Yubo Chen
Animal Re-Identification on Microcontrollers
Dec 09, 2025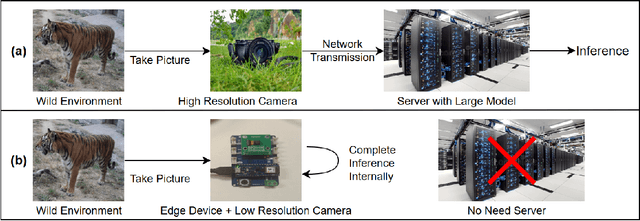
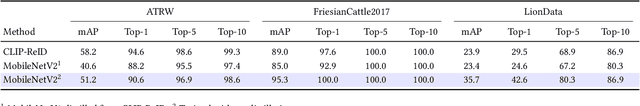
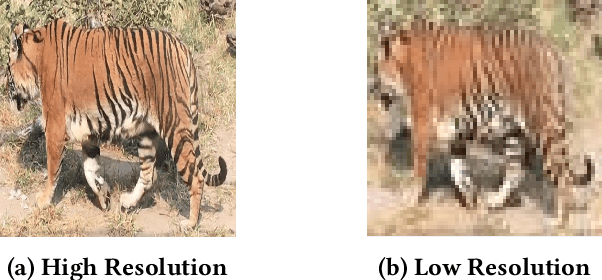
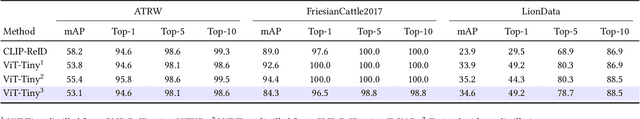
Abstract:Camera-based animal re-identification (Animal Re-ID) can support wildlife monitoring and precision livestock management in large outdoor environments with limited wireless connectivity. In these settings, inference must run directly on collar tags or low-power edge nodes built around microcontrollers (MCUs), yet most Animal Re-ID models are designed for workstations or servers and are too large for devices with small memory and low-resolution inputs. We propose an on-device framework. First, we characterise the gap between state-of-the-art Animal Re-ID models and MCU-class hardware, showing that straightforward knowledge distillation from large teachers offers limited benefit once memory and input resolution are constrained. Second, guided by this analysis, we design a high-accuracy Animal Re-ID architecture by systematically scaling a CNN-based MobileNetV2 backbone for low-resolution inputs. Third, we evaluate the framework with a real-world dataset and introduce a data-efficient fine-tuning strategy to enable fast adaptation with just three images per animal identity at a new site. Across six public Animal Re-ID datasets, our compact model achieves competitive retrieval accuracy while reducing model size by over two orders of magnitude. On a self-collected cattle dataset, the deployed model performs fully on-device inference with only a small accuracy drop and unchanged Top-1 accuracy relative to its cluster version. We demonstrate that practical, adaptable Animal Re-ID is achievable on MCU-class devices, paving the way for scalable deployment in real field environments.
MotivGraph-SoIQ: Integrating Motivational Knowledge Graphs and Socratic Dialogue for Enhanced LLM Ideation
Sep 26, 2025



Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) hold substantial potential for accelerating academic ideation but face critical challenges in grounding ideas and mitigating confirmation bias for further refinement. We propose integrating motivational knowledge graphs and socratic dialogue to address these limitations in enhanced LLM ideation (MotivGraph-SoIQ). This novel framework provides essential grounding and practical idea improvement steps for LLM ideation by integrating a Motivational Knowledge Graph (MotivGraph) with a Q-Driven Socratic Ideator. The MotivGraph structurally stores three key node types(problem, challenge and solution) to offer motivation grounding for the LLM ideation process. The Ideator is a dual-agent system utilizing Socratic questioning, which facilitates a rigorous refinement process that mitigates confirmation bias and improves idea quality across novelty, experimental rigor, and motivational rationality dimensions. On the ICLR25 paper topics dataset, MotivGraph-SoIQ exhibits clear advantages over existing state-of-the-art approaches across LLM-based scoring, ELO ranking, and human evaluation metrics.
RULE: Reinforcement UnLEarning Achieves Forget-Retain Pareto Optimality
Jun 08, 2025Abstract:The widespread deployment of Large Language Models (LLMs) trained on massive, uncurated corpora has raised growing concerns about the inclusion of sensitive, copyrighted, or illegal content. This has led to increasing interest in LLM unlearning: the task of selectively removing specific information from a model without retraining from scratch or degrading overall utility. However, existing methods often rely on large-scale forget and retain datasets, and suffer from unnatural responses, poor generalization, or catastrophic utility loss. In this work, we propose Reinforcement UnLearning (RULE), an efficient framework that formulates unlearning as a refusal boundary optimization problem. RULE is trained with a small portion of the forget set and synthesized boundary queries, using a verifiable reward function that encourages safe refusal on forget--related queries while preserving helpful responses on permissible inputs. We provide both theoretical and empirical evidence demonstrating the effectiveness of RULE in achieving targeted unlearning without compromising model utility. Experimental results show that, with only $12%$ forget set and $8%$ synthesized boundary data, RULE outperforms existing baselines by up to $17.5%$ forget quality and $16.3%$ naturalness response while maintaining general utility, achieving forget--retain Pareto optimality. Remarkably, we further observe that RULE improves the naturalness of model outputs, enhances training efficiency, and exhibits strong generalization ability, generalizing refusal behavior to semantically related but unseen queries.
MMR-V: What's Left Unsaid? A Benchmark for Multimodal Deep Reasoning in Videos
Jun 04, 2025Abstract:The sequential structure of videos poses a challenge to the ability of multimodal large language models (MLLMs) to locate multi-frame evidence and conduct multimodal reasoning. However, existing video benchmarks mainly focus on understanding tasks, which only require models to match frames mentioned in the question (hereafter referred to as "question frame") and perceive a few adjacent frames. To address this gap, we propose MMR-V: A Benchmark for Multimodal Deep Reasoning in Videos. The benchmark is characterized by the following features. (1) Long-range, multi-frame reasoning: Models are required to infer and analyze evidence frames that may be far from the question frame. (2) Beyond perception: Questions cannot be answered through direct perception alone but require reasoning over hidden information. (3) Reliability: All tasks are manually annotated, referencing extensive real-world user understanding to align with common perceptions. (4) Confusability: Carefully designed distractor annotation strategies to reduce model shortcuts. MMR-V consists of 317 videos and 1,257 tasks. Our experiments reveal that current models still struggle with multi-modal reasoning; even the best-performing model, o4-mini, achieves only 52.5% accuracy. Additionally, current reasoning enhancement strategies (Chain-of-Thought and scaling test-time compute) bring limited gains. Further analysis indicates that the CoT demanded for multi-modal reasoning differs from it in textual reasoning, which partly explains the limited performance gains. We hope that MMR-V can inspire further research into enhancing multi-modal reasoning capabilities.
Semantic Pivots Enable Cross-Lingual Transfer in Large Language Models
May 22, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) demonstrate remarkable ability in cross-lingual tasks. Understanding how LLMs acquire this ability is crucial for their interpretability. To quantify the cross-lingual ability of LLMs accurately, we propose a Word-Level Cross-Lingual Translation Task. To find how LLMs learn cross-lingual ability, we trace the outputs of LLMs' intermediate layers in the word translation task. We identify and distinguish two distinct behaviors in the forward pass of LLMs: co-occurrence behavior and semantic pivot behavior. We attribute LLMs' two distinct behaviors to the co-occurrence frequency of words and find the semantic pivot from the pre-training dataset. Finally, to apply our findings to improve the cross-lingual ability of LLMs, we reconstruct a semantic pivot-aware pre-training dataset using documents with a high proportion of semantic pivots. Our experiments validate the effectiveness of our approach in enhancing cross-lingual ability. Our research contributes insights into the interpretability of LLMs and offers a method for improving LLMs' cross-lingual ability.
Revealing the Deceptiveness of Knowledge Editing: A Mechanistic Analysis of Superficial Editing
May 19, 2025Abstract:Knowledge editing, which aims to update the knowledge encoded in language models, can be deceptive. Despite the fact that many existing knowledge editing algorithms achieve near-perfect performance on conventional metrics, the models edited by them are still prone to generating original knowledge. This paper introduces the concept of "superficial editing" to describe this phenomenon. Our comprehensive evaluation reveals that this issue presents a significant challenge to existing algorithms. Through systematic investigation, we identify and validate two key factors contributing to this issue: (1) the residual stream at the last subject position in earlier layers and (2) specific attention modules in later layers. Notably, certain attention heads in later layers, along with specific left singular vectors in their output matrices, encapsulate the original knowledge and exhibit a causal relationship with superficial editing. Furthermore, we extend our analysis to the task of superficial unlearning, where we observe consistent patterns in the behavior of specific attention heads and their corresponding left singular vectors, thereby demonstrating the robustness and broader applicability of our methodology and conclusions. Our code is available here.
Transparentize the Internal and External Knowledge Utilization in LLMs with Trustworthy Citation
Apr 21, 2025Abstract:While hallucinations of large language models could been alleviated through retrieval-augmented generation and citation generation, how the model utilizes internal knowledge is still opaque, and the trustworthiness of its generated answers remains questionable. In this work, we introduce Context-Prior Augmented Citation Generation task, requiring models to generate citations considering both external and internal knowledge while providing trustworthy references, with 5 evaluation metrics focusing on 3 aspects: answer helpfulness, citation faithfulness, and trustworthiness. We introduce RAEL, the paradigm for our task, and also design INTRALIGN, an integrated method containing customary data generation and an alignment algorithm. Our experimental results show that our method achieves a better cross-scenario performance with regard to other baselines. Our extended experiments further reveal that retrieval quality, question types, and model knowledge have considerable influence on the trustworthiness in citation generation.
Rewarding Curse: Analyze and Mitigate Reward Modeling Issues for LLM Reasoning
Mar 07, 2025Abstract:Chain-of-thought (CoT) prompting demonstrates varying performance under different reasoning tasks. Previous work attempts to evaluate it but falls short in providing an in-depth analysis of patterns that influence the CoT. In this paper, we study the CoT performance from the perspective of effectiveness and faithfulness. For the former, we identify key factors that influence CoT effectiveness on performance improvement, including problem difficulty, information gain, and information flow. For the latter, we interpret the unfaithful CoT issue by conducting a joint analysis of the information interaction among the question, CoT, and answer. The result demonstrates that, when the LLM predicts answers, it can recall correct information missing in the CoT from the question, leading to the problem. Finally, we propose a novel algorithm to mitigate this issue, in which we recall extra information from the question to enhance the CoT generation and evaluate CoTs based on their information gain. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our approach enhances both the faithfulness and effectiveness of CoT.
RAG-RewardBench: Benchmarking Reward Models in Retrieval Augmented Generation for Preference Alignment
Dec 18, 2024



Abstract:Despite the significant progress made by existing retrieval augmented language models (RALMs) in providing trustworthy responses and grounding in reliable sources, they often overlook effective alignment with human preferences. In the alignment process, reward models (RMs) act as a crucial proxy for human values to guide optimization. However, it remains unclear how to evaluate and select a reliable RM for preference alignment in RALMs. To this end, we propose RAG-RewardBench, the first benchmark for evaluating RMs in RAG settings. First, we design four crucial and challenging RAG-specific scenarios to assess RMs, including multi-hop reasoning, fine-grained citation, appropriate abstain, and conflict robustness. Then, we incorporate 18 RAG subsets, six retrievers, and 24 RALMs to increase the diversity of data sources. Finally, we adopt an LLM-as-a-judge approach to improve preference annotation efficiency and effectiveness, exhibiting a strong correlation with human annotations. Based on the RAG-RewardBench, we conduct a comprehensive evaluation of 45 RMs and uncover their limitations in RAG scenarios. Additionally, we also reveal that existing trained RALMs show almost no improvement in preference alignment, highlighting the need for a shift towards preference-aligned training.We release our benchmark and code publicly at https://huggingface.co/datasets/jinzhuoran/RAG-RewardBench/ for future work.
OODFace: Benchmarking Robustness of Face Recognition under Common Corruptions and Appearance Variations
Dec 03, 2024



Abstract:With the rise of deep learning, facial recognition technology has seen extensive research and rapid development. Although facial recognition is considered a mature technology, we find that existing open-source models and commercial algorithms lack robustness in certain real-world Out-of-Distribution (OOD) scenarios, raising concerns about the reliability of these systems. In this paper, we introduce OODFace, which explores the OOD challenges faced by facial recognition models from two perspectives: common corruptions and appearance variations. We systematically design 30 OOD scenarios across 9 major categories tailored for facial recognition. By simulating these challenges on public datasets, we establish three robustness benchmarks: LFW-C/V, CFP-FP-C/V, and YTF-C/V. We then conduct extensive experiments on 19 different facial recognition models and 3 commercial APIs, along with extended experiments on face masks, Vision-Language Models (VLMs), and defense strategies to assess their robustness. Based on the results, we draw several key insights, highlighting the vulnerability of facial recognition systems to OOD data and suggesting possible solutions. Additionally, we offer a unified toolkit that includes all corruption and variation types, easily extendable to other datasets. We hope that our benchmarks and findings can provide guidance for future improvements in facial recognition model robustness.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge