Changqing Zhou
RelTopo: Enhancing Relational Modeling for Driving Scene Topology Reasoning
Jun 16, 2025



Abstract:Accurate road topology reasoning is critical for autonomous driving, enabling effective navigation and adherence to traffic regulations. Central to this task are lane perception and topology reasoning. However, existing methods typically focus on either lane detection or Lane-to-Lane (L2L) topology reasoning, often \textit{neglecting} Lane-to-Traffic-element (L2T) relationships or \textit{failing} to optimize these tasks jointly. Furthermore, most approaches either overlook relational modeling or apply it in a limited scope, despite the inherent spatial relationships among road elements. We argue that relational modeling is beneficial for both perception and reasoning, as humans naturally leverage contextual relationships for road element recognition and their connectivity inference. To this end, we introduce relational modeling into both perception and reasoning, \textit{jointly} enhancing structural understanding. Specifically, we propose: 1) a relation-aware lane detector, where our geometry-biased self-attention and \curve\ cross-attention refine lane representations by capturing relational dependencies; 2) relation-enhanced topology heads, including a geometry-enhanced L2L head and a cross-view L2T head, boosting reasoning with relational cues; and 3) a contrastive learning strategy with InfoNCE loss to regularize relationship embeddings. Extensive experiments on OpenLane-V2 demonstrate that our approach significantly improves both detection and topology reasoning metrics, achieving +3.1 in DET$_l$, +5.3 in TOP$_{ll}$, +4.9 in TOP$_{lt}$, and an overall +4.4 in OLS, setting a new state-of-the-art. Code will be released.
Modeling Continuous Motion for 3D Point Cloud Object Tracking
Mar 14, 2023Abstract:The task of 3D single object tracking (SOT) with LiDAR point clouds is crucial for various applications, such as autonomous driving and robotics. However, existing approaches have primarily relied on appearance matching or motion modeling within only two successive frames, thereby overlooking the long-range continuous motion property of objects in 3D space. To address this issue, this paper presents a novel approach that views each tracklet as a continuous stream: at each timestamp, only the current frame is fed into the network to interact with multi-frame historical features stored in a memory bank, enabling efficient exploitation of sequential information. To achieve effective cross-frame message passing, a hybrid attention mechanism is designed to account for both long-range relation modeling and local geometric feature extraction. Furthermore, to enhance the utilization of multi-frame features for robust tracking, a contrastive sequence enhancement strategy is designed, which uses ground truth tracklets to augment training sequences and promote discrimination against false positives in a contrastive manner. Extensive experiments demonstrate that the proposed method outperforms the state-of-the-art method by significant margins (approximately 8%, 6%, and 12% improvements in the success performance on KITTI, nuScenes, and Waymo, respectively).
DETR4D: Direct Multi-View 3D Object Detection with Sparse Attention
Dec 15, 2022Abstract:3D object detection with surround-view images is an essential task for autonomous driving. In this work, we propose DETR4D, a Transformer-based framework that explores sparse attention and direct feature query for 3D object detection in multi-view images. We design a novel projective cross-attention mechanism for query-image interaction to address the limitations of existing methods in terms of geometric cue exploitation and information loss for cross-view objects. In addition, we introduce a heatmap generation technique that bridges 3D and 2D spaces efficiently via query initialization. Furthermore, unlike the common practice of fusing intermediate spatial features for temporal aggregation, we provide a new perspective by introducing a novel hybrid approach that performs cross-frame fusion over past object queries and image features, enabling efficient and robust modeling of temporal information. Extensive experiments on the nuScenes dataset demonstrate the effectiveness and efficiency of the proposed DETR4D.
Exploring Point-BEV Fusion for 3D Point Cloud Object Tracking with Transformer
Aug 10, 2022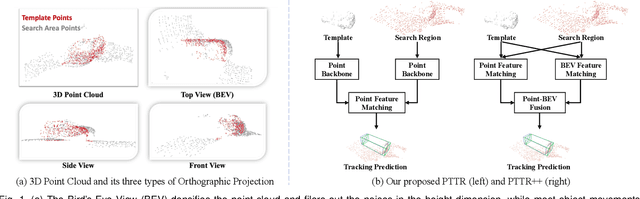
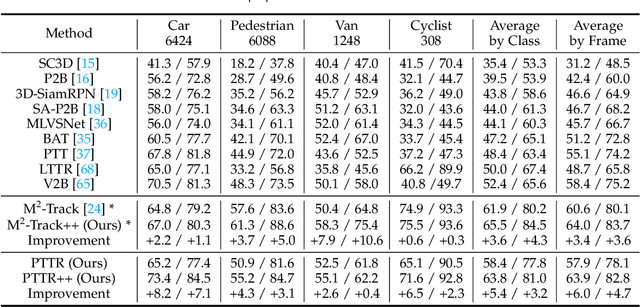
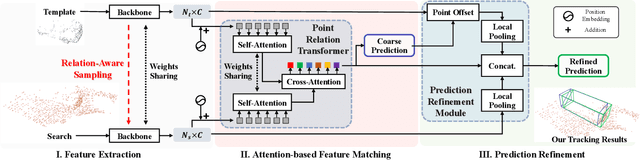
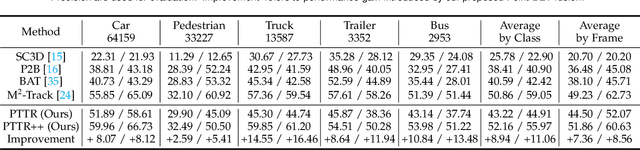
Abstract:With the prevalence of LiDAR sensors in autonomous driving, 3D object tracking has received increasing attention. In a point cloud sequence, 3D object tracking aims to predict the location and orientation of an object in consecutive frames given an object template. Motivated by the success of transformers, we propose Point Tracking TRansformer (PTTR), which efficiently predicts high-quality 3D tracking results in a coarse-to-fine manner with the help of transformer operations. PTTR consists of three novel designs. 1) Instead of random sampling, we design Relation-Aware Sampling to preserve relevant points to the given template during subsampling. 2) We propose a Point Relation Transformer for effective feature aggregation and feature matching between the template and search region. 3) Based on the coarse tracking results, we employ a novel Prediction Refinement Module to obtain the final refined prediction through local feature pooling. In addition, motivated by the favorable properties of the Bird's-Eye View (BEV) of point clouds in capturing object motion, we further design a more advanced framework named PTTR++, which incorporates both the point-wise view and BEV representation to exploit their complementary effect in generating high-quality tracking results. PTTR++ substantially boosts the tracking performance on top of PTTR with low computational overhead. Extensive experiments over multiple datasets show that our proposed approaches achieve superior 3D tracking accuracy and efficiency.
TransPillars: Coarse-to-Fine Aggregation for Multi-Frame 3D Object Detection
Aug 04, 2022



Abstract:3D object detection using point clouds has attracted increasing attention due to its wide applications in autonomous driving and robotics. However, most existing studies focus on single point cloud frames without harnessing the temporal information in point cloud sequences. In this paper, we design TransPillars, a novel transformer-based feature aggregation technique that exploits temporal features of consecutive point cloud frames for multi-frame 3D object detection. TransPillars aggregates spatial-temporal point cloud features from two perspectives. First, it fuses voxel-level features directly from multi-frame feature maps instead of pooled instance features to preserve instance details with contextual information that are essential to accurate object localization. Second, it introduces a hierarchical coarse-to-fine strategy to fuse multi-scale features progressively to effectively capture the motion of moving objects and guide the aggregation of fine features. Besides, a variant of deformable transformer is introduced to improve the effectiveness of cross-frame feature matching. Extensive experiments show that our proposed TransPillars achieves state-of-art performance as compared to existing multi-frame detection approaches. Code will be released.
PTTR: Relational 3D Point Cloud Object Tracking with Transformer
Dec 07, 2021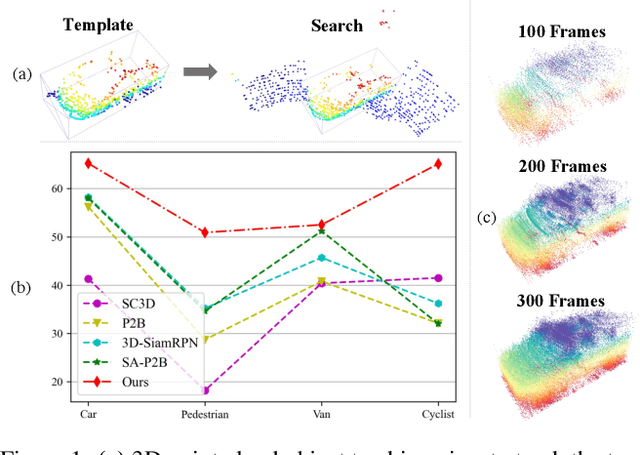
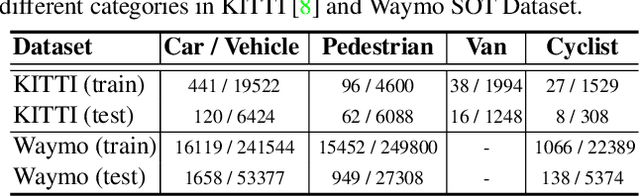

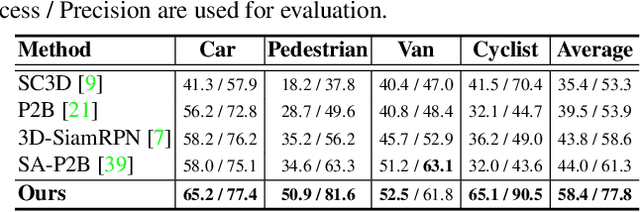
Abstract:In a point cloud sequence, 3D object tracking aims to predict the location and orientation of an object in the current search point cloud given a template point cloud. Motivated by the success of transformers, we propose Point Tracking TRansformer (PTTR), which efficiently predicts high-quality 3D tracking results in a coarse-to-fine manner with the help of transformer operations. PTTR consists of three novel designs. 1) Instead of random sampling, we design Relation-Aware Sampling to preserve relevant points to given templates during subsampling. 2) Furthermore, we propose a Point Relation Transformer (PRT) consisting of a self-attention and a cross-attention module. The global self-attention operation captures long-range dependencies to enhance encoded point features for the search area and the template, respectively. Subsequently, we generate the coarse tracking results by matching the two sets of point features via cross-attention. 3) Based on the coarse tracking results, we employ a novel Prediction Refinement Module to obtain the final refined prediction. In addition, we create a large-scale point cloud single object tracking benchmark based on the Waymo Open Dataset. Extensive experiments show that PTTR achieves superior point cloud tracking in both accuracy and efficiency.
Unsupervised Domain Adaptive 3D Detection with Multi-Level Consistency
Aug 18, 2021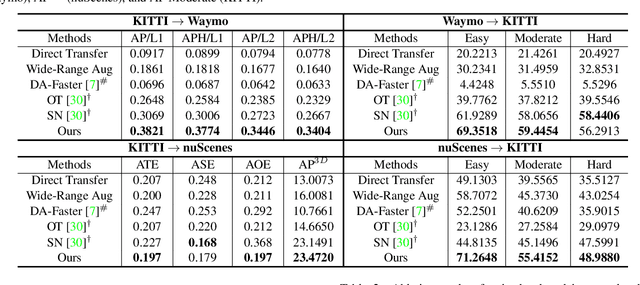
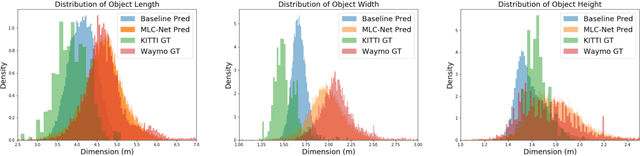
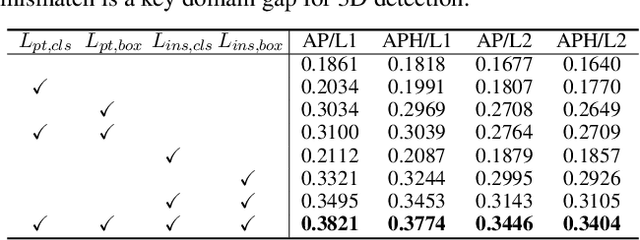
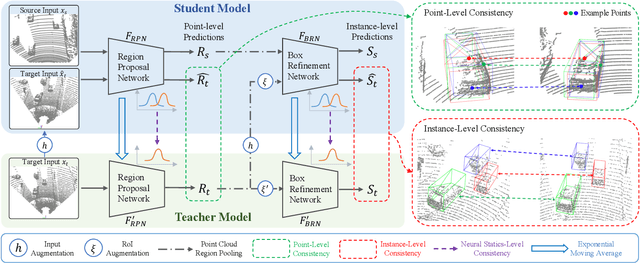
Abstract:Deep learning-based 3D object detection has achieved unprecedented success with the advent of large-scale autonomous driving datasets. However, drastic performance degradation remains a critical challenge for cross-domain deployment. In addition, existing 3D domain adaptive detection methods often assume prior access to the target domain annotations, which is rarely feasible in the real world. To address this challenge, we study a more realistic setting, unsupervised 3D domain adaptive detection, which only utilizes source domain annotations. 1) We first comprehensively investigate the major underlying factors of the domain gap in 3D detection. Our key insight is that geometric mismatch is the key factor of domain shift. 2) Then, we propose a novel and unified framework, Multi-Level Consistency Network (MLC-Net), which employs a teacher-student paradigm to generate adaptive and reliable pseudo-targets. MLC-Net exploits point-, instance- and neural statistics-level consistency to facilitate cross-domain transfer. Extensive experiments demonstrate that MLC-Net outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods (including those using additional target domain information) on standard benchmarks. Notably, our approach is detector-agnostic, which achieves consistent gains on both single- and two-stage 3D detectors.
Sparta: Spatially Attentive and Adversarially Robust Activation
May 18, 2021



Abstract:Adversarial training (AT) is one of the most effective ways for improving the robustness of deep convolution neural networks (CNNs). Just like common network training, the effectiveness of AT relies on the design of basic network components. In this paper, we conduct an in-depth study on the role of the basic ReLU activation component in AT for robust CNNs. We find that the spatially-shared and input-independent properties of ReLU activation make CNNs less robust to white-box adversarial attacks with either standard or adversarial training. To address this problem, we extend ReLU to a novel Sparta activation function (Spatially attentive and Adversarially Robust Activation), which enables CNNs to achieve both higher robustness, i.e., lower error rate on adversarial examples, and higher accuracy, i.e., lower error rate on clean examples, than the existing state-of-the-art (SOTA) activation functions. We further study the relationship between Sparta and the SOTA activation functions, providing more insights about the advantages of our method. With comprehensive experiments, we also find that the proposed method exhibits superior cross-CNN and cross-dataset transferability. For the former, the adversarially trained Sparta function for one CNN (e.g., ResNet-18) can be fixed and directly used to train another adversarially robust CNN (e.g., ResNet-34). For the latter, the Sparta function trained on one dataset (e.g., CIFAR-10) can be employed to train adversarially robust CNNs on another dataset (e.g., SVHN). In both cases, Sparta leads to CNNs with higher robustness than the vanilla ReLU, verifying the flexibility and versatility of the proposed method.
Auto-Exposure Fusion for Single-Image Shadow Removal
Mar 01, 2021



Abstract:Shadow removal is still a challenging task due to its inherent background-dependent and spatial-variant properties, leading to unknown and diverse shadow patterns. Even powerful state-of-the-art deep neural networks could hardly recover traceless shadow-removed background. This paper proposes a new solution for this task by formulating it as an exposure fusion problem to address the challenges. Intuitively, we can first estimate multiple over-exposure images w.r.t. the input image to let the shadow regions in these images have the same color with shadow-free areas in the input image. Then, we fuse the original input with the over-exposure images to generate the final shadow-free counterpart. Nevertheless, the spatial-variant property of the shadow requires the fusion to be sufficiently `smart', that is, it should automatically select proper over-exposure pixels from different images to make the final output natural. To address this challenge, we propose the {\bf shadow-aware FusionNet} that takes the shadow image as input to generate fusion weight maps across all the over-exposure images. Moreover, we propose the {\bf boundary-aware RefineNet} to eliminate the remaining shadow trace further. We conduct extensive experiments on the ISTD, ISTD+, and SRD datasets to validate our method's effectiveness and show better performance in shadow regions and comparable performance in non-shadow regions over the state-of-the-art methods. We release the model and code in https://github.com/tsingqguo/exposure-fusion-shadow-removal.
* accept to cvpr2021
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge