Eduard Hovy
USC/Information Sciences Institute
When Is Rank-1 Enough? Geometry-Guided Initialization for Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) is a standard way to adapt multimodal large language models, yet extremely low-rank settings -- especially rank-1 LoRA -- are often unstable. We show that this instability is not solely due to limited capacity: in the rank-1 regime, optimization is highly sensitive to the update direction. Concretely, pretrained vision and text features form mismatched anisotropic regions, yielding a dominant "gap" direction that acts like a translation component and disproportionately steers early gradients under rank-1 constraints. Analyzing pretrained representations, we identify a modality-gap axis that dominates early gradient flow, while a random rank-1 initialization is unlikely to align with it, leading to weak gradients and training collapse. We propose Gap-Init, a geometry-aware initialization that aligns the rank-1 LoRA direction with an estimated modality-gap vector from a small calibration set, while keeping the initial LoRA update zero. Across multiple vision-language tasks and backbones, Gap-Init consistently stabilizes rank-1 training and can match or outperform strong rank-8 baselines. Our results suggest that at the extreme low-rank limit, initial alignment can matter as much as rank itself.
LLMs for Argument Mining: Detection, Extraction, and Relationship Classification of pre-defined Arguments in Online Comments
May 29, 2025



Abstract:Automated large-scale analysis of public discussions around contested issues like abortion requires detecting and understanding the use of arguments. While Large Language Models (LLMs) have shown promise in language processing tasks, their performance in mining topic-specific, pre-defined arguments in online comments remains underexplored. We evaluate four state-of-the-art LLMs on three argument mining tasks using datasets comprising over 2,000 opinion comments across six polarizing topics. Quantitative evaluation suggests an overall strong performance across the three tasks, especially for large and fine-tuned LLMs, albeit at a significant environmental cost. However, a detailed error analysis revealed systematic shortcomings on long and nuanced comments and emotionally charged language, raising concerns for downstream applications like content moderation or opinion analysis. Our results highlight both the promise and current limitations of LLMs for automated argument analysis in online comments.
Community Moderation and the New Epistemology of Fact Checking on Social Media
May 26, 2025Abstract:Social media platforms have traditionally relied on internal moderation teams and partnerships with independent fact-checking organizations to identify and flag misleading content. Recently, however, platforms including X (formerly Twitter) and Meta have shifted towards community-driven content moderation by launching their own versions of crowd-sourced fact-checking -- Community Notes. If effectively scaled and governed, such crowd-checking initiatives have the potential to combat misinformation with increased scale and speed as successfully as community-driven efforts once did with spam. Nevertheless, general content moderation, especially for misinformation, is inherently more complex. Public perceptions of truth are often shaped by personal biases, political leanings, and cultural contexts, complicating consensus on what constitutes misleading content. This suggests that community efforts, while valuable, cannot replace the indispensable role of professional fact-checkers. Here we systemically examine the current approaches to misinformation detection across major platforms, explore the emerging role of community-driven moderation, and critically evaluate both the promises and challenges of crowd-checking at scale.
FaceID-6M: A Large-Scale, Open-Source FaceID Customization Dataset
Mar 11, 2025Abstract:Due to the data-driven nature of current face identity (FaceID) customization methods, all state-of-the-art models rely on large-scale datasets containing millions of high-quality text-image pairs for training. However, none of these datasets are publicly available, which restricts transparency and hinders further advancements in the field. To address this issue, in this paper, we collect and release FaceID-6M, the first large-scale, open-source FaceID dataset containing 6 million high-quality text-image pairs. Filtered from LAION-5B \cite{schuhmann2022laion}, FaceID-6M undergoes a rigorous image and text filtering steps to ensure dataset quality, including resolution filtering to maintain high-quality images and faces, face filtering to remove images that lack human faces, and keyword-based strategy to retain descriptions containing human-related terms (e.g., nationality, professions and names). Through these cleaning processes, FaceID-6M provides a high-quality dataset optimized for training powerful FaceID customization models, facilitating advancements in the field by offering an open resource for research and development. We conduct extensive experiments to show the effectiveness of our FaceID-6M, demonstrating that models trained on our FaceID-6M dataset achieve performance that is comparable to, and slightly better than currently available industrial models. Additionally, to support and advance research in the FaceID customization community, we make our code, datasets, and models fully publicly available. Our codes, models, and datasets are available at: https://github.com/ShuheSH/FaceID-6M.
Control Illusion: The Failure of Instruction Hierarchies in Large Language Models
Feb 21, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are increasingly deployed with hierarchical instruction schemes, where certain instructions (e.g., system-level directives) are expected to take precedence over others (e.g., user messages). Yet, we lack a systematic understanding of how effectively these hierarchical control mechanisms work. We introduce a systematic evaluation framework based on constraint prioritization to assess how well LLMs enforce instruction hierarchies. Our experiments across six state-of-the-art LLMs reveal that models struggle with consistent instruction prioritization, even for simple formatting conflicts. We find that the widely-adopted system/user prompt separation fails to establish a reliable instruction hierarchy, and models exhibit strong inherent biases toward certain constraint types regardless of their priority designation. While controlled prompt engineering and model fine-tuning show modest improvements, our results indicate that instruction hierarchy enforcement is not robustly realized, calling for deeper architectural innovations beyond surface-level modifications.
Rumor Detection by Multi-task Suffix Learning based on Time-series Dual Sentiments
Feb 20, 2025



Abstract:The widespread dissemination of rumors on social media has a significant impact on people's lives, potentially leading to public panic and fear. Rumors often evoke specific sentiments, resonating with readers and prompting sharing. To effectively detect and track rumors, it is essential to observe the fine-grained sentiments of both source and response message pairs as the rumor evolves over time. However, current rumor detection methods fail to account for this aspect. In this paper, we propose MSuf, the first multi-task suffix learning framework for rumor detection and tracking using time series dual (coupled) sentiments. MSuf includes three modules: (1) an LLM to extract sentiment intensity features and sort them chronologically; (2) a module that fuses the sorted sentiment features with their source text word embeddings to obtain an aligned embedding; (3) two hard prompts are combined with the aligned vector to perform rumor detection and sentiment analysis using one frozen LLM. MSuf effectively enhances the performance of LLMs for rumor detection with only minimal parameter fine-tuning. Evaluating MSuf on four rumor detection benchmarks, we find significant improvements compared to other emotion-based methods.
Turn That Frown Upside Down: FaceID Customization via Cross-Training Data
Jan 26, 2025



Abstract:Existing face identity (FaceID) customization methods perform well but are limited to generating identical faces as the input, while in real-world applications, users often desire images of the same person but with variations, such as different expressions (e.g., smiling, angry) or angles (e.g., side profile). This limitation arises from the lack of datasets with controlled input-output facial variations, restricting models' ability to learn effective modifications. To address this issue, we propose CrossFaceID, the first large-scale, high-quality, and publicly available dataset specifically designed to improve the facial modification capabilities of FaceID customization models. Specifically, CrossFaceID consists of 40,000 text-image pairs from approximately 2,000 persons, with each person represented by around 20 images showcasing diverse facial attributes such as poses, expressions, angles, and adornments. During the training stage, a specific face of a person is used as input, and the FaceID customization model is forced to generate another image of the same person but with altered facial features. This allows the FaceID customization model to acquire the ability to personalize and modify known facial features during the inference stage. Experiments show that models fine-tuned on the CrossFaceID dataset retain its performance in preserving FaceID fidelity while significantly improving its face customization capabilities. To facilitate further advancements in the FaceID customization field, our code, constructed datasets, and trained models are fully available to the public.
Libra-Leaderboard: Towards Responsible AI through a Balanced Leaderboard of Safety and Capability
Dec 24, 2024



Abstract:To address this gap, we introduce Libra-Leaderboard, a comprehensive framework designed to rank LLMs through a balanced evaluation of performance and safety. Combining a dynamic leaderboard with an interactive LLM arena, Libra-Leaderboard encourages the joint optimization of capability and safety. Unlike traditional approaches that average performance and safety metrics, Libra-Leaderboard uses a distance-to-optimal-score method to calculate the overall rankings. This approach incentivizes models to achieve a balance rather than excelling in one dimension at the expense of some other ones. In the first release, Libra-Leaderboard evaluates 26 mainstream LLMs from 14 leading organizations, identifying critical safety challenges even in state-of-the-art models.
Packing Analysis: Packing Is More Appropriate for Large Models or Datasets in Supervised Fine-tuning
Oct 10, 2024



Abstract:Packing, initially utilized in the pre-training phase, is an optimization technique designed to maximize hardware resource efficiency by combining different training sequences to fit the model's maximum input length. Although it has demonstrated effectiveness during pre-training, there remains a lack of comprehensive analysis for the supervised fine-tuning (SFT) stage on the following points: (1) whether packing can effectively enhance training efficiency while maintaining performance, (2) the suitable size of the model and dataset for fine-tuning with the packing method, and (3) whether packing unrelated or related training samples might cause the model to either excessively disregard or over-rely on the context. In this paper, we perform extensive comparisons between SFT methods using padding and packing, covering SFT datasets ranging from 69K to 1.2M and models from 8B to 70B. This provides the first comprehensive analysis of the advantages and limitations of packing versus padding, as well as practical considerations for implementing packing in various training scenarios. Our analysis covers various benchmarks, including knowledge, reasoning, and coding, as well as GPT-based evaluations, time efficiency, and other fine-tuning parameters. We also open-source our code for fine-tuning and evaluation and provide checkpoints fine-tuned on datasets of different sizes, aiming to advance future research on packing methods. Code is available at: https://github.com/ShuheWang1998/Packing-Analysis?tab=readme-ov-file.
Can a Neural Model Guide Fieldwork? A Case Study on Morphological Inflection
Sep 22, 2024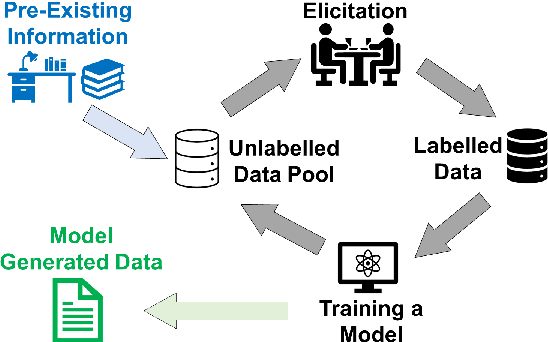
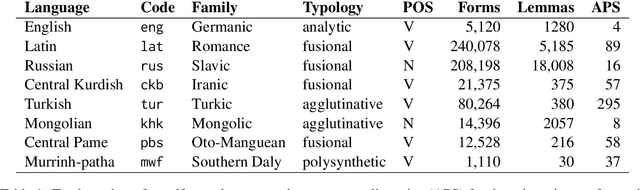
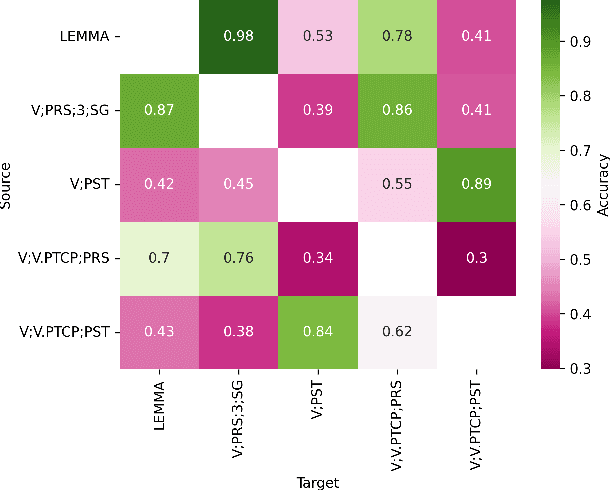
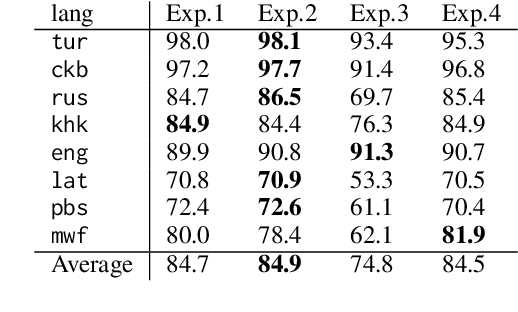
Abstract:Linguistic fieldwork is an important component in language documentation and preservation. However, it is a long, exhaustive, and time-consuming process. This paper presents a novel model that guides a linguist during the fieldwork and accounts for the dynamics of linguist-speaker interactions. We introduce a novel framework that evaluates the efficiency of various sampling strategies for obtaining morphological data and assesses the effectiveness of state-of-the-art neural models in generalising morphological structures. Our experiments highlight two key strategies for improving the efficiency: (1) increasing the diversity of annotated data by uniform sampling among the cells of the paradigm tables, and (2) using model confidence as a guide to enhance positive interaction by providing reliable predictions during annotation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge