Zhiwei Liu
RAAR: Retrieval Augmented Agentic Reasoning for Cross-Domain Misinformation Detection
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:Cross-domain misinformation detection is challenging, as misinformation arises across domains with substantial differences in knowledge and discourse. Existing methods often rely on single-perspective cues and struggle to generalize to challenging or underrepresented domains, while reasoning large language models (LLMs), though effective on complex tasks, are limited to same-distribution data. To address these gaps, we introduce RAAR, the first retrieval-augmented agentic reasoning framework for cross-domain misinformation detection. To enable cross-domain transfer beyond same-distribution assumptions, RAAR retrieves multi-perspective source-domain evidence aligned with each target sample's semantics, sentiment, and writing style. To overcome single-perspective modeling and missing systematic reasoning, RAAR constructs verifiable multi-step reasoning paths through specialized multi-agent collaboration, where perspective-specific agents produce complementary analyses and a summary agent integrates them under verifier guidance. RAAR further applies supervised fine-tuning and reinforcement learning to train a single multi-task verifier to enhance verification and reasoning capabilities. Based on RAAR, we trained the RAAR-8b and RAAR-14b models. Evaluation on three cross-domain misinformation detection tasks shows that RAAR substantially enhances the capabilities of the base models and outperforms other cross-domain methods, advanced LLMs, and LLM-based adaptation approaches. The project will be released at https://github.com/lzw108/RAAR.
All That Glisters Is Not Gold: A Benchmark for Reference-Free Counterfactual Financial Misinformation Detection
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:We introduce RFC Bench, a benchmark for evaluating large language models on financial misinformation under realistic news. RFC Bench operates at the paragraph level and captures the contextual complexity of financial news where meaning emerges from dispersed cues. The benchmark defines two complementary tasks: reference free misinformation detection and comparison based diagnosis using paired original perturbed inputs. Experiments reveal a consistent pattern: performance is substantially stronger when comparative context is available, while reference free settings expose significant weaknesses, including unstable predictions and elevated invalid outputs. These results indicate that current models struggle to maintain coherent belief states without external grounding. By highlighting this gap, RFC Bench provides a structured testbed for studying reference free reasoning and advancing more reliable financial misinformation detection in real world settings.
MisSpans: Fine-Grained False Span Identification in Cross-Domain Fake News
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:Online misinformation is increasingly pervasive, yet most existing benchmarks and methods evaluate veracity at the level of whole claims or paragraphs using coarse binary labels, obscuring how true and false details often co-exist within single sentences. These simplifications also limit interpretability: global explanations cannot identify which specific segments are misleading or differentiate how a detail is false (e.g., distorted vs. fabricated). To address these gaps, we introduce MisSpans, the first multi-domain, human-annotated benchmark for span-level misinformation detection and analysis, consisting of paired real and fake news stories. MisSpans defines three complementary tasks: MisSpansIdentity for pinpointing false spans within sentences, MisSpansType for categorising false spans by misinformation type, and MisSpansExplanation for providing rationales grounded in identified spans. Together, these tasks enable fine-grained localisation, nuanced characterisation beyond true/false and actionable explanations. Expert annotators were guided by standardised guidelines and consistency checks, leading to high inter-annotator agreement. We evaluate 15 representative LLMs, including reasoning-enhanced and non-reasoning variants, under zero-shot and one-shot settings. Results reveal the challenging nature of fine-grained misinformation identification and analysis, and highlight the need for a deeper understanding of how performance may be influenced by multiple interacting factors, including model size and reasoning capabilities, along with domain-specific textual features. This project will be available at https://github.com/lzw108/MisSpans.
MentraSuite: Post-Training Large Language Models for Mental Health Reasoning and Assessment
Dec 16, 2025Abstract:Mental health disorders affect hundreds of millions globally, and the Web now serves as a primary medium for accessing support, information, and assessment. Large language models (LLMs) offer scalable and accessible assistance, yet their deployment in mental-health settings remains risky when their reasoning is incomplete, inconsistent, or ungrounded. Existing psychological LLMs emphasize emotional understanding or knowledge recall but overlook the step-wise, clinically aligned reasoning required for appraisal, diagnosis, intervention planning, abstraction, and verification. To address these issues, we introduce MentraSuite, a unified framework for advancing reliable mental-health reasoning. We propose MentraBench, a comprehensive benchmark spanning five core reasoning aspects, six tasks, and 13 datasets, evaluating both task performance and reasoning quality across five dimensions: conciseness, coherence, hallucination avoidance, task understanding, and internal consistency. We further present Mindora, a post-trained model optimized through a hybrid SFT-RL framework with an inconsistency-detection reward to enforce faithful and coherent reasoning. To support training, we construct high-quality trajectories using a novel reasoning trajectory generation strategy, that strategically filters difficult samples and applies a structured, consistency-oriented rewriting process to produce concise, readable, and well-balanced trajectories. Across 20 evaluated LLMs, Mindora achieves the highest average performance on MentraBench and shows remarkable performances in reasoning reliability, demonstrating its effectiveness for complex mental-health scenarios.
LoCoBench-Agent: An Interactive Benchmark for LLM Agents in Long-Context Software Engineering
Nov 17, 2025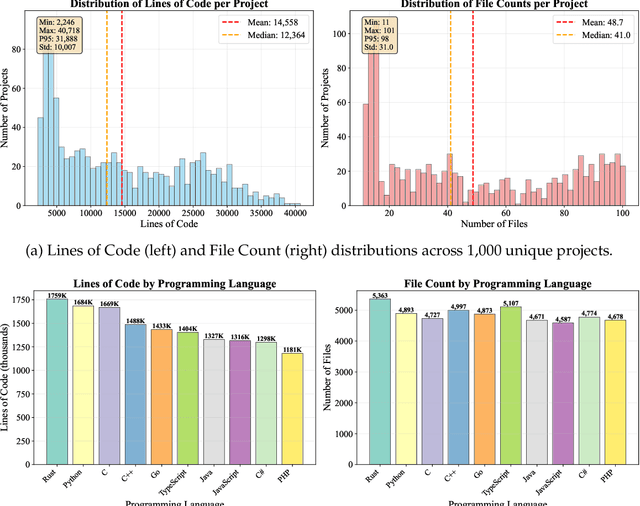
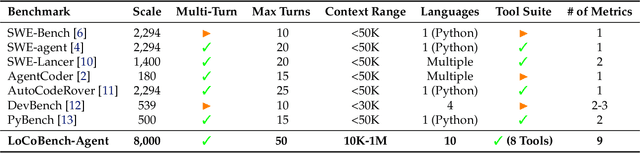

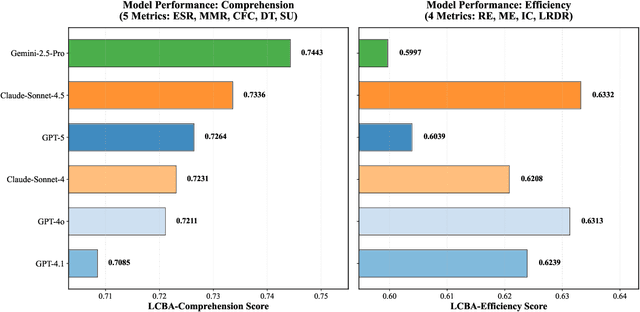
Abstract:As large language models (LLMs) evolve into sophisticated autonomous agents capable of complex software development tasks, evaluating their real-world capabilities becomes critical. While existing benchmarks like LoCoBench~\cite{qiu2025locobench} assess long-context code understanding, they focus on single-turn evaluation and cannot capture the multi-turn interactive nature, tool usage patterns, and adaptive reasoning required by real-world coding agents. We introduce \textbf{LoCoBench-Agent}, a comprehensive evaluation framework specifically designed to assess LLM agents in realistic, long-context software engineering workflows. Our framework extends LoCoBench's 8,000 scenarios into interactive agent environments, enabling systematic evaluation of multi-turn conversations, tool usage efficiency, error recovery, and architectural consistency across extended development sessions. We also introduce an evaluation methodology with 9 metrics across comprehension and efficiency dimensions. Our framework provides agents with 8 specialized tools (file operations, search, code analysis) and evaluates them across context lengths ranging from 10K to 1M tokens, enabling precise assessment of long-context performance. Through systematic evaluation of state-of-the-art models, we reveal several key findings: (1) agents exhibit remarkable long-context robustness; (2) comprehension-efficiency trade-off exists with negative correlation, where thorough exploration increases comprehension but reduces efficiency; and (3) conversation efficiency varies dramatically across models, with strategic tool usage patterns differentiating high-performing agents. As the first long-context LLM agent benchmark for software engineering, LoCoBench-Agent establishes a rigorous foundation for measuring agent capabilities, identifying performance gaps, and advancing autonomous software development at scale.
GeoGNN: Quantifying and Mitigating Semantic Drift in Text-Attributed Graphs
Nov 12, 2025Abstract:Graph neural networks (GNNs) on text--attributed graphs (TAGs) typically encode node texts using pretrained language models (PLMs) and propagate these embeddings through linear neighborhood aggregation. However, the representation spaces of modern PLMs are highly non--linear and geometrically structured, where textual embeddings reside on curved semantic manifolds rather than flat Euclidean spaces. Linear aggregation on such manifolds inevitably distorts geometry and causes semantic drift--a phenomenon where aggregated representations deviate from the intrinsic manifold, losing semantic fidelity and expressive power. To quantitatively investigate this problem, this work introduces a local PCA--based metric that measures the degree of semantic drift and provides the first quantitative framework to analyze how different aggregation mechanisms affect manifold structure. Building upon these insights, we propose Geodesic Aggregation, a manifold--aware mechanism that aggregates neighbor information along geodesics via log--exp mappings on the unit sphere, ensuring that representations remain faithful to the semantic manifold during message passing. We further develop GeoGNN, a practical instantiation that integrates spherical attention with manifold interpolation. Extensive experiments across four benchmark datasets and multiple text encoders show that GeoGNN substantially mitigates semantic drift and consistently outperforms strong baselines, establishing the importance of manifold--aware aggregation in text--attributed graph learning.
Grounded Test-Time Adaptation for LLM Agents
Nov 06, 2025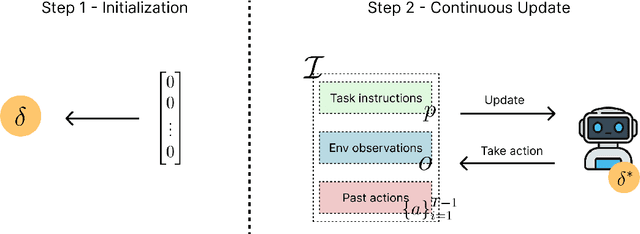
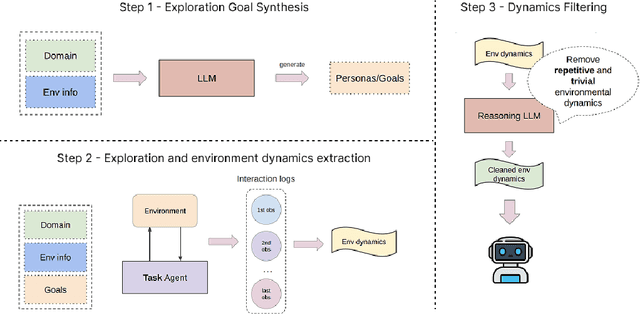
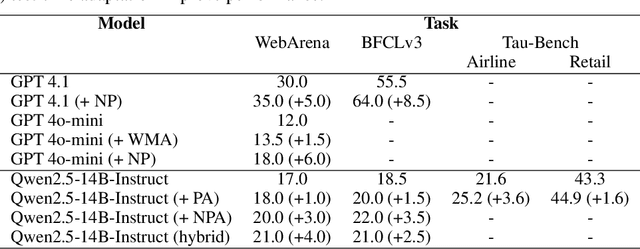
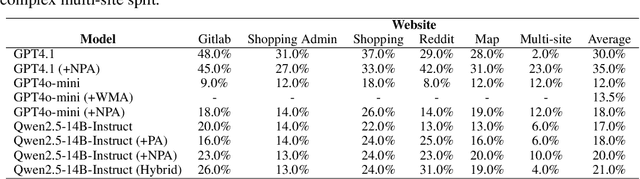
Abstract:Large language model (LLM)-based agents struggle to generalize to novel and complex environments, such as unseen websites or new sets of functions, due to a fundamental mismatch between their pre-training and test-time conditions. This challenge stems from two distinct failure modes: a syntactic misunderstanding of environment-specific components like observation formats, and a semantic misunderstanding of state-transition dynamics, which are only revealed at test time. To address these issues, we propose two distinct and complementary strategies for adapting LLM agents by leveraging environment-specific information available during deployment. First, an online distributional adaptation method parameterizes environmental nuances by learning a lightweight adaptation vector that biases the model's output distribution, enabling rapid alignment with an environment response format. Second, a deployment-time dynamics grounding method employs a persona-driven exploration phase to systematically probe and learn the environment's causal dynamics before task execution, equipping the agent with a nonparametric world model. We evaluate these strategies across diverse agentic benchmarks, including function calling and web navigation. Our empirical results show the effectiveness of both strategies across all benchmarks with minimal computational cost. We find that dynamics grounding is particularly effective in complex environments where unpredictable dynamics pose a major obstacle, demonstrating a robust path toward more generalizable and capable LLM-based agents. For example, on the WebArena multi-site split, this method increases the agent's success rate from 2% to 23%.
ToolLibGen: Scalable Automatic Tool Creation and Aggregation for LLM Reasoning
Oct 09, 2025



Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) equipped with external tools have demonstrated enhanced performance on complex reasoning tasks. The widespread adoption of this tool-augmented reasoning is hindered by the scarcity of domain-specific tools. For instance, in domains such as physics question answering, suitable and specialized tools are often missing. Recent work has explored automating tool creation by extracting reusable functions from Chain-of-Thought (CoT) reasoning traces; however, these approaches face a critical scalability bottleneck. As the number of generated tools grows, storing them in an unstructured collection leads to significant retrieval challenges, including an expanding search space and ambiguity between function-related tools. To address this, we propose a systematic approach to automatically refactor an unstructured collection of tools into a structured tool library. Our system first generates discrete, task-specific tools and clusters them into semantically coherent topics. Within each cluster, we introduce a multi-agent framework to consolidate scattered functionalities: a code agent refactors code to extract shared logic and creates versatile, aggregated tools, while a reviewing agent ensures that these aggregated tools maintain the complete functional capabilities of the original set. This process transforms numerous question-specific tools into a smaller set of powerful, aggregated tools without loss of functionality. Experimental results demonstrate that our approach significantly improves tool retrieval accuracy and overall reasoning performance across multiple reasoning tasks. Furthermore, our method shows enhanced scalability compared with baselines as the number of question-specific increases.
LoCoBench: A Benchmark for Long-Context Large Language Models in Complex Software Engineering
Sep 11, 2025



Abstract:The emergence of long-context language models with context windows extending to millions of tokens has created new opportunities for sophisticated code understanding and software development evaluation. We propose LoCoBench, a comprehensive benchmark specifically designed to evaluate long-context LLMs in realistic, complex software development scenarios. Unlike existing code evaluation benchmarks that focus on single-function completion or short-context tasks, LoCoBench addresses the critical evaluation gap for long-context capabilities that require understanding entire codebases, reasoning across multiple files, and maintaining architectural consistency across large-scale software systems. Our benchmark provides 8,000 evaluation scenarios systematically generated across 10 programming languages, with context lengths spanning 10K to 1M tokens, a 100x variation that enables precise assessment of long-context performance degradation in realistic software development settings. LoCoBench introduces 8 task categories that capture essential long-context capabilities: architectural understanding, cross-file refactoring, multi-session development, bug investigation, feature implementation, code comprehension, integration testing, and security analysis. Through a 5-phase pipeline, we create diverse, high-quality scenarios that challenge LLMs to reason about complex codebases at unprecedented scale. We introduce a comprehensive evaluation framework with 17 metrics across 4 dimensions, including 8 new evaluation metrics, combined in a LoCoBench Score (LCBS). Our evaluation of state-of-the-art long-context models reveals substantial performance gaps, demonstrating that long-context understanding in complex software development represents a significant unsolved challenge that demands more attention. LoCoBench is released at: https://github.com/SalesforceAIResearch/LoCoBench.
UserBench: An Interactive Gym Environment for User-Centric Agents
Jul 29, 2025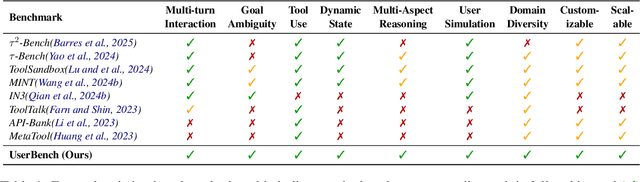
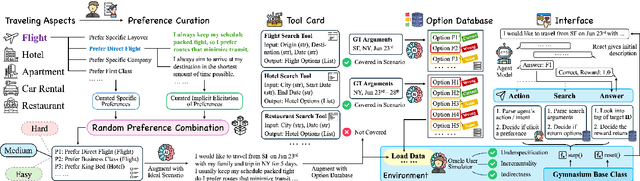
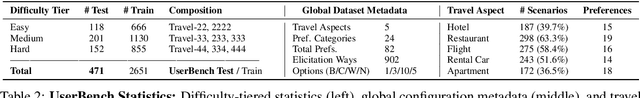
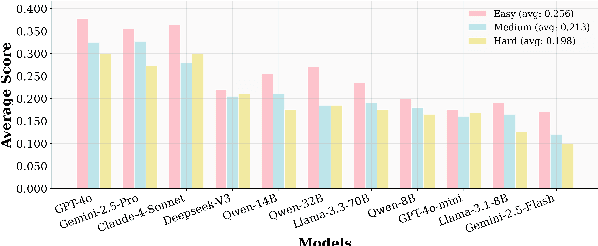
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs)-based agents have made impressive progress in reasoning and tool use, enabling them to solve complex tasks. However, their ability to proactively collaborate with users, especially when goals are vague, evolving, or indirectly expressed, remains underexplored. To address this gap, we introduce UserBench, a user-centric benchmark designed to evaluate agents in multi-turn, preference-driven interactions. UserBench features simulated users who start with underspecified goals and reveal preferences incrementally, requiring agents to proactively clarify intent and make grounded decisions with tools. Our evaluation of leading open- and closed-source LLMs reveals a significant disconnect between task completion and user alignment. For instance, models provide answers that fully align with all user intents only 20% of the time on average, and even the most advanced models uncover fewer than 30% of all user preferences through active interaction. These results highlight the challenges of building agents that are not just capable task executors, but true collaborative partners. UserBench offers an interactive environment to measure and advance this critical capability.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge