Shengping Liu
PARL: Position-Aware Relation Learning Network for Document Layout Analysis
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:Document layout analysis aims to detect and categorize structural elements (e.g., titles, tables, figures) in scanned or digital documents. Popular methods often rely on high-quality Optical Character Recognition (OCR) to merge visual features with extracted text. This dependency introduces two major drawbacks: propagation of text recognition errors and substantial computational overhead, limiting the robustness and practical applicability of multimodal approaches. In contrast to the prevailing multimodal trend, we argue that effective layout analysis depends not on text-visual fusion, but on a deep understanding of documents' intrinsic visual structure. To this end, we propose PARL (Position-Aware Relation Learning Network), a novel OCR-free, vision-only framework that models layout through positional sensitivity and relational structure. Specifically, we first introduce a Bidirectional Spatial Position-Guided Deformable Attention module to embed explicit positional dependencies among layout elements directly into visual features. Second, we design a Graph Refinement Classifier (GRC) to refine predictions by modeling contextual relationships through a dynamically constructed layout graph. Extensive experiments show PARL achieves state-of-the-art results. It establishes a new benchmark for vision-only methods on DocLayNet and, notably, surpasses even strong multimodal models on M6Doc. Crucially, PARL (65M) is highly efficient, using roughly four times fewer parameters than large multimodal models (256M), demonstrating that sophisticated visual structure modeling can be both more efficient and robust than multimodal fusion.
FocalOrder: Focal Preference Optimization for Reading Order Detection
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:Reading order detection is the foundation of document understanding. Most existing methods rely on uniform supervision, implicitly assuming a constant difficulty distribution across layout regions. In this work, we challenge this assumption by revealing a critical flaw: \textbf{Positional Disparity}, a phenomenon where models demonstrate mastery over the deterministic start and end regions but suffer a performance collapse in the complex intermediate sections. This degradation arises because standard training allows the massive volume of easy patterns to drown out the learning signals from difficult layouts. To address this, we propose \textbf{FocalOrder}, a framework driven by \textbf{Focal Preference Optimization (FPO)}. Specifically, FocalOrder employs adaptive difficulty discovery with exponential moving average mechanism to dynamically pinpoint hard-to-learn transitions, while introducing a difficulty-calibrated pairwise ranking objective to enforce global logical consistency. Extensive experiments demonstrate that FocalOrder establishes new state-of-the-art results on OmniDocBench v1.0 and Comp-HRDoc. Our compact model not only outperforms competitive specialized baselines but also significantly surpasses large-scale general VLMs. These results demonstrate that aligning the optimization with intrinsic structural ambiguity of documents is critical for mastering complex document structures.
BayesRAG: Probabilistic Mutual Evidence Corroboration for Multimodal Retrieval-Augmented Generation
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) has become a pivotal paradigm for Large Language Models (LLMs), yet current approaches struggle with visually rich documents by treating text and images as isolated retrieval targets. Existing methods relying solely on cosine similarity often fail to capture the semantic reinforcement provided by cross-modal alignment and layout-induced coherence. To address these limitations, we propose BayesRAG, a novel multimodal retrieval framework grounded in Bayesian inference and Dempster-Shafer evidence theory. Unlike traditional approaches that rank candidates strictly by similarity, BayesRAG models the intrinsic consistency of retrieved candidates across modalities as probabilistic evidence to refine retrieval confidence. Specifically, our method computes the posterior association probability for combinations of multimodal retrieval results, prioritizing text-image pairs that mutually corroborate each other in terms of both semantics and layout. Extensive experiments demonstrate that BayesRAG significantly outperforms state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods on challenging multimodal benchmarks. This study establishes a new paradigm for multimodal retrieval fusion that effectively resolves the isolation of heterogeneous modalities through an evidence fusion mechanism and enhances the robustness of retrieval outcomes. Our code is available at https://github.com/TioeAre/BayesRAG.
Semantic Pivots Enable Cross-Lingual Transfer in Large Language Models
May 22, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) demonstrate remarkable ability in cross-lingual tasks. Understanding how LLMs acquire this ability is crucial for their interpretability. To quantify the cross-lingual ability of LLMs accurately, we propose a Word-Level Cross-Lingual Translation Task. To find how LLMs learn cross-lingual ability, we trace the outputs of LLMs' intermediate layers in the word translation task. We identify and distinguish two distinct behaviors in the forward pass of LLMs: co-occurrence behavior and semantic pivot behavior. We attribute LLMs' two distinct behaviors to the co-occurrence frequency of words and find the semantic pivot from the pre-training dataset. Finally, to apply our findings to improve the cross-lingual ability of LLMs, we reconstruct a semantic pivot-aware pre-training dataset using documents with a high proportion of semantic pivots. Our experiments validate the effectiveness of our approach in enhancing cross-lingual ability. Our research contributes insights into the interpretability of LLMs and offers a method for improving LLMs' cross-lingual ability.
A general physics-constrained method for the modelling of equation's closure terms with sparse data
Apr 30, 2025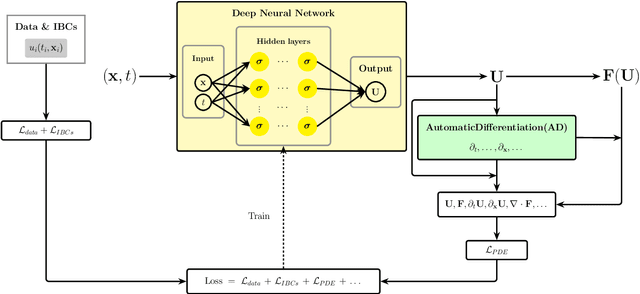
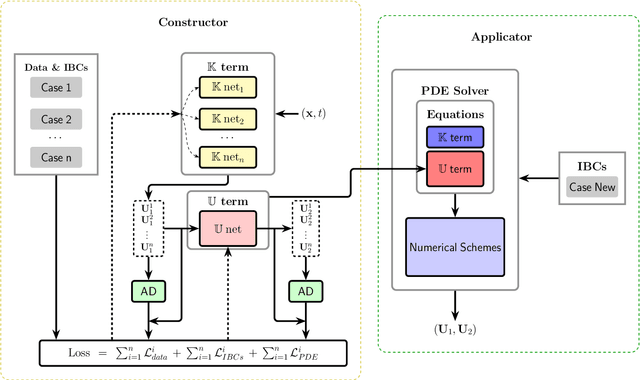

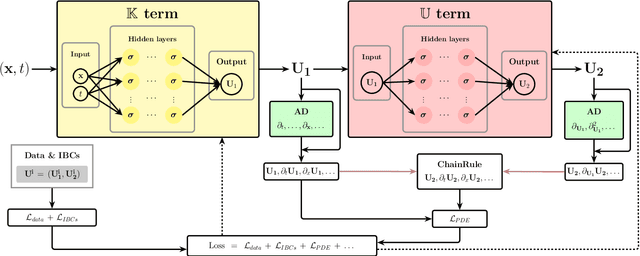
Abstract:Accurate modeling of closure terms is a critical challenge in engineering and scientific research, particularly when data is sparse (scarse or incomplete), making widely applicable models difficult to develop. This study proposes a novel approach for constructing closure models in such challenging scenarios. We introduce a Series-Parallel Multi-Network Architecture that integrates Physics-Informed Neural Networks (PINNs) to incorporate physical constraints and heterogeneous data from multiple initial and boundary conditions, while employing dedicated subnetworks to independently model unknown closure terms, enhancing generalizability across diverse problems. These closure models are integrated into an accurate Partial Differential Equation (PDE) solver, enabling robust solutions to complex predictive simulations in engineering applications.
Transparentize the Internal and External Knowledge Utilization in LLMs with Trustworthy Citation
Apr 21, 2025Abstract:While hallucinations of large language models could been alleviated through retrieval-augmented generation and citation generation, how the model utilizes internal knowledge is still opaque, and the trustworthiness of its generated answers remains questionable. In this work, we introduce Context-Prior Augmented Citation Generation task, requiring models to generate citations considering both external and internal knowledge while providing trustworthy references, with 5 evaluation metrics focusing on 3 aspects: answer helpfulness, citation faithfulness, and trustworthiness. We introduce RAEL, the paradigm for our task, and also design INTRALIGN, an integrated method containing customary data generation and an alignment algorithm. Our experimental results show that our method achieves a better cross-scenario performance with regard to other baselines. Our extended experiments further reveal that retrieval quality, question types, and model knowledge have considerable influence on the trustworthiness in citation generation.
From Instance Training to Instruction Learning: Task Adapters Generation from Instructions
Jun 18, 2024



Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have acquired the ability to solve general tasks by utilizing instruction finetuning (IFT). However, IFT still relies heavily on instance training of extensive task data, which greatly limits the adaptability of LLMs to real-world scenarios where labeled task instances are scarce and broader task generalization becomes paramount. Contrary to LLMs, humans acquire skills and complete tasks not merely through repeated practice but also by understanding and following instructional guidelines. This paper is dedicated to simulating human learning to address the shortcomings of instance training, focusing on instruction learning to enhance cross-task generalization. Within this context, we introduce Task Adapters Generation from Instructions (TAGI), which automatically constructs the task-specific model in a parameter generation manner based on the given task instructions without retraining for unseen tasks. Specifically, we utilize knowledge distillation to enhance the consistency between TAGI developed through Learning with Instruction and task-specific models developed through Training with Instance, by aligning the labels, output logits, and adapter parameters between them. TAGI is endowed with cross-task generalization capabilities through a two-stage training process that includes hypernetwork pretraining and finetuning. We evaluate TAGI on the Super-Natural Instructions and P3 datasets. The experimental results demonstrate that TAGI can match or even outperform traditional meta-trained models and other hypernetwork models, while significantly reducing computational requirements.
Imagination Augmented Generation: Learning to Imagine Richer Context for Question Answering over Large Language Models
Mar 28, 2024



Abstract:Retrieval-Augmented-Generation and Gener-ation-Augmented-Generation have been proposed to enhance the knowledge required for question answering over Large Language Models (LLMs). However, the former depends on external resources, and both require incorporating the explicit documents into the context, which results in longer contexts that lead to more resource consumption. Recent works indicate that LLMs have modeled rich knowledge, albeit not effectively triggered or activated. Inspired by this, we propose a novel knowledge-augmented framework, Imagination-Augmented-Generation (IAG), which simulates the human capacity to compensate for knowledge deficits while answering questions solely through imagination, without relying on external resources. Guided by IAG, we propose an imagine richer context method for question answering (IMcQA), which obtains richer context through the following two modules: explicit imagination by generating a short dummy document with long context compress and implicit imagination with HyperNetwork for generating adapter weights. Experimental results on three datasets demonstrate that IMcQA exhibits significant advantages in both open-domain and closed-book settings, as well as in both in-distribution performance and out-of-distribution generalizations. Our code will be available at https://github.com/Xnhyacinth/IAG.
The Da Vinci Code of Large Pre-trained Language Models: Deciphering Degenerate Knowledge Neurons
Feb 21, 2024Abstract:This study explores the mechanism of factual knowledge storage in pre-trained language models (PLMs). Previous research suggests that factual knowledge is stored within multi-layer perceptron weights, and some storage units exhibit degeneracy, referred to as Degenerate Knowledge Neurons (DKNs). This paper provides a comprehensive definition of DKNs that covers both structural and functional aspects, pioneering the study of structures in PLMs' factual knowledge storage units. Based on this, we introduce the Neurological Topology Clustering method, which allows the formation of DKNs in any numbers and structures, leading to a more accurate DKN acquisition. Furthermore, we introduce the Neuro-Degeneracy Analytic Analysis Framework, which uniquely integrates model robustness, evolvability, and complexity for a holistic assessment of PLMs. Within this framework, our execution of 34 experiments across 2 PLMs, 4 datasets, and 6 settings highlights the critical role of DKNs. The code will be available soon.
Discerning and Resolving Knowledge Conflicts through Adaptive Decoding with Contextual Information-Entropy Constraint
Feb 19, 2024Abstract:Large language models internalize enormous parametric knowledge during pre-training. Concurrently, realistic applications necessitate external contextual knowledge to aid models on the underlying tasks. This raises a crucial dilemma known as knowledge conflicts, where the contextual knowledge clashes with the However, existing decoding works are specialized in resolving knowledge conflicts and could inadvertently deteriorate performance in absence of conflicts. In this paper, we propose an adaptive decoding method, termed as contextual information-entropy constraint decoding (COIECD), to discern whether the knowledge conflicts occur and resolve them. It can improve the model's faithfulness to conflicting context, and simultaneously maintain high performance among non- Our experiments show that COIECD exhibits strong performance and robustness over knowledge conflicts in realistic datasets. Code is available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge