Zhuoya Zhao
Brain-inspired and Self-based Artificial Intelligence
Feb 29, 2024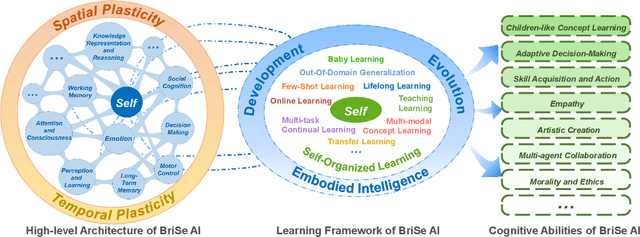
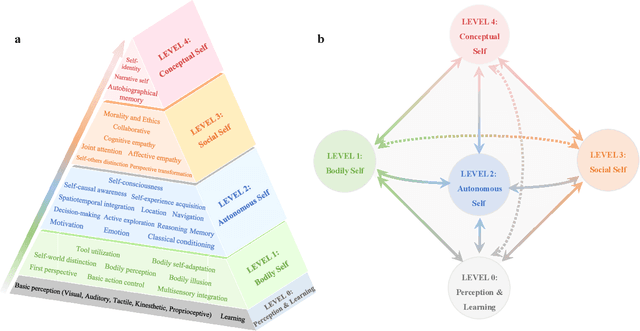
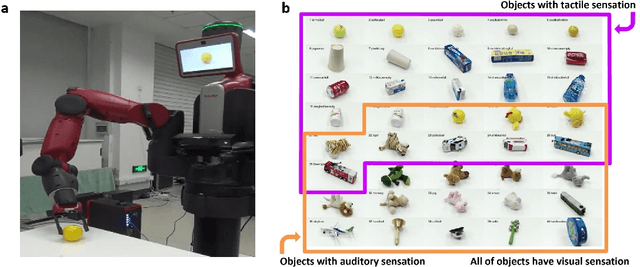
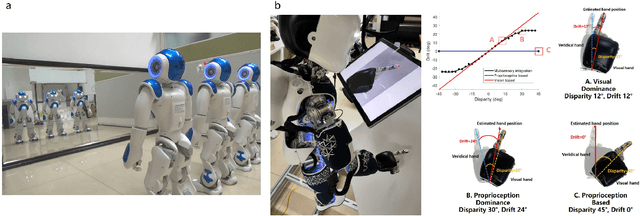
Abstract:The question "Can machines think?" and the Turing Test to assess whether machines could achieve human-level intelligence is one of the roots of AI. With the philosophical argument "I think, therefore I am", this paper challenge the idea of a "thinking machine" supported by current AIs since there is no sense of self in them. Current artificial intelligence is only seemingly intelligent information processing and does not truly understand or be subjectively aware of oneself and perceive the world with the self as human intelligence does. In this paper, we introduce a Brain-inspired and Self-based Artificial Intelligence (BriSe AI) paradigm. This BriSe AI paradigm is dedicated to coordinating various cognitive functions and learning strategies in a self-organized manner to build human-level AI models and robotic applications. Specifically, BriSe AI emphasizes the crucial role of the Self in shaping the future AI, rooted with a practical hierarchical Self framework, including Perception and Learning, Bodily Self, Autonomous Self, Social Self, and Conceptual Self. The hierarchical framework of the Self highlights self-based environment perception, self-bodily modeling, autonomous interaction with the environment, social interaction and collaboration with others, and even more abstract understanding of the Self. Furthermore, the positive mutual promotion and support among multiple levels of Self, as well as between Self and learning, enhance the BriSe AI's conscious understanding of information and flexible adaptation to complex environments, serving as a driving force propelling BriSe AI towards real Artificial General Intelligence.
Brain-inspired Evolutionary Architectures for Spiking Neural Networks
Sep 11, 2023



Abstract:The complex and unique neural network topology of the human brain formed through natural evolution enables it to perform multiple cognitive functions simultaneously. Automated evolutionary mechanisms of biological network structure inspire us to explore efficient architectural optimization for Spiking Neural Networks (SNNs). Instead of manually designed fixed architectures or hierarchical Network Architecture Search (NAS), this paper evolves SNNs architecture by incorporating brain-inspired local modular structure and global cross-module connectivity. Locally, the brain region-inspired module consists of multiple neural motifs with excitatory and inhibitory connections; Globally, we evolve free connections among modules, including long-term cross-module feedforward and feedback connections. We further introduce an efficient multi-objective evolutionary algorithm based on a few-shot performance predictor, endowing SNNs with high performance, efficiency and low energy consumption. Extensive experiments on static datasets (CIFAR10, CIFAR100) and neuromorphic datasets (CIFAR10-DVS, DVS128-Gesture) demonstrate that our proposed model boosts energy efficiency, archiving consistent and remarkable performance. This work explores brain-inspired neural architectures suitable for SNNs and also provides preliminary insights into the evolutionary mechanisms of biological neural networks in the human brain.
Multi-compartment Neuron and Population Encoding improved Spiking Neural Network for Deep Distributional Reinforcement Learning
Jan 18, 2023



Abstract:Inspired by the information processing with binary spikes in the brain, the spiking neural networks (SNNs) exhibit significant low energy consumption and are more suitable for incorporating multi-scale biological characteristics. Spiking Neurons, as the basic information processing unit of SNNs, are often simplified in most SNNs which only consider LIF point neuron and do not take into account the multi-compartmental structural properties of biological neurons. This limits the computational and learning capabilities of SNNs. In this paper, we proposed a brain-inspired SNN-based deep distributional reinforcement learning algorithm with combination of bio-inspired multi-compartment neuron (MCN) model and population coding method. The proposed multi-compartment neuron built the structure and function of apical dendritic, basal dendritic, and somatic computing compartments to achieve the computational power close to that of biological neurons. Besides, we present an implicit fractional embedding method based on spiking neuron population encoding. We tested our model on Atari games, and the experiment results show that the performance of our model surpasses the vanilla ANN-based FQF model and ANN-SNN conversion method based Spiking-FQF models. The ablation experiments show that the proposed multi-compartment neural model and quantile fraction implicit population spike representation play an important role in realizing SNN-based deep distributional reinforcement learning.
BrainCog: A Spiking Neural Network based Brain-inspired Cognitive Intelligence Engine for Brain-inspired AI and Brain Simulation
Jul 18, 2022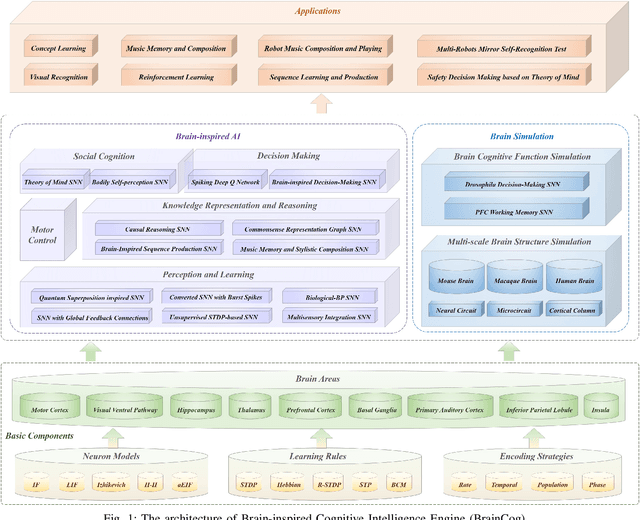
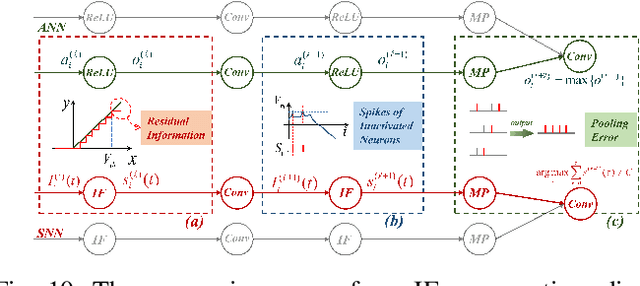
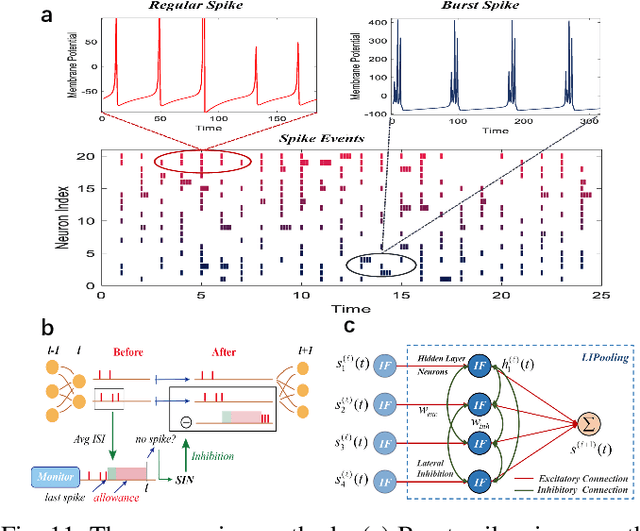
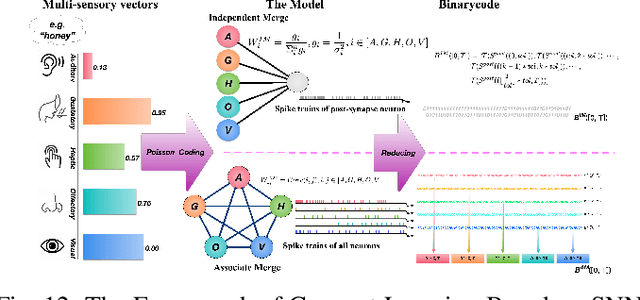
Abstract:Spiking neural networks (SNNs) have attracted extensive attentions in Brain-inspired Artificial Intelligence and computational neuroscience. They can be used to simulate biological information processing in the brain at multiple scales. More importantly, SNNs serve as an appropriate level of abstraction to bring inspirations from brain and cognition to Artificial Intelligence. In this paper, we present the Brain-inspired Cognitive Intelligence Engine (BrainCog) for creating brain-inspired AI and brain simulation models. BrainCog incorporates different types of spiking neuron models, learning rules, brain areas, etc., as essential modules provided by the platform. Based on these easy-to-use modules, BrainCog supports various brain-inspired cognitive functions, including Perception and Learning, Decision Making, Knowledge Representation and Reasoning, Motor Control, and Social Cognition. These brain-inspired AI models have been effectively validated on various supervised, unsupervised, and reinforcement learning tasks, and they can be used to enable AI models to be with multiple brain-inspired cognitive functions. For brain simulation, BrainCog realizes the function simulation of decision-making, working memory, the structure simulation of the Neural Circuit, and whole brain structure simulation of Mouse brain, Macaque brain, and Human brain. An AI engine named BORN is developed based on BrainCog, and it demonstrates how the components of BrainCog can be integrated and used to build AI models and applications. To enable the scientific quest to decode the nature of biological intelligence and create AI, BrainCog aims to provide essential and easy-to-use building blocks, and infrastructural support to develop brain-inspired spiking neural network based AI, and to simulate the cognitive brains at multiple scales. The online repository of BrainCog can be found at https://github.com/braincog-x.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge