Weiwei Chen
Institute of Logic and Cognition and Department of Philosophy, Sun Yat-sen University
Sensing Framework Design and Performance Optimization with Action Detection for ISCC
May 05, 2025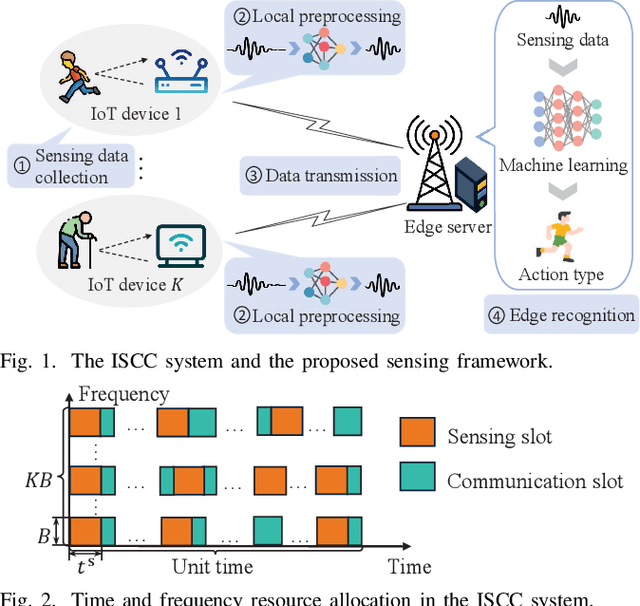
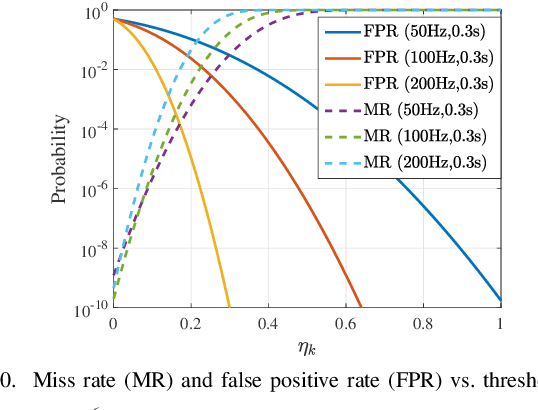
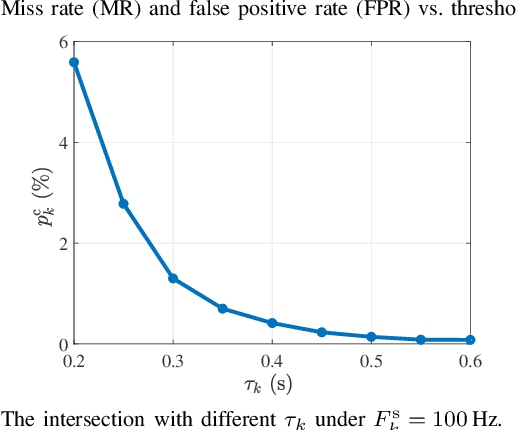
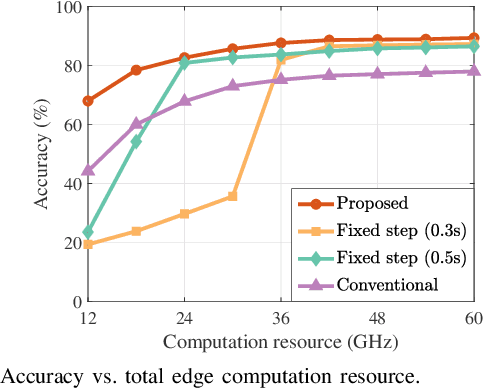
Abstract:Integrated sensing, communication, and computation (ISCC) has been regarded as a prospective technology for the next-generation wireless network, supporting humancentric intelligent applications. However, the delay sensitivity of these computation-intensive applications, especially in a multidevice ISCC system with limited resources, highlights the urgent need for efficient sensing task execution frameworks. To address this, we propose a resource-efficient sensing framework in this paper. Different from existing solutions, it features a novel action detection module deployed at each device to detect the onset of an action. Only time windows filled with signals of interest are offloaded to the edge server and processed by the edge recognition module, thus reducing overhead. Furthermore, we quantitatively analyze the sensing performance of the proposed sensing framework and formulate a sensing accuracy maximization problem under power, delay, and resource limitations for the multi-device ISCC system. By decomposing it into two subproblems, we develop an alternating direction method of multipliers (ADMM)-based distributed algorithm. It alternatively solves a sensing accuracy maximization subproblem at each device and employs a closed-form computation resource allocation strategy at the edge server till convergence. Finally, a real-world test is conducted using commodity wireless devices to validate the sensing performance analysis. Extensive test results demonstrate that our proposal achieves higher sensing accuracy under the limited resource compared to two baselines.
NHA12D: A New Pavement Crack Dataset and a Comparison Study Of Crack Detection Algorithms
May 02, 2022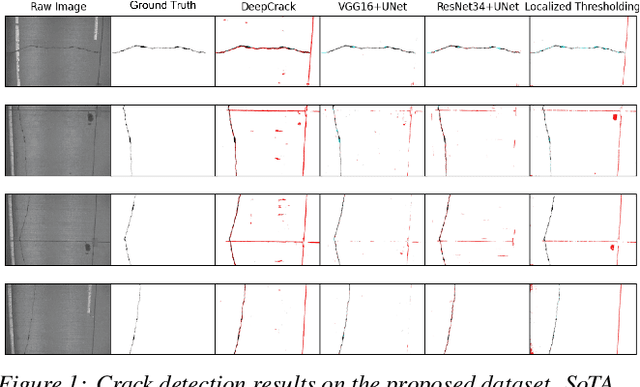
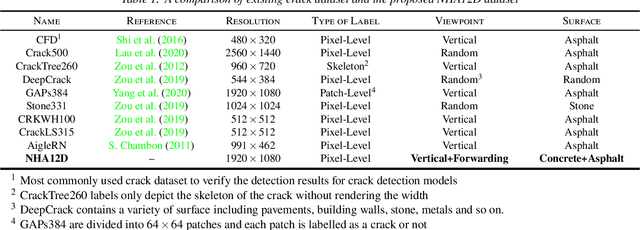
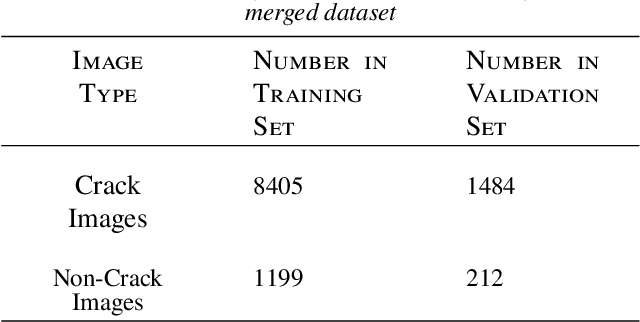
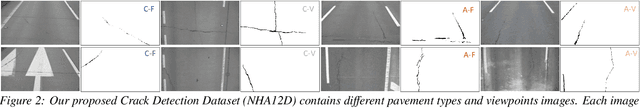
Abstract:Crack detection plays a key role in automated pavement inspection. Although a large number of algorithms have been developed in recent years to further boost performance, there are still remaining challenges in practice, due to the complexity of pavement images. To further accelerate the development and identify the remaining challenges, this paper conducts a comparison study to evaluate the performance of the state of the art crack detection algorithms quantitatively and objectively. A more comprehensive annotated pavement crack dataset (NHA12D) that contains images with different viewpoints and pavements types is proposed. In the comparison study, crack detection algorithms were trained equally on the largest public crack dataset collected and evaluated on the proposed dataset (NHA12D). Overall, the U-Net model with VGG-16 as backbone has the best all-around performance, but models generally fail to distinguish cracks from concrete joints, leading to a high false-positive rate. It also found that detecting cracks from concrete pavement images still has huge room for improvement. Dataset for concrete pavement images is also missing in the literature. Future directions in this area include filling the gap for concrete pavement images and using domain adaptation techniques to enhance the detection results on unseen datasets.
Partial Symbol Recovery for Interference Resilience in Low-Power Wide Area Networks
Sep 08, 2021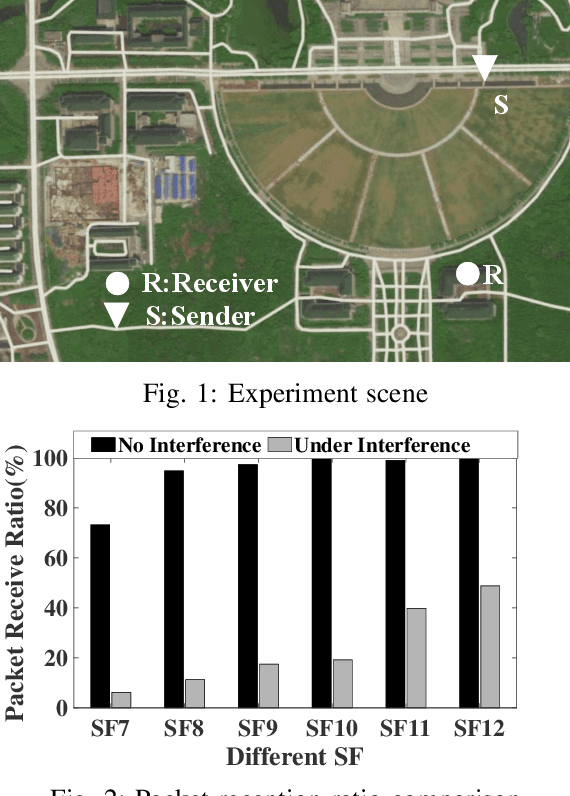
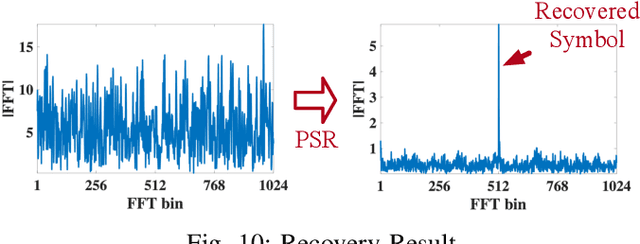
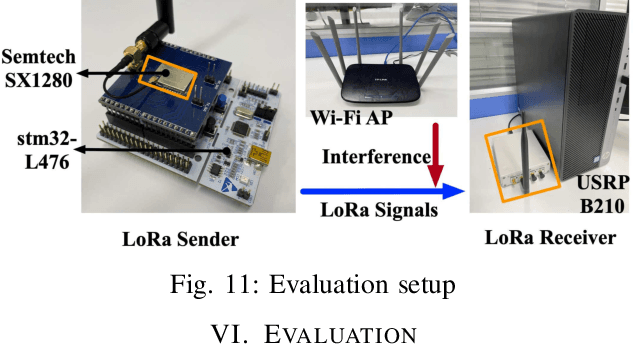
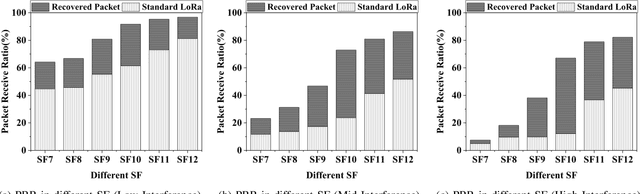
Abstract:Recent years have witnessed the proliferation of Low-power Wide Area Networks (LPWANs) in the unlicensed band for various Internet-of-Things (IoT) applications. Due to the ultra-low transmission power and long transmission duration, LPWAN devices inevitably suffer from high power Cross Technology Interference (CTI), such as interference from Wi-Fi, coexisting in the same spectrum. To alleviate this issue, this paper introduces the Partial Symbol Recovery (PSR) scheme for improving the CTI resilience of LPWAN. We verify our idea on LoRa, a widely adopted LPWAN technique, as a proof of concept. At the PHY layer, although CTI has much higher power, its duration is relatively shorter compared with LoRa symbols, leaving part of a LoRa symbol uncorrupted. Moreover, due to its high redundancy, LoRa chips within a symbol are highly correlated. This opens the possibility of detecting a LoRa symbol with only part of the chips. By examining the unique frequency patterns in LoRa symbols with time-frequency analysis, our design effectively detects the clean LoRa chips that are free of CTI. This enables PSR to only rely on clean LoRa chips for successfully recovering from communication failures. We evaluate our PSR design with real-world testbeds, including SX1280 LoRa chips and USRP B210, under Wi-Fi interference in various scenarios. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our design offers reliable packet recovery performance, successfully boosting the LoRa packet reception ratio from 45.2% to 82.2% with a performance gain of 1.8 times.
Collective Argumentation: The Case of Aggregating Support-Relations of Bipolar Argumentation Frameworks
Jun 22, 2021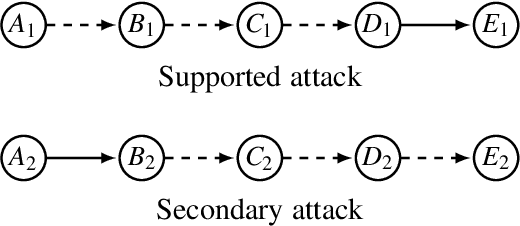
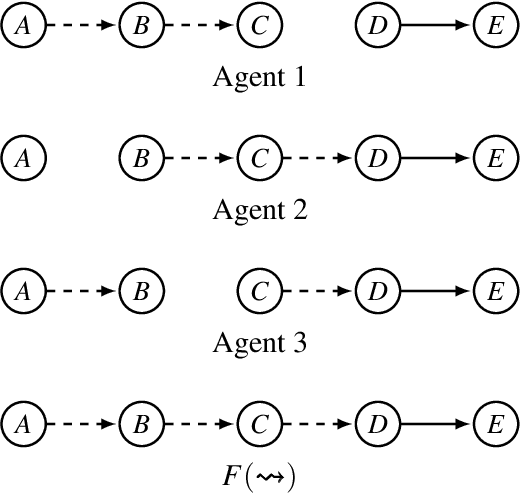
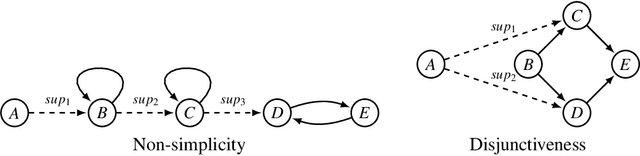
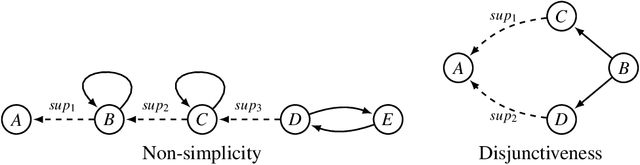
Abstract:In many real-life situations that involve exchanges of arguments, individuals may differ on their assessment of which supports between the arguments are in fact justified, i.e., they put forward different support-relations. When confronted with such situations, we may wish to aggregate individuals' argumentation views on support-relations into a collective view, which is acceptable to the group. In this paper, we assume that under bipolar argumentation frameworks, individuals are equipped with a set of arguments and a set of attacks between arguments, but with possibly different support-relations. Using the methodology in social choice theory, we analyze what semantic properties of bipolar argumentation frameworks can be preserved by aggregation rules during the aggregation of support-relations.
* In Proceedings TARK 2021, arXiv:2106.10886. Accepted by the 18th conference on theoretical aspects of rationality and knowledge (TARK-2021)
Continuous Transition: Improving Sample Efficiency for Continuous Control Problems via MixUp
Nov 30, 2020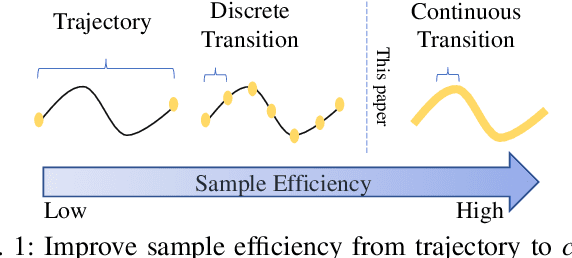
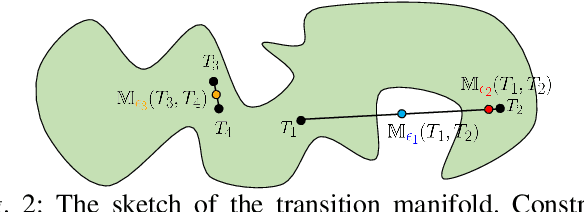
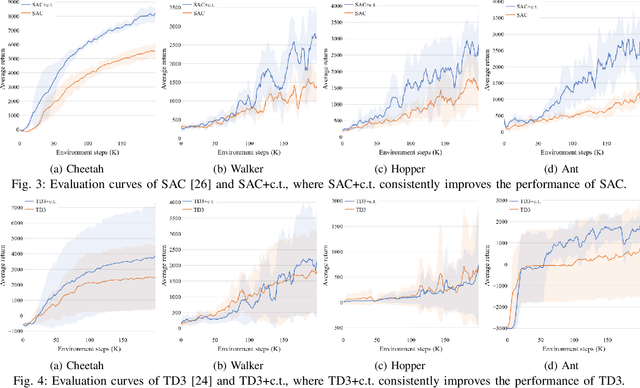
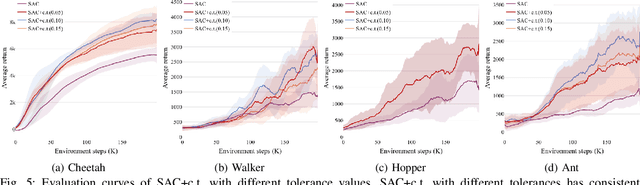
Abstract:Although deep reinforcement learning~(RL) has been successfully applied to a variety of robotic control tasks, it's still challenging to apply it to real-world tasks, due to the poor sample efficiency. Attempting to overcome this shortcoming, several works focus on reusing the collected trajectory data during the training by decomposing them into a set of policy-irrelevant discrete transitions. However, their improvements are somewhat marginal since i) the amount of the transitions is usually small, and ii) the value assignment only happens in the joint states. To address these issues, this paper introduces a concise yet powerful method to construct \textit{Continuous Transition}, which exploits the trajectory information by exploiting the potential transitions along the trajectory. Specifically, we propose to synthesize new transitions for training by linearly interpolating the conjunctive transitions. To keep the constructed transitions authentic, we also develop a discriminator to guide the construction process automatically. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our proposed method achieves a significant improvement in sample efficiency on various complex continuous robotic control problems in MuJoCo and outperforms the advanced model-based / model-free RL methods.
Preservation of Semantic Properties during the Aggregation of Abstract Argumentation Frameworks
Jul 27, 2017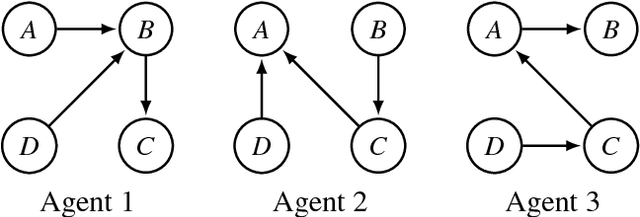
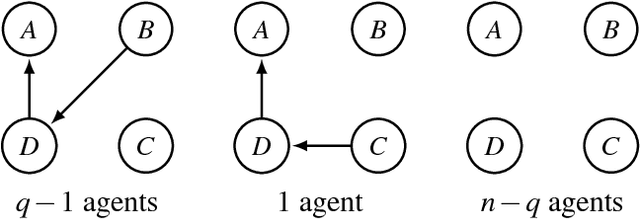
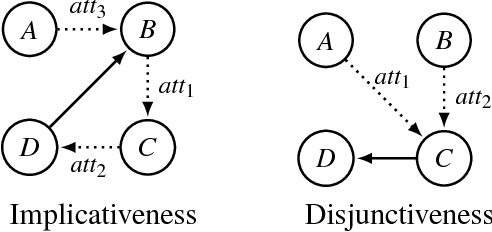
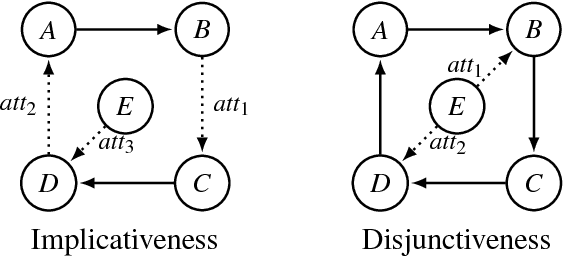
Abstract:An abstract argumentation framework can be used to model the argumentative stance of an agent at a high level of abstraction, by indicating for every pair of arguments that is being considered in a debate whether the first attacks the second. When modelling a group of agents engaged in a debate, we may wish to aggregate their individual argumentation frameworks to obtain a single such framework that reflects the consensus of the group. Even when agents disagree on many details, there may well be high-level agreement on important semantic properties, such as the acceptability of a given argument. Using techniques from social choice theory, we analyse under what circumstances such semantic properties agreed upon by the individual agents can be preserved under aggregation.
* In Proceedings TARK 2017, arXiv:1707.08250
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge