Yanlin Xiang
Adaptive Transformer Attention and Multi-Scale Fusion for Spine 3D Segmentation
Mar 17, 2025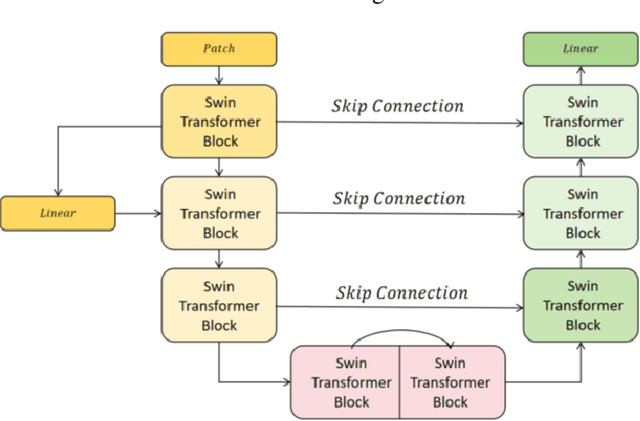
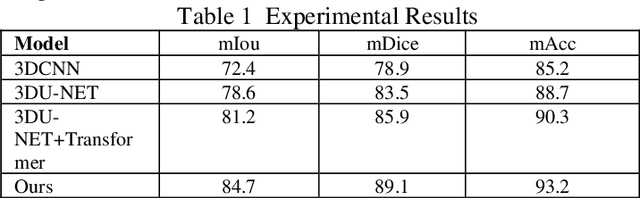
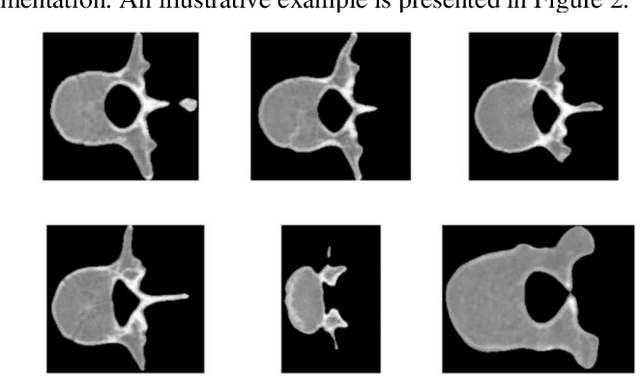
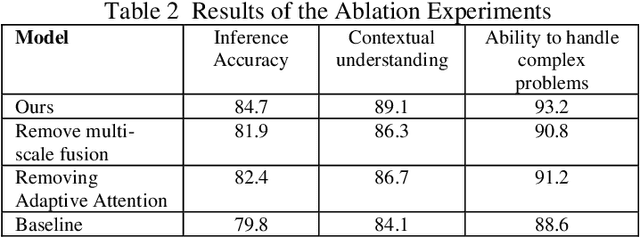
Abstract:This study proposes a 3D semantic segmentation method for the spine based on the improved SwinUNETR to improve segmentation accuracy and robustness. Aiming at the complex anatomical structure of spinal images, this paper introduces a multi-scale fusion mechanism to enhance the feature extraction capability by using information of different scales, thereby improving the recognition accuracy of the model for the target area. In addition, the introduction of the adaptive attention mechanism enables the model to dynamically adjust the attention to the key area, thereby optimizing the boundary segmentation effect. The experimental results show that compared with 3D CNN, 3D U-Net, and 3D U-Net + Transformer, the model of this study has achieved significant improvements in mIoU, mDice, and mAcc indicators, and has better segmentation performance. The ablation experiment further verifies the effectiveness of the proposed improved method, proving that multi-scale fusion and adaptive attention mechanism have a positive effect on the segmentation task. Through the visualization analysis of the inference results, the model can better restore the real anatomical structure of the spinal image. Future research can further optimize the Transformer structure and expand the data scale to improve the generalization ability of the model. This study provides an efficient solution for the task of medical image segmentation, which is of great significance to intelligent medical image analysis.
A Hybrid CNN-Transformer Model for Heart Disease Prediction Using Life History Data
Mar 03, 2025Abstract:This study proposed a hybrid model of a convolutional neural network (CNN) and a Transformer to predict and diagnose heart disease. Based on CNN's strength in detecting local features and the Transformer's high capacity in sensing global relations, the model is able to successfully detect risk factors of heart disease from high-dimensional life history data. Experimental results show that the proposed model outperforms traditional benchmark models like support vector machine (SVM), convolutional neural network (CNN), and long short-term memory network (LSTM) on several measures like accuracy, precision, and recall. This demonstrates its strong ability to deal with multi-dimensional and unstructured data. In order to verify the effectiveness of the model, experiments removing certain parts were carried out, and the results of the experiments showed that it is important to use both CNN and Transformer modules in enhancing the model. This paper also discusses the incorporation of additional features and approaches in future studies to enhance the model's performance and enable it to operate effectively in diverse conditions. This study presents novel insights and methods for predicting heart disease using machine learning, with numerous potential applications especially in personalized medicine and health management.
Multi-Scale Transformer Architecture for Accurate Medical Image Classification
Feb 10, 2025



Abstract:This study introduces an AI-driven skin lesion classification algorithm built on an enhanced Transformer architecture, addressing the challenges of accuracy and robustness in medical image analysis. By integrating a multi-scale feature fusion mechanism and refining the self-attention process, the model effectively extracts both global and local features, enhancing its ability to detect lesions with ambiguous boundaries and intricate structures. Performance evaluation on the ISIC 2017 dataset demonstrates that the improved Transformer surpasses established AI models, including ResNet50, VGG19, ResNext, and Vision Transformer, across key metrics such as accuracy, AUC, F1-Score, and Precision. Grad-CAM visualizations further highlight the interpretability of the model, showcasing strong alignment between the algorithm's focus areas and actual lesion sites. This research underscores the transformative potential of advanced AI models in medical imaging, paving the way for more accurate and reliable diagnostic tools. Future work will explore the scalability of this approach to broader medical imaging tasks and investigate the integration of multimodal data to enhance AI-driven diagnostic frameworks for intelligent healthcare.
Deep Learning in Image Classification: Evaluating VGG19's Performance on Complex Visual Data
Dec 29, 2024



Abstract:This study aims to explore the automatic classification method of pneumonia X-ray images based on VGG19 deep convolutional neural network, and evaluate its application effect in pneumonia diagnosis by comparing with classic models such as SVM, XGBoost, MLP, and ResNet50. The experimental results show that VGG19 performs well in multiple indicators such as accuracy (92%), AUC (0.95), F1 score (0.90) and recall rate (0.87), which is better than other comparison models, especially in image feature extraction and classification accuracy. Although ResNet50 performs well in some indicators, it is slightly inferior to VGG19 in recall rate and F1 score. Traditional machine learning models SVM and XGBoost are obviously limited in image classification tasks, especially in complex medical image analysis tasks, and their performance is relatively mediocre. The research results show that deep learning, especially convolutional neural networks, have significant advantages in medical image classification tasks, especially in pneumonia X-ray image analysis, and can provide efficient and accurate automatic diagnosis support. This research provides strong technical support for the early detection of pneumonia and the development of automated diagnosis systems and also lays the foundation for further promoting the application and development of automated medical image processing technology.
Accurate Medical Named Entity Recognition Through Specialized NLP Models
Dec 11, 2024


Abstract:This study evaluated the effect of BioBERT in medical text processing for the task of medical named entity recognition. Through comparative experiments with models such as BERT, ClinicalBERT, SciBERT, and BlueBERT, the results showed that BioBERT achieved the best performance in both precision and F1 score, verifying its applicability and superiority in the medical field. BioBERT enhances its ability to understand professional terms and complex medical texts through pre-training on biomedical data, providing a powerful tool for medical information extraction and clinical decision support. The study also explored the privacy and compliance challenges of BioBERT when processing medical data, and proposed future research directions for combining other medical-specific models to improve generalization and robustness. With the development of deep learning technology, the potential of BioBERT in application fields such as intelligent medicine, personalized treatment, and disease prediction will be further expanded. Future research can focus on the real-time and interpretability of the model to promote its widespread application in the medical field.
Adversarial Neural Networks in Medical Imaging Advancements and Challenges in Semantic Segmentation
Oct 17, 2024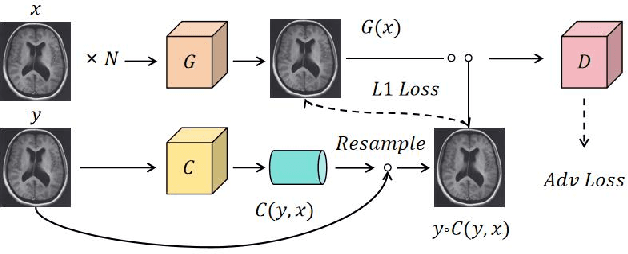
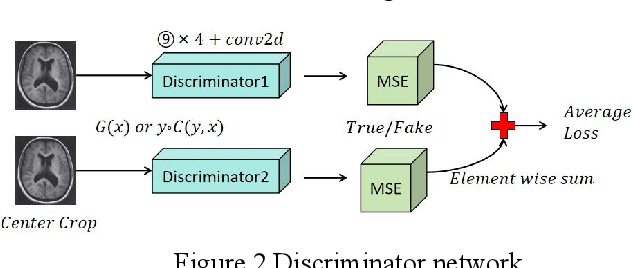
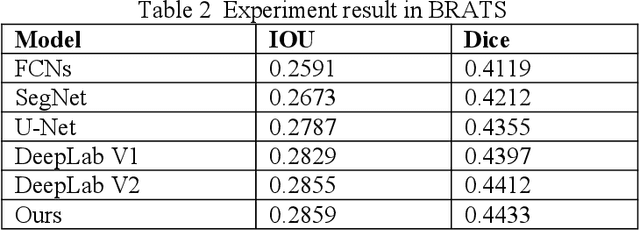
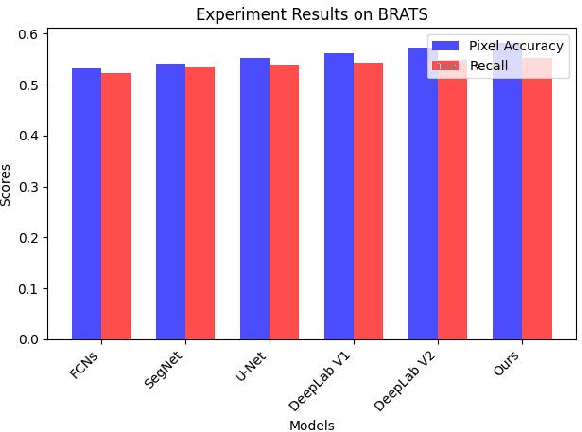
Abstract:Recent advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) have precipitated a paradigm shift in medical imaging, particularly revolutionizing the domain of brain imaging. This paper systematically investigates the integration of deep learning -- a principal branch of AI -- into the semantic segmentation of brain images. Semantic segmentation serves as an indispensable technique for the delineation of discrete anatomical structures and the identification of pathological markers, essential for the diagnosis of complex neurological disorders. Historically, the reliance on manual interpretation by radiologists, while noteworthy for its accuracy, is plagued by inherent subjectivity and inter-observer variability. This limitation becomes more pronounced with the exponential increase in imaging data, which traditional methods struggle to process efficiently and effectively. In response to these challenges, this study introduces the application of adversarial neural networks, a novel AI approach that not only automates but also refines the semantic segmentation process. By leveraging these advanced neural networks, our approach enhances the precision of diagnostic outputs, reducing human error and increasing the throughput of imaging data analysis. The paper provides a detailed discussion on how adversarial neural networks facilitate a more robust, objective, and scalable solution, thereby significantly improving diagnostic accuracies in neurological evaluations. This exploration highlights the transformative impact of AI on medical imaging, setting a new benchmark for future research and clinical practice in neurology.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge