Andreas Scherbakov
Can a Neural Model Guide Fieldwork? A Case Study on Morphological Inflection
Sep 22, 2024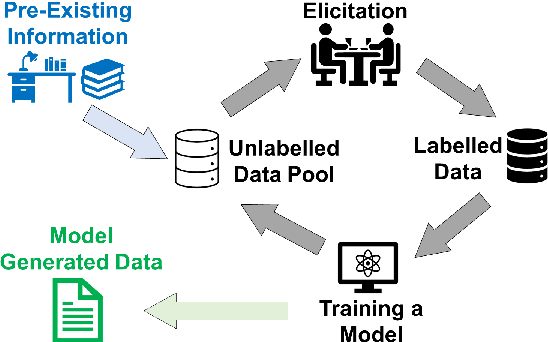
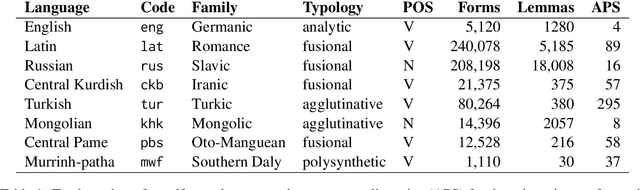
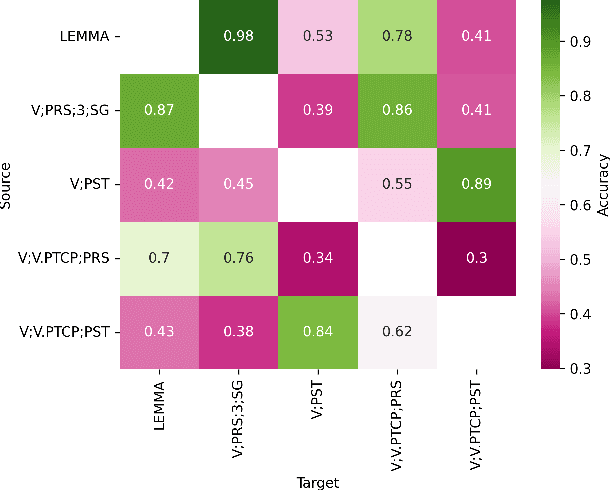
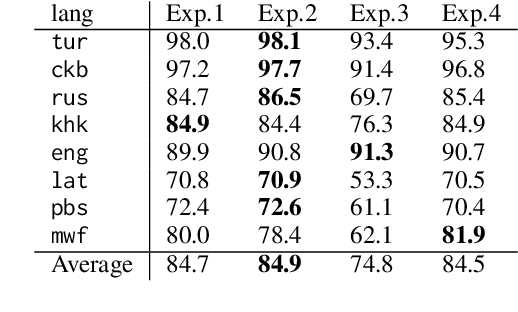
Abstract:Linguistic fieldwork is an important component in language documentation and preservation. However, it is a long, exhaustive, and time-consuming process. This paper presents a novel model that guides a linguist during the fieldwork and accounts for the dynamics of linguist-speaker interactions. We introduce a novel framework that evaluates the efficiency of various sampling strategies for obtaining morphological data and assesses the effectiveness of state-of-the-art neural models in generalising morphological structures. Our experiments highlight two key strategies for improving the efficiency: (1) increasing the diversity of annotated data by uniform sampling among the cells of the paradigm tables, and (2) using model confidence as a guide to enhance positive interaction by providing reliable predictions during annotation.
From Incremental Meaning to Semantic Unit (phrase by phrase)
Apr 17, 2016



Abstract:This paper describes an experimental approach to Detection of Minimal Semantic Units and their Meaning (DiMSUM), explored within the framework of SemEval 2016 Task 10. The approach is primarily based on a combination of word embeddings and parserbased features, and employs unidirectional incremental computation of compositional embeddings for multiword expressions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge