Erlong Li
RelTopo: Enhancing Relational Modeling for Driving Scene Topology Reasoning
Jun 16, 2025



Abstract:Accurate road topology reasoning is critical for autonomous driving, enabling effective navigation and adherence to traffic regulations. Central to this task are lane perception and topology reasoning. However, existing methods typically focus on either lane detection or Lane-to-Lane (L2L) topology reasoning, often \textit{neglecting} Lane-to-Traffic-element (L2T) relationships or \textit{failing} to optimize these tasks jointly. Furthermore, most approaches either overlook relational modeling or apply it in a limited scope, despite the inherent spatial relationships among road elements. We argue that relational modeling is beneficial for both perception and reasoning, as humans naturally leverage contextual relationships for road element recognition and their connectivity inference. To this end, we introduce relational modeling into both perception and reasoning, \textit{jointly} enhancing structural understanding. Specifically, we propose: 1) a relation-aware lane detector, where our geometry-biased self-attention and \curve\ cross-attention refine lane representations by capturing relational dependencies; 2) relation-enhanced topology heads, including a geometry-enhanced L2L head and a cross-view L2T head, boosting reasoning with relational cues; and 3) a contrastive learning strategy with InfoNCE loss to regularize relationship embeddings. Extensive experiments on OpenLane-V2 demonstrate that our approach significantly improves both detection and topology reasoning metrics, achieving +3.1 in DET$_l$, +5.3 in TOP$_{ll}$, +4.9 in TOP$_{lt}$, and an overall +4.4 in OLS, setting a new state-of-the-art. Code will be released.
Topo2Seq: Enhanced Topology Reasoning via Topology Sequence Learning
Feb 13, 2025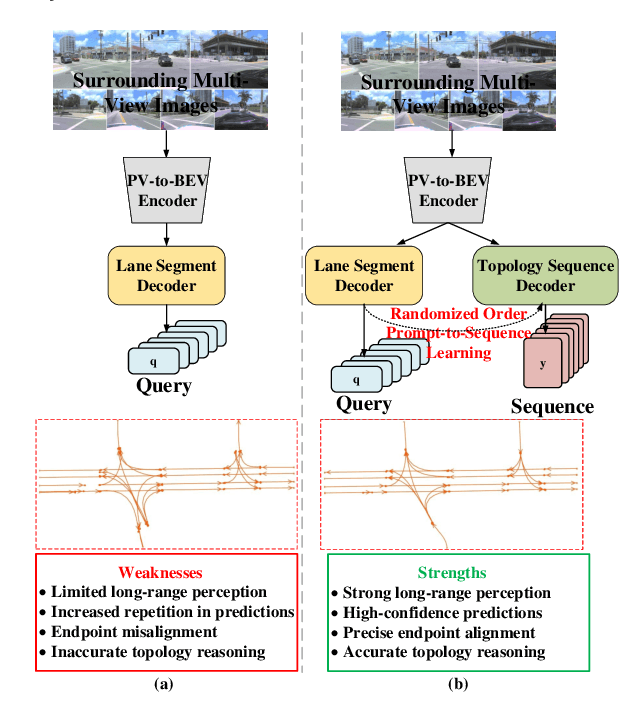
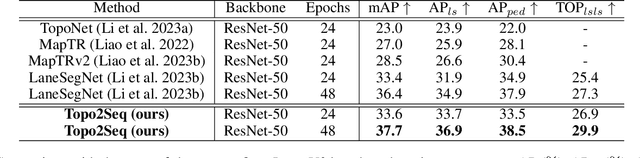
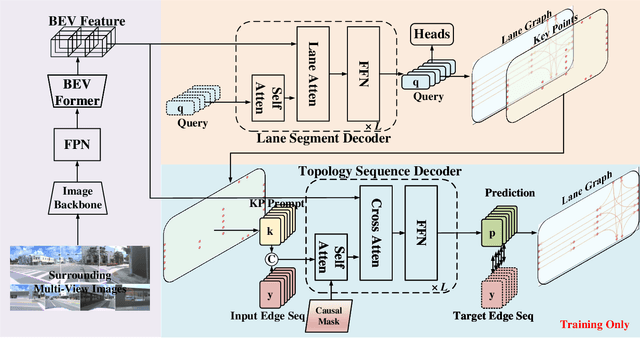
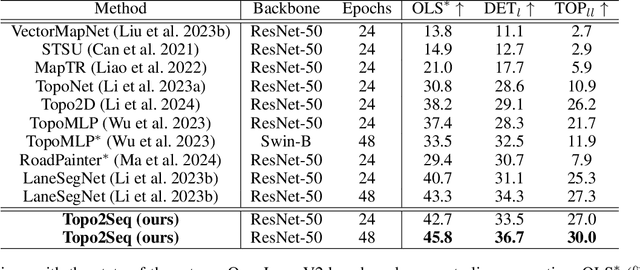
Abstract:Extracting lane topology from perspective views (PV) is crucial for planning and control in autonomous driving. This approach extracts potential drivable trajectories for self-driving vehicles without relying on high-definition (HD) maps. However, the unordered nature and weak long-range perception of the DETR-like framework can result in misaligned segment endpoints and limited topological prediction capabilities. Inspired by the learning of contextual relationships in language models, the connectivity relations in roads can be characterized as explicit topology sequences. In this paper, we introduce Topo2Seq, a novel approach for enhancing topology reasoning via topology sequences learning. The core concept of Topo2Seq is a randomized order prompt-to-sequence learning between lane segment decoder and topology sequence decoder. The dual-decoder branches simultaneously learn the lane topology sequences extracted from the Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) and the lane graph containing geometric information. Randomized order prompt-to-sequence learning extracts unordered key points from the lane graph predicted by the lane segment decoder, which are then fed into the prompt design of the topology sequence decoder to reconstruct an ordered and complete lane graph. In this way, the lane segment decoder learns powerful long-range perception and accurate topological reasoning from the topology sequence decoder. Notably, topology sequence decoder is only introduced during training and does not affect the inference efficiency. Experimental evaluations on the OpenLane-V2 dataset demonstrate the state-of-the-art performance of Topo2Seq in topology reasoning.
Flexible 3D Lane Detection by Hierarchical Shape MatchingFlexible 3D Lane Detection by Hierarchical Shape Matching
Aug 13, 2024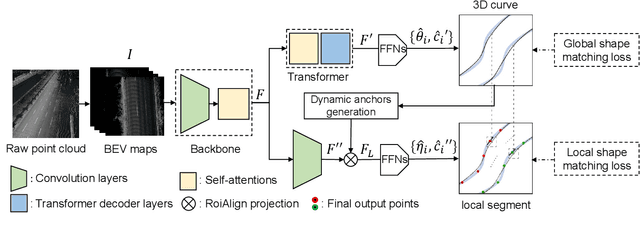
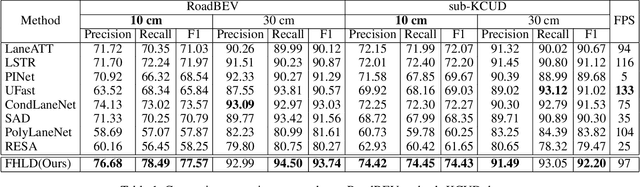
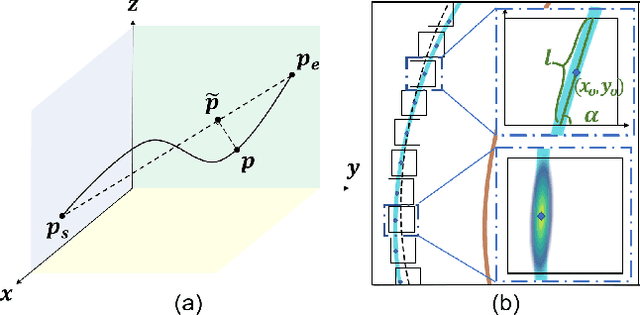
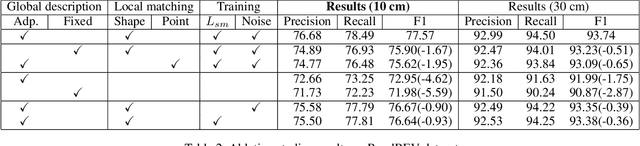
Abstract:As one of the basic while vital technologies for HD map construction, 3D lane detection is still an open problem due to varying visual conditions, complex typologies, and strict demands for precision. In this paper, an end-to-end flexible and hierarchical lane detector is proposed to precisely predict 3D lane lines from point clouds. Specifically, we design a hierarchical network predicting flexible representations of lane shapes at different levels, simultaneously collecting global instance semantics and avoiding local errors. In the global scope, we propose to regress parametric curves w.r.t adaptive axes that help to make more robust predictions towards complex scenes, while in the local vision the structure of lane segment is detected in each of the dynamic anchor cells sampled along the global predicted curves. Moreover, corresponding global and local shape matching losses and anchor cell generation strategies are designed. Experiments on two datasets show that we overwhelm current top methods under high precision standards, and full ablation studies also verify each part of our method. Our codes will be released at https://github.com/Doo-do/FHLD.
A Survey on Multimodal Large Language Models for Autonomous Driving
Nov 21, 2023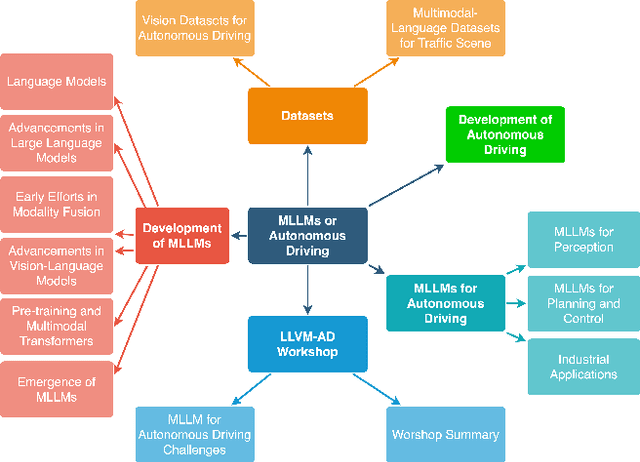


Abstract:With the emergence of Large Language Models (LLMs) and Vision Foundation Models (VFMs), multimodal AI systems benefiting from large models have the potential to equally perceive the real world, make decisions, and control tools as humans. In recent months, LLMs have shown widespread attention in autonomous driving and map systems. Despite its immense potential, there is still a lack of a comprehensive understanding of key challenges, opportunities, and future endeavors to apply in LLM driving systems. In this paper, we present a systematic investigation in this field. We first introduce the background of Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs), the multimodal models development using LLMs, and the history of autonomous driving. Then, we overview existing MLLM tools for driving, transportation, and map systems together with existing datasets and benchmarks. Moreover, we summarized the works in The 1st WACV Workshop on Large Language and Vision Models for Autonomous Driving (LLVM-AD), which is the first workshop of its kind regarding LLMs in autonomous driving. To further promote the development of this field, we also discuss several important problems regarding using MLLMs in autonomous driving systems that need to be solved by both academia and industry.
THMA: Tencent HD Map AI System for Creating HD Map Annotations
Dec 14, 2022Abstract:Nowadays, autonomous vehicle technology is becoming more and more mature. Critical to progress and safety, high-definition (HD) maps, a type of centimeter-level map collected using a laser sensor, provide accurate descriptions of the surrounding environment. The key challenge of HD map production is efficient, high-quality collection and annotation of large-volume datasets. Due to the demand for high quality, HD map production requires significant manual human effort to create annotations, a very time-consuming and costly process for the map industry. In order to reduce manual annotation burdens, many artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms have been developed to pre-label the HD maps. However, there still exists a large gap between AI algorithms and the traditional manual HD map production pipelines in accuracy and robustness. Furthermore, it is also very resource-costly to build large-scale annotated datasets and advanced machine learning algorithms for AI-based HD map automatic labeling systems. In this paper, we introduce the Tencent HD Map AI (THMA) system, an innovative end-to-end, AI-based, active learning HD map labeling system capable of producing and labeling HD maps with a scale of hundreds of thousands of kilometers. In THMA, we train AI models directly from massive HD map datasets via supervised, self-supervised, and weakly supervised learning to achieve high accuracy and efficiency required by downstream users. THMA has been deployed by the Tencent Map team to provide services to downstream companies and users, serving over 1,000 labeling workers and producing more than 30,000 kilometers of HD map data per day at most. More than 90 percent of the HD map data in Tencent Map is labeled automatically by THMA, accelerating the traditional HD map labeling process by more than ten times.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge