Junliang Du
Information-Theoretic Greedy Layer-wise Training for Traffic Sign Recognition
Oct 31, 2025



Abstract:Modern deep neural networks (DNNs) are typically trained with a global cross-entropy loss in a supervised end-to-end manner: neurons need to store their outgoing weights; training alternates between a forward pass (computation) and a top-down backward pass (learning) which is biologically implausible. Alternatively, greedy layer-wise training eliminates the need for cross-entropy loss and backpropagation. By avoiding the computation of intermediate gradients and the storage of intermediate outputs, it reduces memory usage and helps mitigate issues such as vanishing or exploding gradients. However, most existing layer-wise training approaches have been evaluated only on relatively small datasets with simple deep architectures. In this paper, we first systematically analyze the training dynamics of popular convolutional neural networks (CNNs) trained by stochastic gradient descent (SGD) through an information-theoretic lens. Our findings reveal that networks converge layer-by-layer from bottom to top and that the flow of information adheres to a Markov information bottleneck principle. Building on these observations, we propose a novel layer-wise training approach based on the recently developed deterministic information bottleneck (DIB) and the matrix-based R\'enyi's $\alpha$-order entropy functional. Specifically, each layer is trained jointly with an auxiliary classifier that connects directly to the output layer, enabling the learning of minimal sufficient task-relevant representations. We empirically validate the effectiveness of our training procedure on CIFAR-10 and CIFAR-100 using modern deep CNNs and further demonstrate its applicability to a practical task involving traffic sign recognition. Our approach not only outperforms existing layer-wise training baselines but also achieves performance comparable to SGD.
Unified Representation Learning for Multi-Intent Diversity and Behavioral Uncertainty in Recommender Systems
Sep 04, 2025Abstract:This paper addresses the challenge of jointly modeling user intent diversity and behavioral uncertainty in recommender systems. A unified representation learning framework is proposed. The framework builds a multi-intent representation module and an uncertainty modeling mechanism. It extracts multi-granularity interest structures from user behavior sequences. Behavioral ambiguity and preference fluctuation are captured using Bayesian distribution modeling. In the multi-intent modeling part, the model introduces multiple latent intent vectors. These vectors are weighted and fused using an attention mechanism to generate semantically rich representations of long-term user preferences. In the uncertainty modeling part, the model learns the mean and covariance of behavior representations through Gaussian distributions. This reflects the user's confidence in different behavioral contexts. Next, a learnable fusion strategy is used to combine long-term intent and short-term behavior signals. This produces the final user representation, improving both recommendation accuracy and robustness. The method is evaluated on standard public datasets. Experimental results show that it outperforms existing representative models across multiple metrics. It also demonstrates greater stability and adaptability under cold-start and behavioral disturbance scenarios. The approach alleviates modeling bottlenecks faced by traditional methods when dealing with complex user behavior. These findings confirm the effectiveness and practical value of the unified modeling strategy in real-world recommendation tasks.
Knowledge Graph-Infused Fine-Tuning for Structured Reasoning in Large Language Models
Aug 20, 2025Abstract:This paper addresses the problems of missing reasoning chains and insufficient entity-level semantic understanding in large language models when dealing with tasks that require structured knowledge. It proposes a fine-tuning algorithm framework based on knowledge graph injection. The method builds on pretrained language models and introduces structured graph information for auxiliary learning. A graph neural network is used to encode entities and their relations, constructing a graph-based semantic representation. A fusion mechanism is then designed to jointly model the knowledge graph embeddings with the contextual representations from the language model. To enhance the robustness of knowledge integration, a gating mechanism is introduced to dynamically balance the contributions of linguistic semantics and structural knowledge. This effectively mitigates conflicts between different representational spaces. During training, a joint loss function is constructed to account for both task performance and structural alignment objectives. This helps improve the accuracy of entity prediction and semantic reasoning. The study also includes a series of systematic sensitivity experiments. It evaluates the effects of learning rate, graph coverage, and structural perturbations on model performance. The results further validate the effectiveness and stability of the proposed method across tasks such as entity recognition, question answering, and language generation. Experimental findings show that the proposed structure-aware fine-tuning framework significantly enhances the model's ability to represent complex semantic units. It demonstrates better semantic consistency and contextual logic modeling in scenarios involving structural reasoning and entity extraction.
Modeling Multi-Hop Semantic Paths for Recommendation in Heterogeneous Information Networks
May 09, 2025



Abstract:This study focuses on the problem of path modeling in heterogeneous information networks and proposes a multi-hop path-aware recommendation framework. The method centers on multi-hop paths composed of various types of entities and relations. It models user preferences through three stages: path selection, semantic representation, and attention-based fusion. In the path selection stage, a path filtering mechanism is introduced to remove redundant and noisy information. In the representation learning stage, a sequential modeling structure is used to jointly encode entities and relations, preserving the semantic dependencies within paths. In the fusion stage, an attention mechanism assigns different weights to each path to generate a global user interest representation. Experiments conducted on real-world datasets such as Amazon-Book show that the proposed method significantly outperforms existing recommendation models across multiple evaluation metrics, including HR@10, Recall@10, and Precision@10. The results confirm the effectiveness of multi-hop paths in capturing high-order interaction semantics and demonstrate the expressive modeling capabilities of the framework in heterogeneous recommendation scenarios. This method provides both theoretical and practical value by integrating structural information modeling in heterogeneous networks with recommendation algorithm design. It offers a more expressive and flexible paradigm for learning user preferences in complex data environments.
Towards Robust Few-Shot Text Classification Using Transformer Architectures and Dual Loss Strategies
May 09, 2025
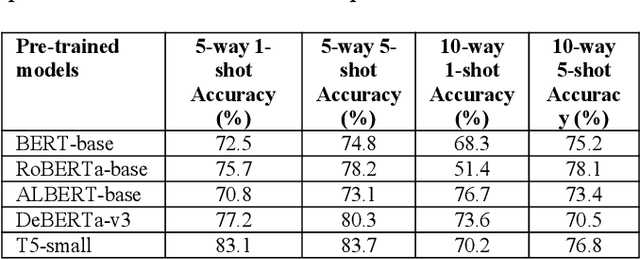
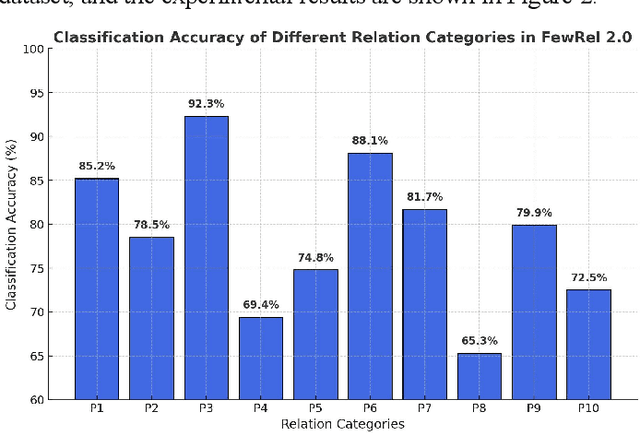
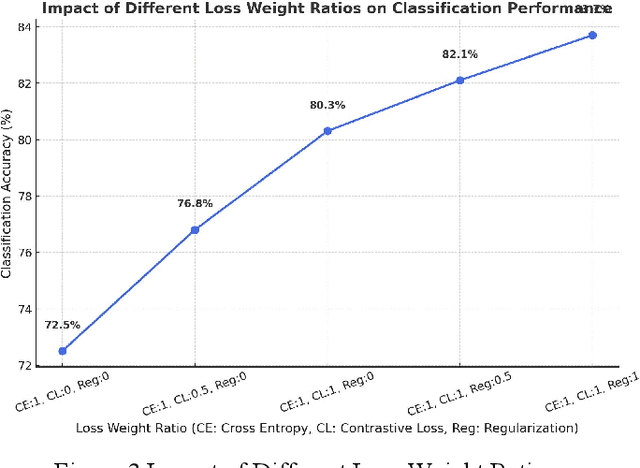
Abstract:Few-shot text classification has important application value in low-resource environments. This paper proposes a strategy that combines adaptive fine-tuning, contrastive learning, and regularization optimization to improve the classification performance of Transformer-based models. Experiments on the FewRel 2.0 dataset show that T5-small, DeBERTa-v3, and RoBERTa-base perform well in few-shot tasks, especially in the 5-shot setting, which can more effectively capture text features and improve classification accuracy. The experiment also found that there are significant differences in the classification difficulty of different relationship categories. Some categories have fuzzy semantic boundaries or complex feature distributions, making it difficult for the standard cross entropy loss to learn the discriminative information required to distinguish categories. By introducing contrastive loss and regularization loss, the generalization ability of the model is enhanced, effectively alleviating the overfitting problem in few-shot environments. In addition, the research results show that the use of Transformer models or generative architectures with stronger self-attention mechanisms can help improve the stability and accuracy of few-shot classification.
Contrastive and Variational Approaches in Self-Supervised Learning for Complex Data Mining
Apr 05, 2025Abstract:Complex data mining has wide application value in many fields, especially in the feature extraction and classification tasks of unlabeled data. This paper proposes an algorithm based on self-supervised learning and verifies its effectiveness through experiments. The study found that in terms of the selection of optimizer and learning rate, the combination of AdamW optimizer and 0.002 learning rate performed best in all evaluation indicators, indicating that the adaptive optimization method can improve the performance of the model in complex data mining tasks. In addition, the ablation experiment further analyzed the contribution of each module. The results show that contrastive learning, variational modules, and data augmentation strategies play a key role in the generalization ability and robustness of the model. Through the convergence curve analysis of the loss function, the experiment verifies that the method can converge stably during the training process and effectively avoid serious overfitting. Further experimental results show that the model has strong adaptability on different data sets, can effectively extract high-quality features from unlabeled data, and improves classification accuracy. At the same time, under different data distribution conditions, the method can still maintain high detection accuracy, proving its applicability in complex data environments. This study analyzed the role of self-supervised learning methods in complex data mining through systematic experiments and verified its advantages in improving feature extraction quality, optimizing classification performance, and enhancing model stability
Improving Harmful Text Detection with Joint Retrieval and External Knowledge
Apr 03, 2025Abstract:Harmful text detection has become a crucial task in the development and deployment of large language models, especially as AI-generated content continues to expand across digital platforms. This study proposes a joint retrieval framework that integrates pre-trained language models with knowledge graphs to improve the accuracy and robustness of harmful text detection. Experimental results demonstrate that the joint retrieval approach significantly outperforms single-model baselines, particularly in low-resource training scenarios and multilingual environments. The proposed method effectively captures nuanced harmful content by leveraging external contextual information, addressing the limitations of traditional detection models. Future research should focus on optimizing computational efficiency, enhancing model interpretability, and expanding multimodal detection capabilities to better tackle evolving harmful content patterns. This work contributes to the advancement of AI safety, ensuring more trustworthy and reliable content moderation systems.
A Hybrid CNN-Transformer Model for Heart Disease Prediction Using Life History Data
Mar 03, 2025Abstract:This study proposed a hybrid model of a convolutional neural network (CNN) and a Transformer to predict and diagnose heart disease. Based on CNN's strength in detecting local features and the Transformer's high capacity in sensing global relations, the model is able to successfully detect risk factors of heart disease from high-dimensional life history data. Experimental results show that the proposed model outperforms traditional benchmark models like support vector machine (SVM), convolutional neural network (CNN), and long short-term memory network (LSTM) on several measures like accuracy, precision, and recall. This demonstrates its strong ability to deal with multi-dimensional and unstructured data. In order to verify the effectiveness of the model, experiments removing certain parts were carried out, and the results of the experiments showed that it is important to use both CNN and Transformer modules in enhancing the model. This paper also discusses the incorporation of additional features and approaches in future studies to enhance the model's performance and enable it to operate effectively in diverse conditions. This study presents novel insights and methods for predicting heart disease using machine learning, with numerous potential applications especially in personalized medicine and health management.
Multi-Scale Transformer Architecture for Accurate Medical Image Classification
Feb 10, 2025



Abstract:This study introduces an AI-driven skin lesion classification algorithm built on an enhanced Transformer architecture, addressing the challenges of accuracy and robustness in medical image analysis. By integrating a multi-scale feature fusion mechanism and refining the self-attention process, the model effectively extracts both global and local features, enhancing its ability to detect lesions with ambiguous boundaries and intricate structures. Performance evaluation on the ISIC 2017 dataset demonstrates that the improved Transformer surpasses established AI models, including ResNet50, VGG19, ResNext, and Vision Transformer, across key metrics such as accuracy, AUC, F1-Score, and Precision. Grad-CAM visualizations further highlight the interpretability of the model, showcasing strong alignment between the algorithm's focus areas and actual lesion sites. This research underscores the transformative potential of advanced AI models in medical imaging, paving the way for more accurate and reliable diagnostic tools. Future work will explore the scalability of this approach to broader medical imaging tasks and investigate the integration of multimodal data to enhance AI-driven diagnostic frameworks for intelligent healthcare.
A Structured Reasoning Framework for Unbalanced Data Classification Using Probabilistic Models
Feb 05, 2025

Abstract:This paper studies a Markov network model for unbalanced data, aiming to solve the problems of classification bias and insufficient minority class recognition ability of traditional machine learning models in environments with uneven class distribution. By constructing joint probability distribution and conditional dependency, the model can achieve global modeling and reasoning optimization of sample categories. The study introduced marginal probability estimation and weighted loss optimization strategies, combined with regularization constraints and structured reasoning methods, effectively improving the generalization ability and robustness of the model. In the experimental stage, a real credit card fraud detection dataset was selected and compared with models such as logistic regression, support vector machine, random forest and XGBoost. The experimental results show that the Markov network performs well in indicators such as weighted accuracy, F1 score, and AUC-ROC, significantly outperforming traditional classification models, demonstrating its strong decision-making ability and applicability in unbalanced data scenarios. Future research can focus on efficient model training, structural optimization, and deep learning integration in large-scale unbalanced data environments and promote its wide application in practical applications such as financial risk control, medical diagnosis, and intelligent monitoring.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge