. In this paper, we present a novel navigation pipeline named ''ClipRover'' for simultaneous exploration and target discovery in unknown environments, leveraging the capabilities of a vision-language model named CLIP. Our approach requires only monocular vision and operates without any prior map or knowledge about the target. For comprehensive evaluations, we design the functional prototype of a UGV (unmanned ground vehicle) system named ''Rover Master'', a customized platform for general-purpose VLN tasks. We integrate and deploy the ClipRover pipeline on Rover Master to evaluate its throughput, obstacle avoidance capability, and trajectory performance across various real-world scenarios. Experimental results demonstrate that ClipRover consistently outperforms traditional map traversal algorithms and achieves performance comparable to path-planning methods that depend on prior map and target knowledge. Notably, ClipRover offers real-time active navigation without requiring pre-captured candidate images or pre-built node graphs, addressing key limitations of existing VLN pipelines.
Demonstrating CavePI: Autonomous Exploration of Underwater Caves by Semantic Guidance
Feb 07, 2025Abstract:Enabling autonomous robots to safely and efficiently navigate, explore, and map underwater caves is of significant importance to water resource management, hydrogeology, archaeology, and marine robotics. In this work, we demonstrate the system design and algorithmic integration of a visual servoing framework for semantically guided autonomous underwater cave exploration. We present the hardware and edge-AI design considerations to deploy this framework on a novel AUV (Autonomous Underwater Vehicle) named CavePI. The guided navigation is driven by a computationally light yet robust deep visual perception module, delivering a rich semantic understanding of the environment. Subsequently, a robust control mechanism enables CavePI to track the semantic guides and navigate within complex cave structures. We evaluate the system through field experiments in natural underwater caves and spring-water sites and further validate its ROS (Robot Operating System)-based digital twin in a simulation environment. Our results highlight how these integrated design choices facilitate reliable navigation under feature-deprived, GPS-denied, and low-visibility conditions.
Human-Machine Interfaces for Subsea Telerobotics: From Soda-straw to Natural Language Interactions
Dec 02, 2024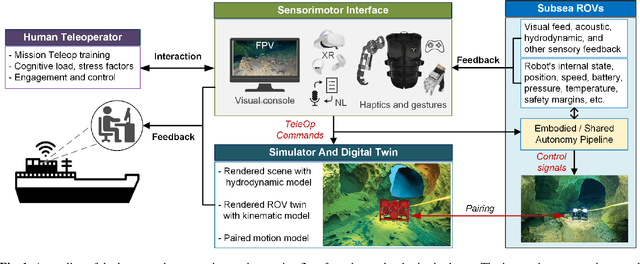
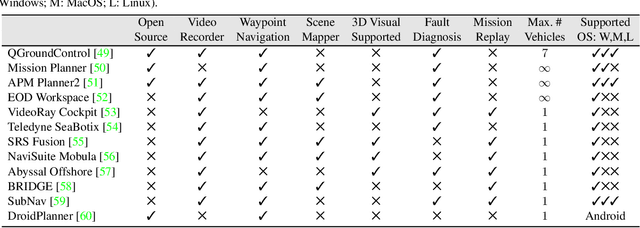
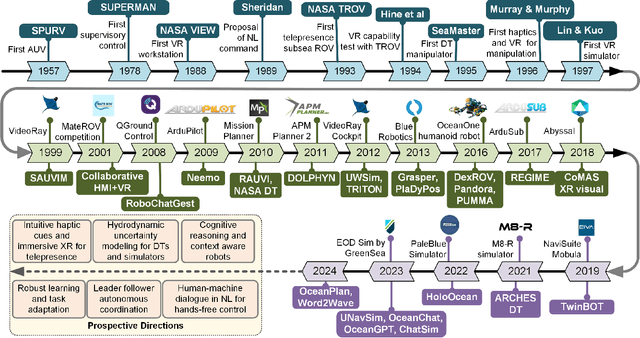
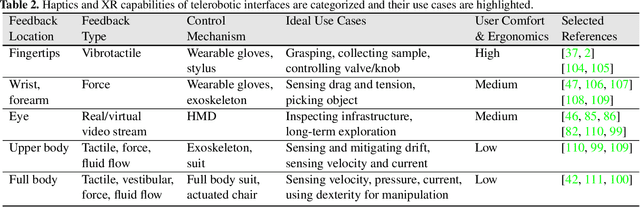
Abstract:This review explores the evolution of human-machine interfaces (HMIs) for subsea telerobotics, tracing back the transition from traditional first-person "soda-straw" consoles (narrow field-of-view camera feed) to advanced interfaces powered by gesture recognition, virtual reality, and natural language models. First, we discuss various forms of subsea telerobotics applications, current state-of-the-art (SOTA) interface systems, and the challenges they face in robust underwater sensing, real-time estimation, and low-latency communication. Through this analysis, we highlight how advanced HMIs facilitate intuitive interactions between human operators and robots to overcome these challenges. A detailed review then categorizes and evaluates the cutting-edge HMI systems based on their offered features from both human perspectives (e.g., enhancing operator control and situational awareness) and machine perspectives (e.g., improving safety, mission accuracy, and task efficiency). Moreover, we examine the literature on bidirectional interaction and intelligent collaboration in terms of sensory feedback and intuitive control mechanisms for both physical and virtual interfaces. The paper concludes by identifying critical challenges, open research questions, and future directions, emphasizing the need for multidisciplinary collaboration in subsea telerobotics.
Optimized Vessel Segmentation: A Structure-Agnostic Approach with Small Vessel Enhancement and Morphological Correction
Nov 22, 2024Abstract:Accurate segmentation of blood vessels is essential for various clinical assessments and postoperative analyses. However, the inherent challenges of vascular imaging, such as sparsity, fine granularity, low contrast, data distribution variability, and the critical need for preserving topological structure, making generalized vessel segmentation particularly complex. While specialized segmentation methods have been developed for specific anatomical regions, their over-reliance on tailored models hinders broader applicability and generalization. General-purpose segmentation models introduced in medical imaging often fail to address critical vascular characteristics, including the connectivity of segmentation results. To overcome these limitations, we propose an optimized vessel segmentation framework: a structure-agnostic approach incorporating small vessel enhancement and morphological correction for multi-modality vessel segmentation. To train and validate this framework, we compiled a comprehensive multi-modality dataset spanning 17 datasets and benchmarked our model against six SAM-based methods and 17 expert models. The results demonstrate that our approach achieves superior segmentation accuracy, generalization, and a 34.6% improvement in connectivity, underscoring its clinical potential. An ablation study further validates the effectiveness of the proposed improvements. We will release the code and dataset at github following the publication of this work.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge