Zibo Liu
VNU-Bench: A Benchmarking Dataset for Multi-Source Multimodal News Video Understanding
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:News videos are carefully edited multimodal narratives that combine narration, visuals, and external quotations into coherent storylines. In recent years, there have been significant advances in evaluating multimodal large language models (MLLMs) for news video understanding. However, existing benchmarks largely focus on single-source, intra-video reasoning, where each report is processed in isolation. In contrast, real-world news consumption is inherently multi-sourced: the same event is reported by different outlets with complementary details, distinct narrative choices, and sometimes conflicting claims that unfold over time. Robust news understanding, therefore, requires models to compare perspectives from different sources, align multimodal evidence across sources, and synthesize multi-source information. To fill this gap, we introduce VNU-Bench, the first benchmark for multi-source, cross-video understanding in the news domain. We design a set of new question types that are unique in testing models' ability of understanding multi-source multimodal news from a variety of different angles. We design a novel hybrid human-model QA generation process that addresses the issues of scalability and quality control in building a large dataset for cross-source news understanding. The dataset comprises 429 news groups, 1,405 videos, and 2,501 high-quality questions. Comprehensive evaluation of both closed- and open-source multimodal models shows that VNU-Bench poses substantial challenges for current MLLMs.
A Fast AI Surrogate for Coastal Ocean Circulation Models
Oct 19, 2024



Abstract:Nearly 900 million people live in low-lying coastal zones around the world and bear the brunt of impacts from more frequent and severe hurricanes and storm surges. Oceanographers simulate ocean current circulation along the coasts to develop early warning systems that save lives and prevent loss and damage to property from coastal hazards. Traditionally, such simulations are conducted using coastal ocean circulation models such as the Regional Ocean Modeling System (ROMS), which usually runs on an HPC cluster with multiple CPU cores. However, the process is time-consuming and energy expensive. While coarse-grained ROMS simulations offer faster alternatives, they sacrifice detail and accuracy, particularly in complex coastal environments. Recent advances in deep learning and GPU architecture have enabled the development of faster AI (neural network) surrogates. This paper introduces an AI surrogate based on a 4D Swin Transformer to simulate coastal tidal wave propagation in an estuary for both hindcast and forecast (up to 12 days). Our approach not only accelerates simulations but also incorporates a physics-based constraint to detect and correct inaccurate results, ensuring reliability while minimizing manual intervention. We develop a fully GPU-accelerated workflow, optimizing the model training and inference pipeline on NVIDIA DGX-2 A100 GPUs. Our experiments demonstrate that our AI surrogate reduces the time cost of 12-day forecasting of traditional ROMS simulations from 9,908 seconds (on 512 CPU cores) to 22 seconds (on one A100 GPU), achieving over 450$\times$ speedup while maintaining high-quality simulation results. This work contributes to oceanographic modeling by offering a fast, accurate, and physically consistent alternative to traditional simulation models, particularly for real-time forecasting in rapid disaster response.
Deep Learning-Based Channel Squeeze U-Structure for Lung Nodule Detection and Segmentation
Sep 20, 2024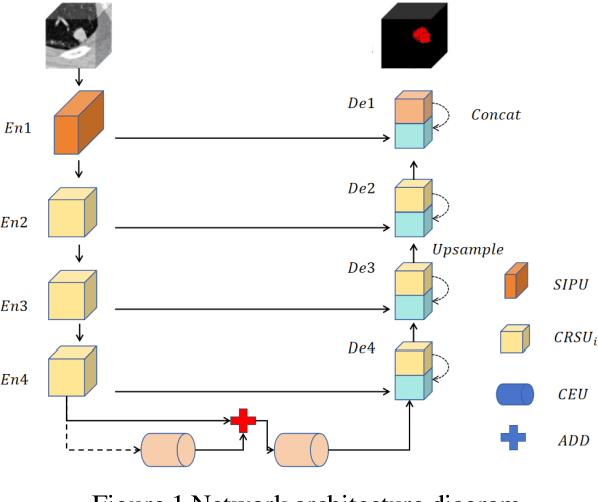
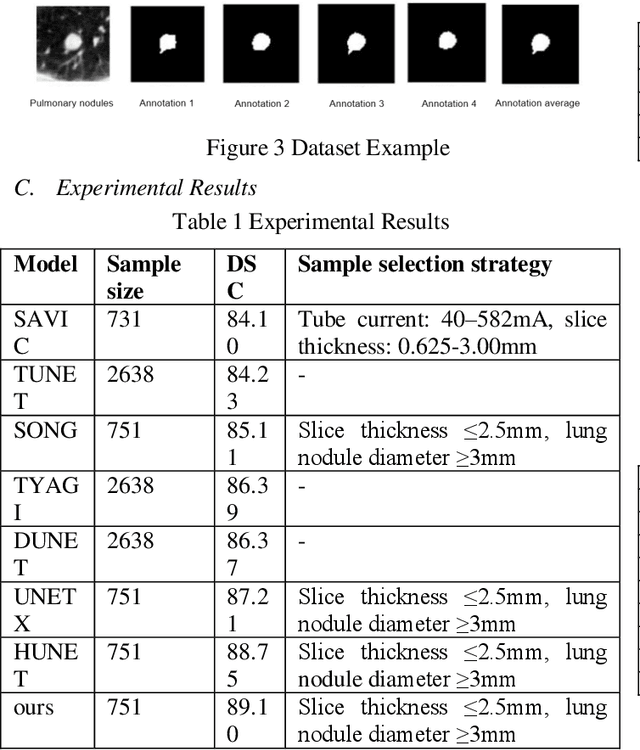
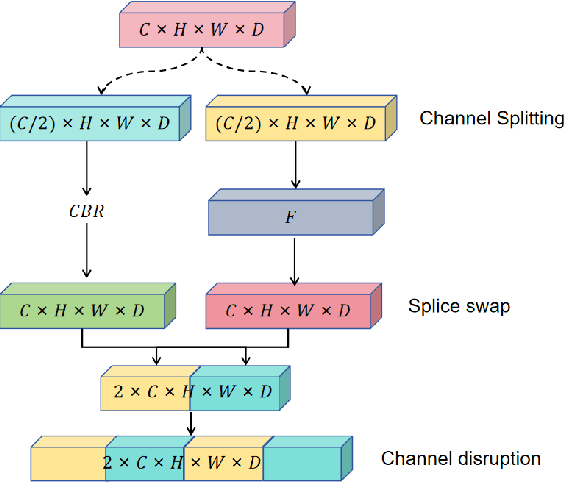
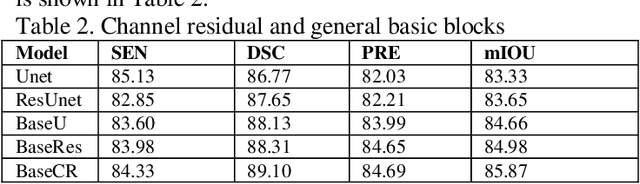
Abstract:This paper introduces a novel deep-learning method for the automatic detection and segmentation of lung nodules, aimed at advancing the accuracy of early-stage lung cancer diagnosis. The proposed approach leverages a unique "Channel Squeeze U-Structure" that optimizes feature extraction and information integration across multiple semantic levels of the network. This architecture includes three key modules: shallow information processing, channel residual structure, and channel squeeze integration. These modules enhance the model's ability to detect and segment small, imperceptible, or ground-glass nodules, which are critical for early diagnosis. The method demonstrates superior performance in terms of sensitivity, Dice similarity coefficient, precision, and mean Intersection over Union (IoU). Extensive experiments were conducted on the Lung Image Database Consortium (LIDC) dataset using five-fold cross-validation, showing excellent stability and robustness. The results indicate that this approach holds significant potential for improving computer-aided diagnosis systems, providing reliable support for radiologists in clinical practice and aiding in the early detection of lung cancer, especially in resource-limited settings
Multi-View Neural Differential Equations for Continuous-Time Stream Data in Long-Term Traffic Forecasting
Aug 12, 2024Abstract:Long-term traffic flow forecasting plays a crucial role in intelligent transportation as it allows traffic managers to adjust their decisions in advance. However, the problem is challenging due to spatio-temporal correlations and complex dynamic patterns in continuous-time stream data. Neural Differential Equations (NDEs) are among the state-of-the-art methods for learning continuous-time traffic dynamics. However, the traditional NDE models face issues in long-term traffic forecasting due to failures in capturing delayed traffic patterns, dynamic edge (location-to-location correlation) patterns, and abrupt trend patterns. To fill this gap, we propose a new NDE architecture called Multi-View Neural Differential Equations. Our model captures current states, delayed states, and trends in different state variables (views) by learning latent multiple representations within Neural Differential Equations. Extensive experiments conducted on several real-world traffic datasets demonstrate that our proposed method outperforms the state-of-the-art and achieves superior prediction accuracy for long-term forecasting and robustness with noisy or missing inputs.
Spatio-Temporal Partial Sensing Forecast for Long-term Traffic
Aug 02, 2024Abstract:Traffic forecasting uses recent measurements by sensors installed at chosen locations to forecast the future road traffic. Existing work either assumes all locations are equipped with sensors or focuses on short-term forecast. This paper studies partial sensing traffic forecast of long-term traffic, assuming sensors only at some locations. The study is important in lowering the infrastructure investment cost in traffic management since deploying sensors at all locations could incur prohibitively high cost. However, the problem is challenging due to the unknown distribution at unsensed locations, the intricate spatio-temporal correlation in long-term forecasting, as well as noise in data and irregularities in traffic patterns (e.g., road closure). We propose a Spatio-Temporal Partial Sensing (STPS) forecast model for long-term traffic prediction, with several novel contributions, including a rank-based embedding technique to capture irregularities and overcome noise, a spatial transfer matrix to overcome the spatial distribution shift from permanently sensed locations to unsensed locations, and a multi-step training process that utilizes all available data to successively refine the model parameters for better accuracy. Extensive experiments on several real-world traffic datasets demonstrate that STPS outperforms the state-of-the-art and achieves superior accuracy in partial sensing long-term forecasting.
Graph-based Multi-ODE Neural Networks for Spatio-Temporal Traffic Forecasting
Jun 01, 2023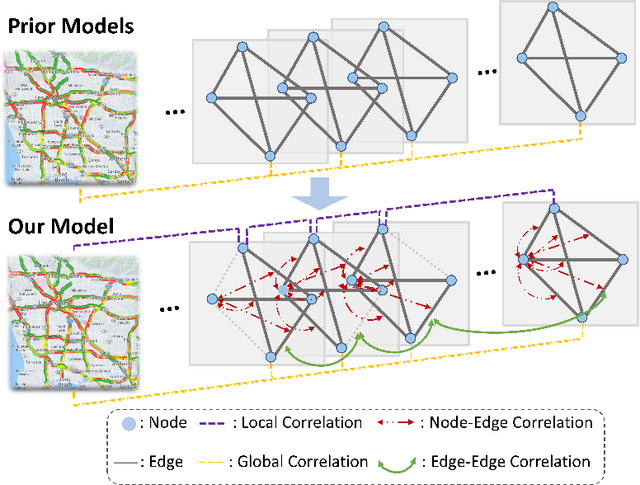
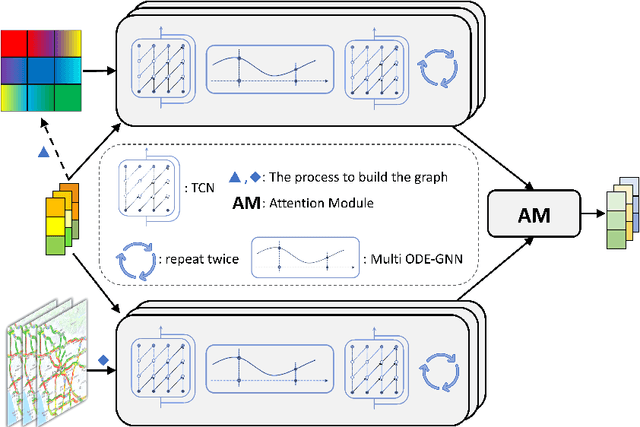
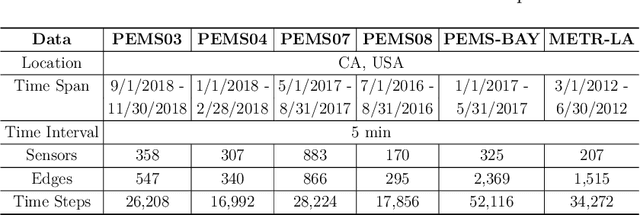
Abstract:There is a recent surge in the development of spatio-temporal forecasting models in the transportation domain. Long-range traffic forecasting, however, remains a challenging task due to the intricate and extensive spatio-temporal correlations observed in traffic networks. Current works primarily rely on road networks with graph structures and learn representations using graph neural networks (GNNs), but this approach suffers from over-smoothing problem in deep architectures. To tackle this problem, recent methods introduced the combination of GNNs with residual connections or neural ordinary differential equations (ODE). However, current graph ODE models face two key limitations in feature extraction: (1) they lean towards global temporal patterns, overlooking local patterns that are important for unexpected events; and (2) they lack dynamic semantic edges in their architectural design. In this paper, we propose a novel architecture called Graph-based Multi-ODE Neural Networks (GRAM-ODE) which is designed with multiple connective ODE-GNN modules to learn better representations by capturing different views of complex local and global dynamic spatio-temporal dependencies. We also add some techniques like shared weights and divergence constraints into the intermediate layers of distinct ODE-GNN modules to further improve their communication towards the forecasting task. Our extensive set of experiments conducted on six real-world datasets demonstrate the superior performance of GRAM-ODE compared with state-of-the-art baselines as well as the contribution of different components to the overall performance. The code is available at https://github.com/zbliu98/GRAM-ODE
* Published in Transactions on Machine Learning Research, 2023
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge