Aso Mahmudi
End-to-End Transformer-based Automatic Speech Recognition for Northern Kurdish: A Pioneering Approach
Oct 19, 2024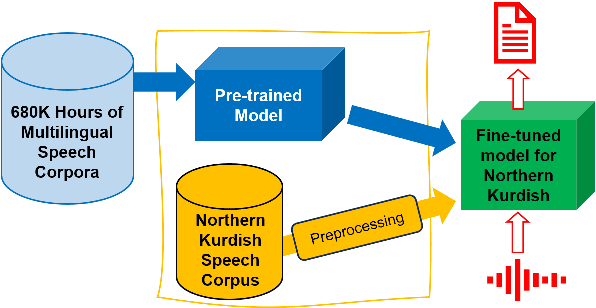
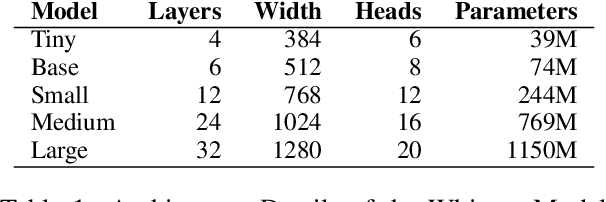
Abstract:Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) for low-resource languages remains a challenging task due to limited training data. This paper introduces a comprehensive study exploring the effectiveness of Whisper, a pre-trained ASR model, for Northern Kurdish (Kurmanji) an under-resourced language spoken in the Middle East. We investigate three fine-tuning strategies: vanilla, specific parameters, and additional modules. Using a Northern Kurdish fine-tuning speech corpus containing approximately 68 hours of validated transcribed data, our experiments demonstrate that the additional module fine-tuning strategy significantly improves ASR accuracy on a specialized test set, achieving a Word Error Rate (WER) of 10.5% and Character Error Rate (CER) of 5.7% with Whisper version 3. These results underscore the potential of sophisticated transformer models for low-resource ASR and emphasize the importance of tailored fine-tuning techniques for optimal performance.
Can a Neural Model Guide Fieldwork? A Case Study on Morphological Inflection
Sep 22, 2024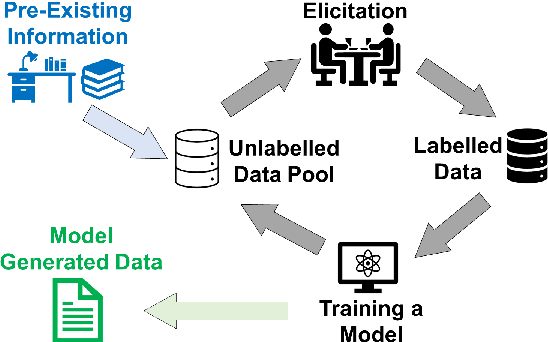
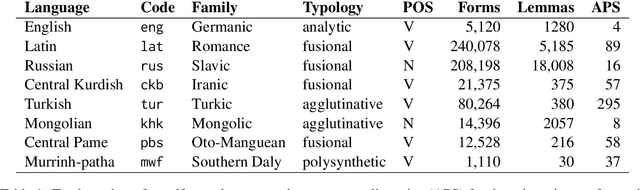
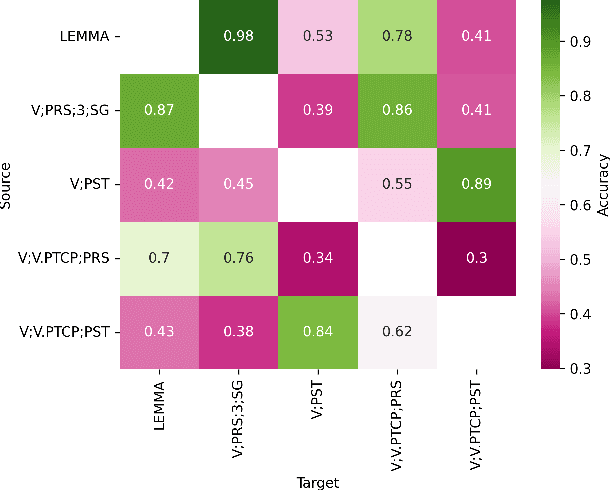
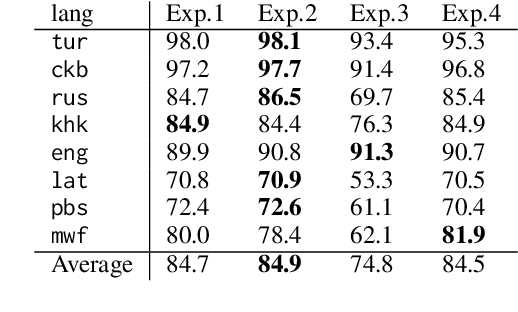
Abstract:Linguistic fieldwork is an important component in language documentation and preservation. However, it is a long, exhaustive, and time-consuming process. This paper presents a novel model that guides a linguist during the fieldwork and accounts for the dynamics of linguist-speaker interactions. We introduce a novel framework that evaluates the efficiency of various sampling strategies for obtaining morphological data and assesses the effectiveness of state-of-the-art neural models in generalising morphological structures. Our experiments highlight two key strategies for improving the efficiency: (1) increasing the diversity of annotated data by uniform sampling among the cells of the paradigm tables, and (2) using model confidence as a guide to enhance positive interaction by providing reliable predictions during annotation.
Low-Resource Machine Translation through Retrieval-Augmented LLM Prompting: A Study on the Mambai Language
Apr 07, 2024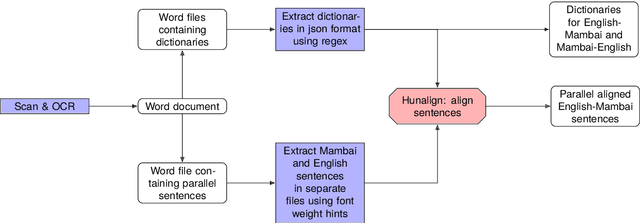
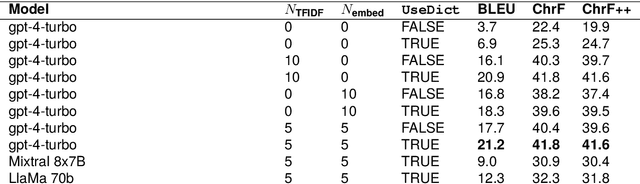
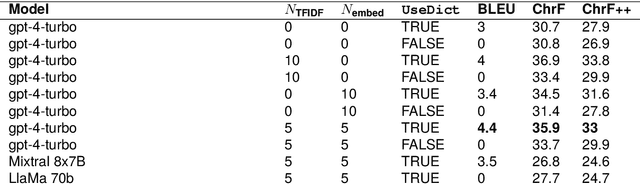
Abstract:This study explores the use of large language models (LLMs) for translating English into Mambai, a low-resource Austronesian language spoken in Timor-Leste, with approximately 200,000 native speakers. Leveraging a novel corpus derived from a Mambai language manual and additional sentences translated by a native speaker, we examine the efficacy of few-shot LLM prompting for machine translation (MT) in this low-resource context. Our methodology involves the strategic selection of parallel sentences and dictionary entries for prompting, aiming to enhance translation accuracy, using open-source and proprietary LLMs (LlaMa 2 70b, Mixtral 8x7B, GPT-4). We find that including dictionary entries in prompts and a mix of sentences retrieved through TF-IDF and semantic embeddings significantly improves translation quality. However, our findings reveal stark disparities in translation performance across test sets, with BLEU scores reaching as high as 21.2 on materials from the language manual, in contrast to a maximum of 4.4 on a test set provided by a native speaker. These results underscore the importance of diverse and representative corpora in assessing MT for low-resource languages. Our research provides insights into few-shot LLM prompting for low-resource MT, and makes available an initial corpus for the Mambai language.
CKMorph: A Comprehensive Morphological Analyzer for Central Kurdish
Sep 17, 2021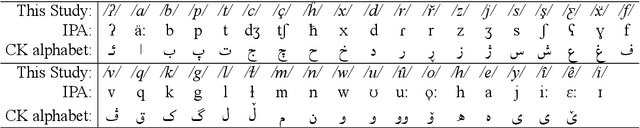
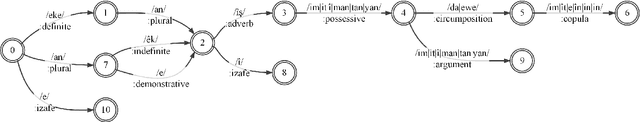
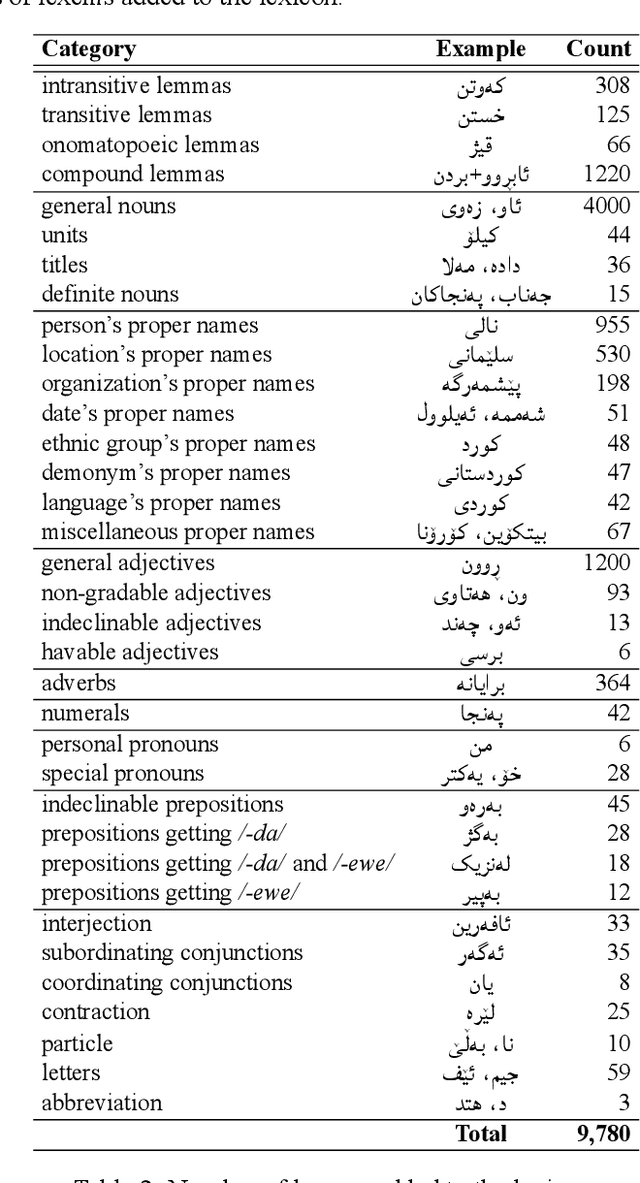
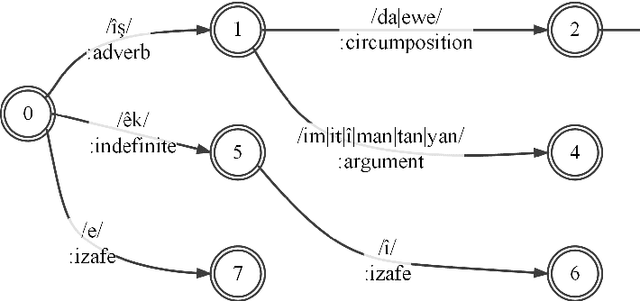
Abstract:A morphological analyzer, which is a significant component of many natural language processing applications especially for morphologically rich languages, divides an input word into all its composing morphemes and identifies their morphological roles. In this paper, we introduce a comprehensive morphological analyzer for Central Kurdish (CK), a low-resourced language with a rich morphology. Building upon the limited existing literature, we first assembled and systematically categorized a comprehensive collection of the morphological and morphophonological rules of the language. Additionally, we collected and manually labeled a generative lexicon containing nearly 10,000 verb, noun and adjective stems, named entities, and other types of word stems. We used these rule sets and resources to implement CKMorph Analyzer based on finite-state transducers. In order to provide a benchmark for future research, we collected, manually labeled, and publicly shared test sets for evaluating accuracy and coverage of the analyzer. CKMorph was able to correctly analyze 95.9% of the accuracy test set, containing 1,000 CK words morphologically analyzed according to the context. Moreover, CKMorph gave at least one analysis for 95.5% of 4.22M CK tokens of the coverage test set. The demonstration of the application and resources including CK verb database and test sets are openly accessible at https://github.com/CKMorph.
Automatic Meter Classification of Kurdish Poems
Feb 24, 2021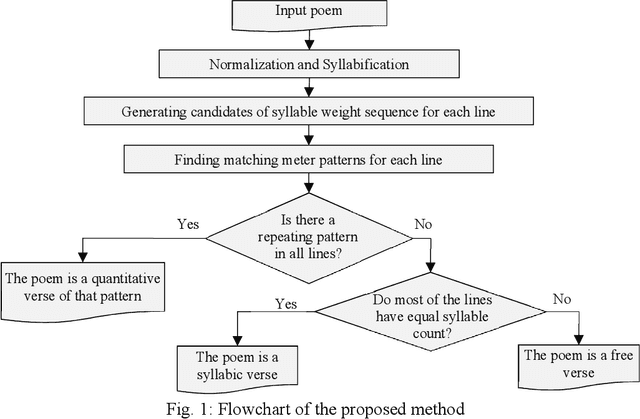
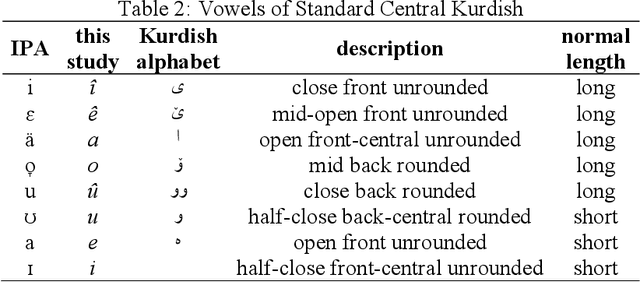
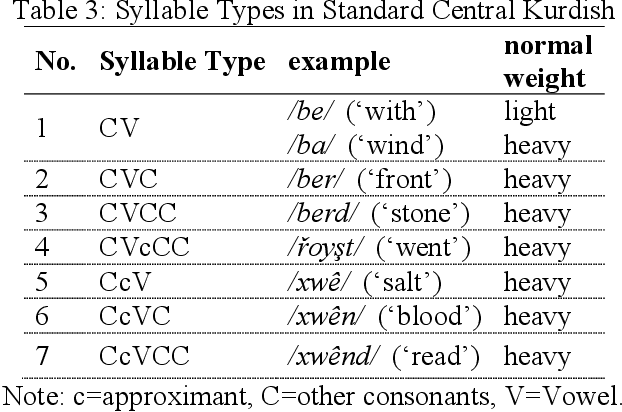
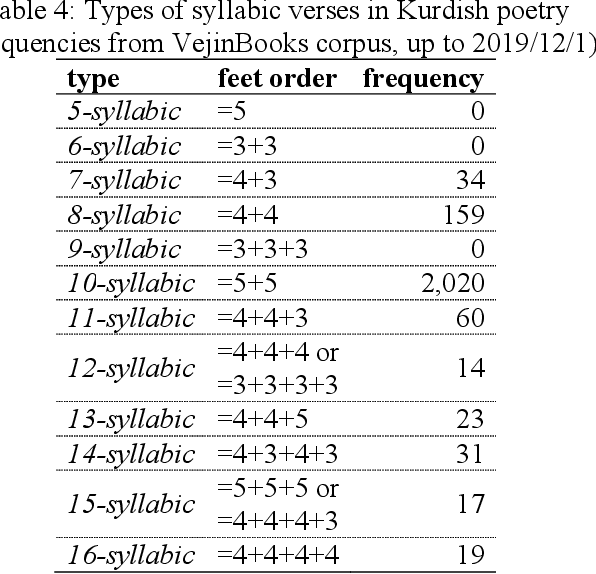
Abstract:Most of the classic texts in Kurdish literature are poems. Knowing the meter of the poems is helpful for correct reading, a better understanding of the meaning, and avoidance of ambiguity. This paper presents a rule-based method for automatic classification of the poem meter for the Central Kurdish language. The metrical system of Kurdish poetry is divided into three classes of quantitative, syllabic, and free verses. As the vowel length is not phonemic in the language, there are uncertainties in syllable weight and meter identification. The proposed method generates all the possible situations and then, by considering all lines of the input poem and the common meter patterns of Kurdish poetry, identifies the most probable meter type and pattern of the input poem. Evaluation of the method on a dataset from VejinBooks Kurdish corpus resulted in 97.3% of precision in meter type and 96.2% of precision in pattern identification.
Jira: a Kurdish Speech Recognition System Designing and Building Speech Corpus and Pronunciation Lexicon
Feb 15, 2021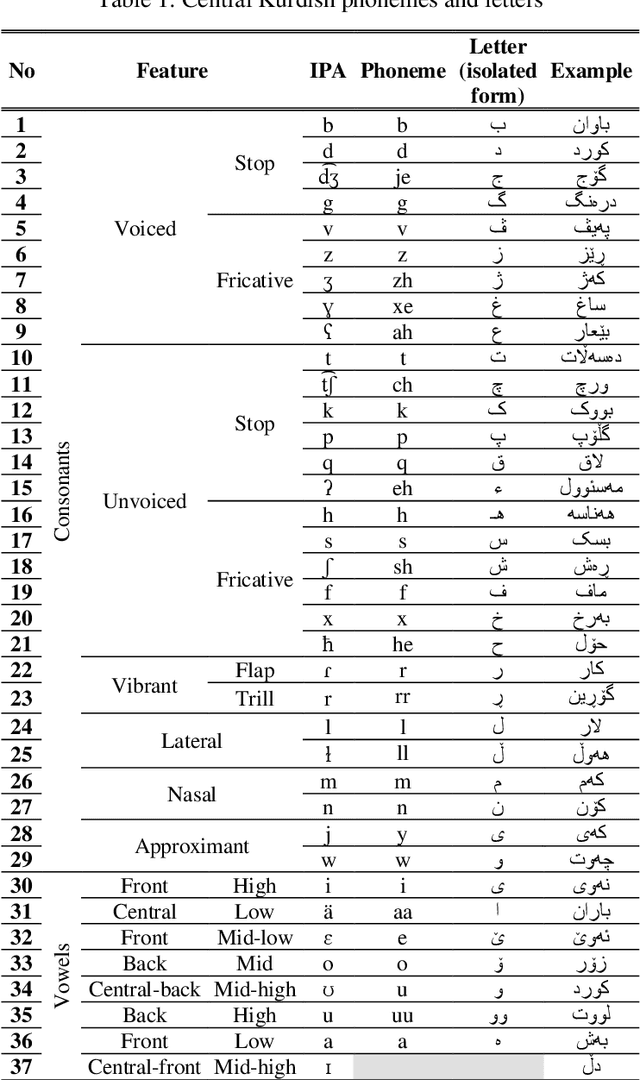
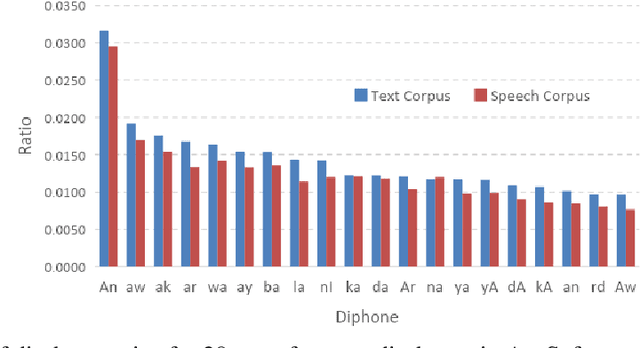
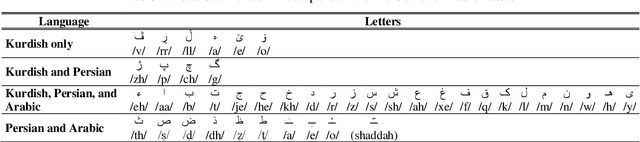
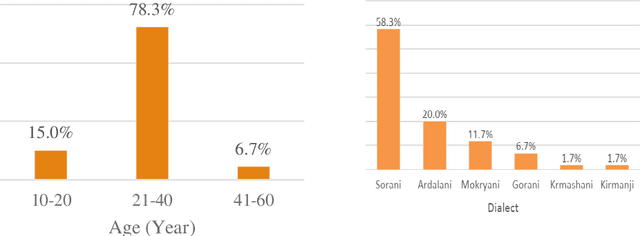
Abstract:In this paper, we introduce the first large vocabulary speech recognition system (LVSR) for the Central Kurdish language, named Jira. The Kurdish language is an Indo-European language spoken by more than 30 million people in several countries, but due to the lack of speech and text resources, there is no speech recognition system for this language. To fill this gap, we introduce the first speech corpus and pronunciation lexicon for the Kurdish language. Regarding speech corpus, we designed a sentence collection in which the ratio of di-phones in the collection resembles the real data of the Central Kurdish language. The designed sentences are uttered by 576 speakers in a controlled environment with noise-free microphones (called AsoSoft Speech-Office) and in Telegram social network environment using mobile phones (denoted as AsoSoft Speech-Crowdsourcing), resulted in 43.68 hours of speech. Besides, a test set including 11 different document topics is designed and recorded in two corresponding speech conditions (i.e., Office and Crowdsourcing). Furthermore, a 60K pronunciation lexicon is prepared in this research in which we faced several challenges and proposed solutions for them. The Kurdish language has several dialects and sub-dialects that results in many lexical variations. Our methods for script standardization of lexical variations and automatic pronunciation of the lexicon tokens are presented in detail. To setup the recognition engine, we used the Kaldi toolkit. A statistical tri-gram language model that is extracted from the AsoSoft text corpus is used in the system. Several standard recipes including HMM-based models (i.e., mono, tri1, tr2, tri2, tri3), SGMM, and DNN methods are used to generate the acoustic model. These methods are trained with AsoSoft Speech-Office and AsoSoft Speech-Crowdsourcing and a combination of them. The best performance achieved by the SGMM acoustic model which results in 13.9% of the average word error rate (on different document topics) and 4.9% for the general topic.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge