Tong Zhou
MotivGraph-SoIQ: Integrating Motivational Knowledge Graphs and Socratic Dialogue for Enhanced LLM Ideation
Sep 26, 2025



Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) hold substantial potential for accelerating academic ideation but face critical challenges in grounding ideas and mitigating confirmation bias for further refinement. We propose integrating motivational knowledge graphs and socratic dialogue to address these limitations in enhanced LLM ideation (MotivGraph-SoIQ). This novel framework provides essential grounding and practical idea improvement steps for LLM ideation by integrating a Motivational Knowledge Graph (MotivGraph) with a Q-Driven Socratic Ideator. The MotivGraph structurally stores three key node types(problem, challenge and solution) to offer motivation grounding for the LLM ideation process. The Ideator is a dual-agent system utilizing Socratic questioning, which facilitates a rigorous refinement process that mitigates confirmation bias and improves idea quality across novelty, experimental rigor, and motivational rationality dimensions. On the ICLR25 paper topics dataset, MotivGraph-SoIQ exhibits clear advantages over existing state-of-the-art approaches across LLM-based scoring, ELO ranking, and human evaluation metrics.
OMGSR: You Only Need One Mid-timestep Guidance for Real-World Image Super-Resolution
Aug 11, 2025Abstract:Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models (DDPM) and Flow Matching (FM) generative models show promising potential for one-step Real-World Image Super-Resolution (Real-ISR). Recent one-step Real-ISR models typically inject a Low-Quality (LQ) image latent distribution at the initial timestep. However, a fundamental gap exists between the LQ image latent distribution and the Gaussian noisy latent distribution, limiting the effective utilization of generative priors. We observe that the noisy latent distribution at DDPM/FM mid-timesteps aligns more closely with the LQ image latent distribution. Based on this insight, we present One Mid-timestep Guidance Real-ISR (OMGSR), a universal framework applicable to DDPM/FM-based generative models. OMGSR injects the LQ image latent distribution at a pre-computed mid-timestep, incorporating the proposed Latent Distribution Refinement loss to alleviate the latent distribution gap. We also design the Overlap-Chunked LPIPS/GAN loss to eliminate checkerboard artifacts in image generation. Within this framework, we instantiate OMGSR for DDPM/FM-based generative models with two variants: OMGSR-S (SD-Turbo) and OMGSR-F (FLUX.1-dev). Experimental results demonstrate that OMGSR-S/F achieves balanced/excellent performance across quantitative and qualitative metrics at 512-resolution. Notably, OMGSR-F establishes overwhelming dominance in all reference metrics. We further train a 1k-resolution OMGSR-F to match the default resolution of FLUX.1-dev, which yields excellent results, especially in the details of the image generation. We also generate 2k-resolution images by the 1k-resolution OMGSR-F using our two-stage Tiled VAE & Diffusion.
RULE: Reinforcement UnLEarning Achieves Forget-Retain Pareto Optimality
Jun 08, 2025Abstract:The widespread deployment of Large Language Models (LLMs) trained on massive, uncurated corpora has raised growing concerns about the inclusion of sensitive, copyrighted, or illegal content. This has led to increasing interest in LLM unlearning: the task of selectively removing specific information from a model without retraining from scratch or degrading overall utility. However, existing methods often rely on large-scale forget and retain datasets, and suffer from unnatural responses, poor generalization, or catastrophic utility loss. In this work, we propose Reinforcement UnLearning (RULE), an efficient framework that formulates unlearning as a refusal boundary optimization problem. RULE is trained with a small portion of the forget set and synthesized boundary queries, using a verifiable reward function that encourages safe refusal on forget--related queries while preserving helpful responses on permissible inputs. We provide both theoretical and empirical evidence demonstrating the effectiveness of RULE in achieving targeted unlearning without compromising model utility. Experimental results show that, with only $12%$ forget set and $8%$ synthesized boundary data, RULE outperforms existing baselines by up to $17.5%$ forget quality and $16.3%$ naturalness response while maintaining general utility, achieving forget--retain Pareto optimality. Remarkably, we further observe that RULE improves the naturalness of model outputs, enhances training efficiency, and exhibits strong generalization ability, generalizing refusal behavior to semantically related but unseen queries.
Semantic Pivots Enable Cross-Lingual Transfer in Large Language Models
May 22, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) demonstrate remarkable ability in cross-lingual tasks. Understanding how LLMs acquire this ability is crucial for their interpretability. To quantify the cross-lingual ability of LLMs accurately, we propose a Word-Level Cross-Lingual Translation Task. To find how LLMs learn cross-lingual ability, we trace the outputs of LLMs' intermediate layers in the word translation task. We identify and distinguish two distinct behaviors in the forward pass of LLMs: co-occurrence behavior and semantic pivot behavior. We attribute LLMs' two distinct behaviors to the co-occurrence frequency of words and find the semantic pivot from the pre-training dataset. Finally, to apply our findings to improve the cross-lingual ability of LLMs, we reconstruct a semantic pivot-aware pre-training dataset using documents with a high proportion of semantic pivots. Our experiments validate the effectiveness of our approach in enhancing cross-lingual ability. Our research contributes insights into the interpretability of LLMs and offers a method for improving LLMs' cross-lingual ability.
Transparentize the Internal and External Knowledge Utilization in LLMs with Trustworthy Citation
Apr 21, 2025Abstract:While hallucinations of large language models could been alleviated through retrieval-augmented generation and citation generation, how the model utilizes internal knowledge is still opaque, and the trustworthiness of its generated answers remains questionable. In this work, we introduce Context-Prior Augmented Citation Generation task, requiring models to generate citations considering both external and internal knowledge while providing trustworthy references, with 5 evaluation metrics focusing on 3 aspects: answer helpfulness, citation faithfulness, and trustworthiness. We introduce RAEL, the paradigm for our task, and also design INTRALIGN, an integrated method containing customary data generation and an alignment algorithm. Our experimental results show that our method achieves a better cross-scenario performance with regard to other baselines. Our extended experiments further reveal that retrieval quality, question types, and model knowledge have considerable influence on the trustworthiness in citation generation.
ProDiF: Protecting Domain-Invariant Features to Secure Pre-Trained Models Against Extraction
Mar 17, 2025Abstract:Pre-trained models are valuable intellectual property, capturing both domain-specific and domain-invariant features within their weight spaces. However, model extraction attacks threaten these assets by enabling unauthorized source-domain inference and facilitating cross-domain transfer via the exploitation of domain-invariant features. In this work, we introduce **ProDiF**, a novel framework that leverages targeted weight space manipulation to secure pre-trained models against extraction attacks. **ProDiF** quantifies the transferability of filters and perturbs the weights of critical filters in unsecured memory, while preserving actual critical weights in a Trusted Execution Environment (TEE) for authorized users. A bi-level optimization further ensures resilience against adaptive fine-tuning attacks. Experimental results show that **ProDiF** reduces source-domain accuracy to near-random levels and decreases cross-domain transferability by 74.65\%, providing robust protection for pre-trained models. This work offers comprehensive protection for pre-trained DNN models and highlights the potential of weight space manipulation as a novel approach to model security.
Deep Learning in Image Classification: Evaluating VGG19's Performance on Complex Visual Data
Dec 29, 2024



Abstract:This study aims to explore the automatic classification method of pneumonia X-ray images based on VGG19 deep convolutional neural network, and evaluate its application effect in pneumonia diagnosis by comparing with classic models such as SVM, XGBoost, MLP, and ResNet50. The experimental results show that VGG19 performs well in multiple indicators such as accuracy (92%), AUC (0.95), F1 score (0.90) and recall rate (0.87), which is better than other comparison models, especially in image feature extraction and classification accuracy. Although ResNet50 performs well in some indicators, it is slightly inferior to VGG19 in recall rate and F1 score. Traditional machine learning models SVM and XGBoost are obviously limited in image classification tasks, especially in complex medical image analysis tasks, and their performance is relatively mediocre. The research results show that deep learning, especially convolutional neural networks, have significant advantages in medical image classification tasks, especially in pneumonia X-ray image analysis, and can provide efficient and accurate automatic diagnosis support. This research provides strong technical support for the early detection of pneumonia and the development of automated diagnosis systems and also lays the foundation for further promoting the application and development of automated medical image processing technology.
DTELS: Towards Dynamic Granularity of Timeline Summarization
Nov 14, 2024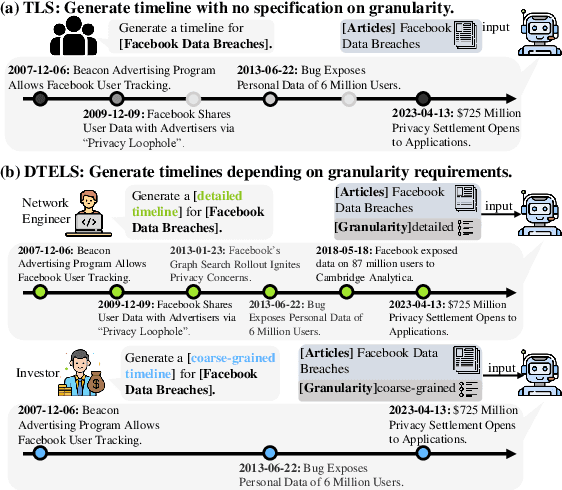
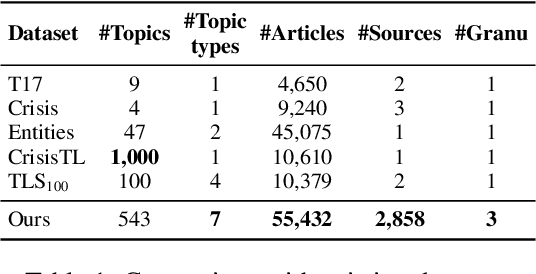
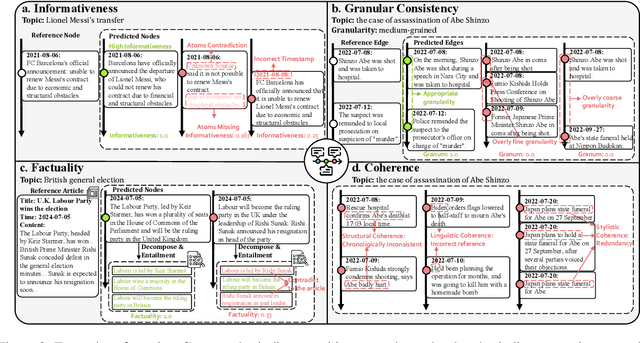

Abstract:The rapid proliferation of online news has posed significant challenges in tracking the continuous development of news topics. Traditional timeline summarization constructs a chronological summary of the events but often lacks the flexibility to meet the diverse granularity needs. To overcome this limitation, we introduce a new paradigm, Dynamic-granularity TimELine Summarization, (DTELS), which aims to construct adaptive timelines based on user instructions or requirements. This paper establishes a comprehensive benchmark for DTLES that includes: (1) an evaluation framework grounded in journalistic standards to assess the timeline quality across four dimensions: Informativeness, Granular Consistency, Factuality, and Coherence; (2) a large-scale, multi-source dataset with multiple granularity timeline annotations based on a consensus process to facilitate authority; (3) extensive experiments and analysis with two proposed solutions based on Large Language Models (LLMs) and existing state-of-the-art TLS methods. The experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of LLM-based solutions. However, even the most advanced LLMs struggle to consistently generate timelines that are both informative and granularly consistent, highlighting the challenges of the DTELS task.
Deep Learning with HM-VGG: AI Strategies for Multi-modal Image Analysis
Oct 31, 2024



Abstract:This study introduces the Hybrid Multi-modal VGG (HM-VGG) model, a cutting-edge deep learning approach for the early diagnosis of glaucoma. The HM-VGG model utilizes an attention mechanism to process Visual Field (VF) data, enabling the extraction of key features that are vital for identifying early signs of glaucoma. Despite the common reliance on large annotated datasets, the HM-VGG model excels in scenarios with limited data, achieving remarkable results with small sample sizes. The model's performance is underscored by its high metrics in Precision, Accuracy, and F1-Score, indicating its potential for real-world application in glaucoma detection. The paper also discusses the challenges associated with ophthalmic image analysis, particularly the difficulty of obtaining large volumes of annotated data. It highlights the importance of moving beyond single-modality data, such as VF or Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) images alone, to a multimodal approach that can provide a richer, more comprehensive dataset. This integration of different data types is shown to significantly enhance diagnostic accuracy. The HM- VGG model offers a promising tool for doctors, streamlining the diagnostic process and improving patient outcomes. Furthermore, its applicability extends to telemedicine and mobile healthcare, making diagnostic services more accessible. The research presented in this paper is a significant step forward in the field of medical image processing and has profound implications for clinical ophthalmology.
Deep Learning-Based Channel Squeeze U-Structure for Lung Nodule Detection and Segmentation
Sep 20, 2024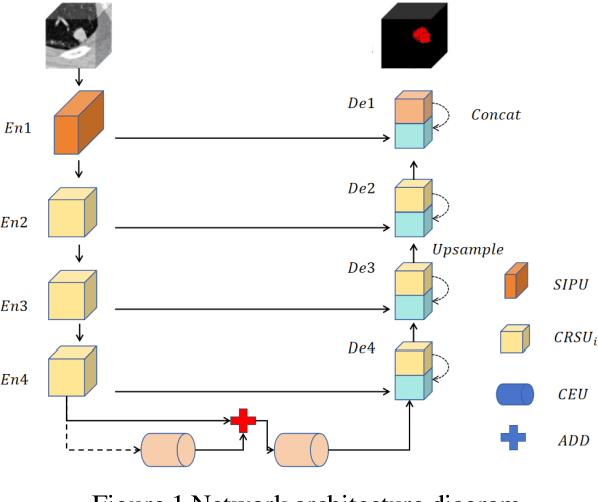
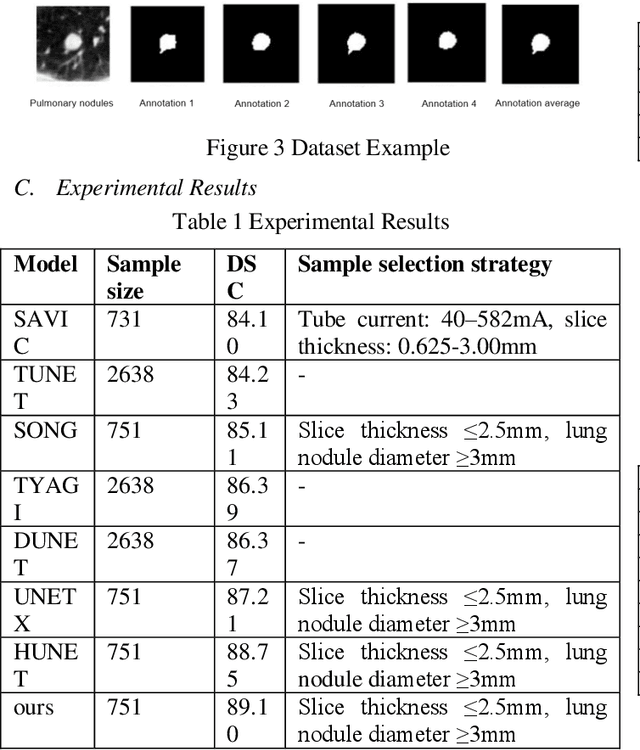
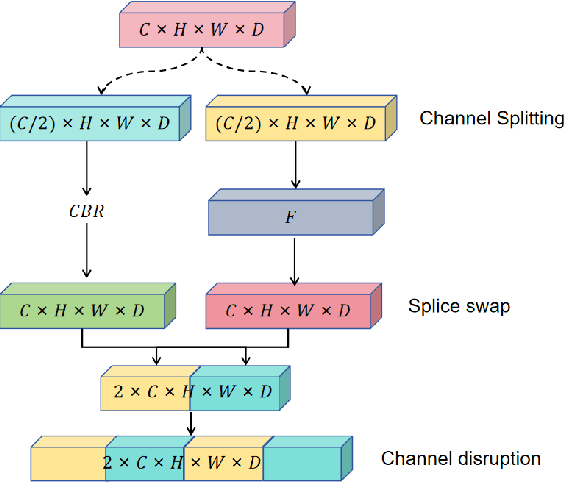
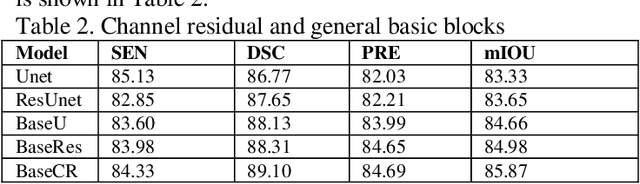
Abstract:This paper introduces a novel deep-learning method for the automatic detection and segmentation of lung nodules, aimed at advancing the accuracy of early-stage lung cancer diagnosis. The proposed approach leverages a unique "Channel Squeeze U-Structure" that optimizes feature extraction and information integration across multiple semantic levels of the network. This architecture includes three key modules: shallow information processing, channel residual structure, and channel squeeze integration. These modules enhance the model's ability to detect and segment small, imperceptible, or ground-glass nodules, which are critical for early diagnosis. The method demonstrates superior performance in terms of sensitivity, Dice similarity coefficient, precision, and mean Intersection over Union (IoU). Extensive experiments were conducted on the Lung Image Database Consortium (LIDC) dataset using five-fold cross-validation, showing excellent stability and robustness. The results indicate that this approach holds significant potential for improving computer-aided diagnosis systems, providing reliable support for radiologists in clinical practice and aiding in the early detection of lung cancer, especially in resource-limited settings
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge